8.6.2.2.4 Supported Modbus Function Codes
Modbus protocol has many function codes. CR1000 commands support the
following.
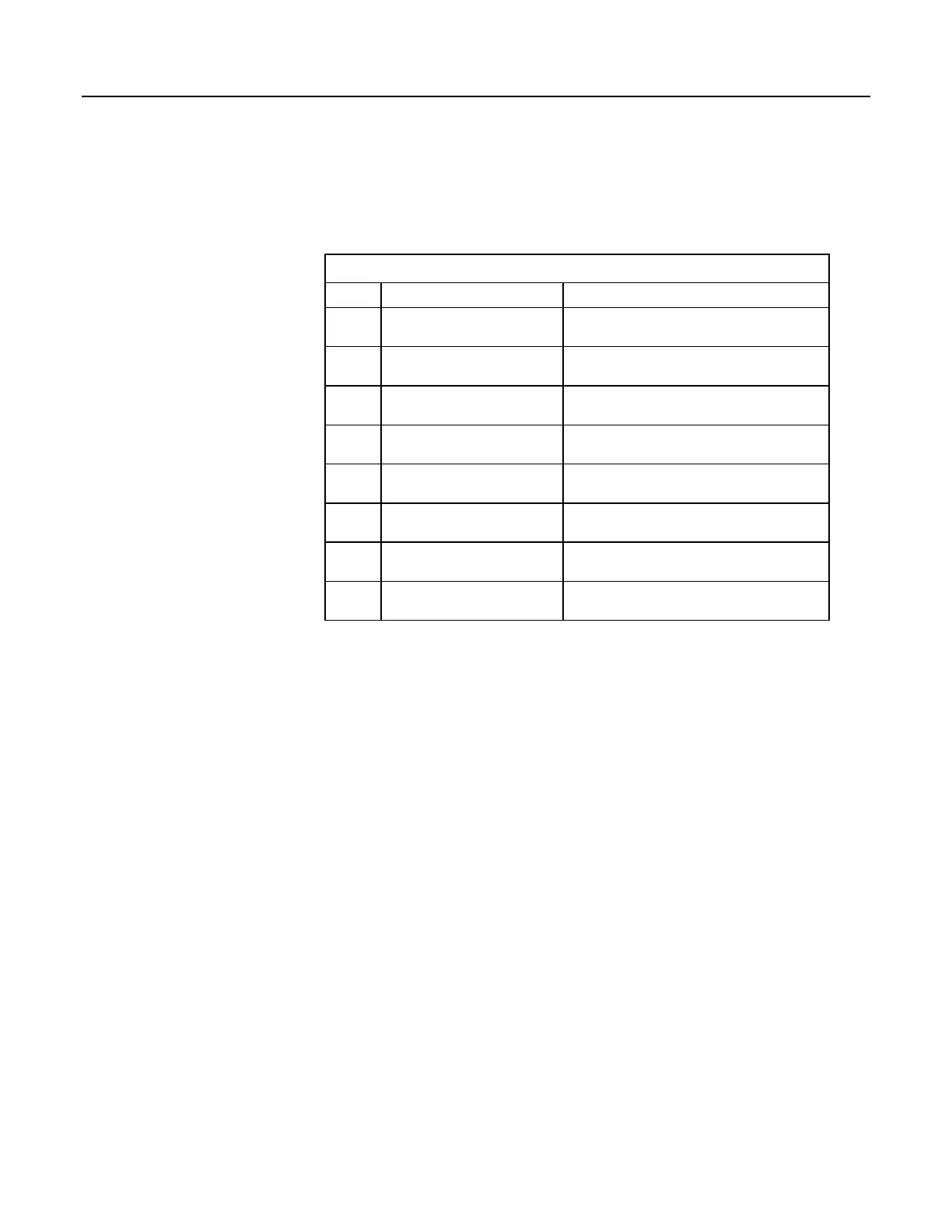
Table 108. Supported Modbus Function Codes
Code Name Description
01
Read coil/port status Reads the on/off status of discrete output(s) in the
ModBusSlave
02
Read input status Reads the on/off status of discrete input(s) in the
ModBusSlave
03
Read holding registers Reads the binary contents of holding register(s) in
the ModBusSlave
04
Read input registers Reads the binary contents of input register(s) in
the ModBusSlave
05
Force single coil/port Forces a single coil/port in the ModBusSlave to
either on or off
06
Write single register Writes a value into a holding register in the
ModBusSlave
15
Force multiple coils/ports Forces multiple coils/ports in the ModBusSlave to
either on or off
16
Write multiple registers Writes values into a series of holding registers in
the ModBusSlave
8.6.2.2.5 Reading Inverse-Format Modbus Registers
Some Modbus devices require reverse byte order words (CDAB vs. ABCD). This
can be true for either floating point, or integer formats. Since a slave CR1000
uses the ABCD format, either the master has to make an adjustment, which is
sometimes possible, or the CR1000 needs to output reverse-byte order words. To
reverse the byte order in the CR1000, use the MoveBytes() instruction as shown
in the sample code below.
for i = 1 to k
MoveBytes(InverseFloat(i),2,Float(i),0,2)
MoveBytes(InverseFloat(i),0,Float(i),2,2)
next
In the example above, InverseFloat(i) is the array holding the inverse-byte
ordered word (CDAB). Array Float(i) holds the obverse-byte ordered word
(ABCD).
See the appendix Endianness
(p. 643).
8.6.2.3 Troubleshooting (Modbus)
Test Modbus functions on the CR1000 with third party Modbus software. Further
information is available at the following links:
• www.simplyModbus.ca/FAQ.htm
• www.Modbus.org/tech.php
• www.lammertbies.nl/comm/info/modbus.html
415

 Loading...
Loading...