Table 22. Logical Expression Examples
The NOT operator complements every bit in the word. A Boolean can be FALSE (0 or all bits set to 0) or TRUE (-1 or all bits set to 1).
“Complementing” a Boolean turns TRUE to FALSE (all bits complemented to 0).
Example Program
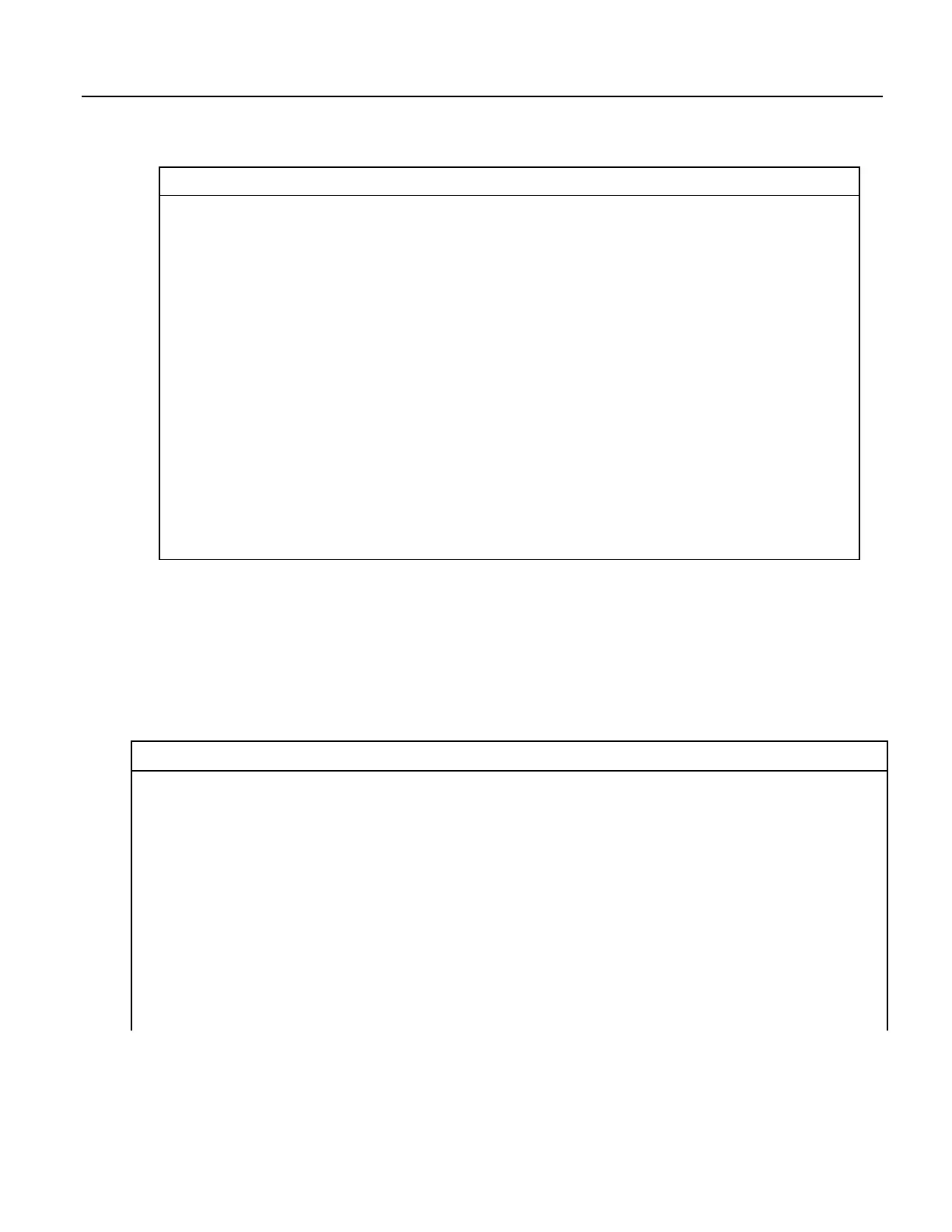
'(a AND b) = (26 AND 26) = (&b11010 AND &b11010) =
'&b11010. NOT (&b11010) yields &b00101.
'This is non-zero, so when converted to a
'BOOLEAN, it becomes TRUE.
Public a As LONG
Public b As LONG
Public is_true As Boolean
Public not_is_true As Boolean
Public not_a_and_b As Boolean
BeginProg
a = 26
b = a
Scan (1,Sec,0,0)
is_true = a AND b 'This evaluates to TRUE.
not_is_true = NOT (is_true) 'This evaluates to FALSE.
not_a_and_b = NOT (a AND b) 'This evaluates to TRUE!
NextScan
7.8.4.15.5 String Expressions
CRBasic facilitates concatenation of string variables to variables of all data types
using & and + operators. To ensure consistent results, use & when concatenating
strings. Use + when concatenating strings to other variable types. CRBasic
example String and Variable Concatenation
(p. 166) demonstrates CRBasic code for
concatenating strings and integers. See section String Operations
(p. 282) in the
Programming Resource Library
(p. 169) for more information on string
programming.
CRBasic Example 21. String and Variable Concatenation
'This program example demonstrates the concatenation of variables declared As String to
'other strings and to variables declared as other data types.
'
'Declare Variables
Dim PhraseNum(2) As Long
Dim Word(15) As String * 10
Public Phrase(2) As String * 80
'Declare Data Table
DataTable(HAL,1,-1)
DataInterval(0,15,Sec,10)
'Write phrases to data table "Test"
Sample(2,Phrase,String)
EndTable
166
 Loading...
Loading...