The CAM is represented in an XML le, which contains the
following information:
•
Master scaling (optional)
•
Slave scaling (optional)
•
Control loop parameter (optional; both sets)
•
Following error settings (optional)
•
Basic cam or advanced cam denition
The CAM conguration consists of the following
information:
•
Cyclic/non-cyclic
•
Master absolute/relative
•
Slave absolute/ relative (only applicable for basic
CAM)
For general information about the format of an XML le,
see chapter 10.2 General XML Conventions.
When parsing a CAM prole, the servo drive checks the
format and the plausibility. The result is available in the
sub-indexes 3 and 4 of the same objects (see
chapter 7.14.4 Parameters: CAM Prole 1–8 (0x3810–0x3817)).
These sub-indexes contain detailed information about the
parsing state, error result, and more detailed information
for debugging.
The factor group (see chapter 2.3.2 Factor Group) is not
used in CAM mode. The velocity must be given as a
unitless factor between rotor angle and angle of guide
value. The acceleration must be given as velocity per
degree of guide value. A CAM prole is running based on
the guide value. This value always runs from 0 to 1. To
adjust this to the real application environment, it is
possible to specify a factor (master scaling) to reduce or
increase the value that is considered as a full cycle.
There are 2 possible CAM buer layouts available:
•
8 CAM proles
•
2 CAM proles with more data
The CAM buer layout can be selected in object 0x380F
(see chapter 7.14.1 Parameter: CAM Prole Memory Layout
(0x380F)). Carry out a power-cycle to activate the selection.
All nodes are non-signaling nodes. The axis does not
automatically signal if it passes a node. However, for
example for debugging purpose, it is possible to enable
this signaling for selected nodes.
NOTICE
The factor group (feed constant, gear ratio, and so on)
has no eect in CAM mode.
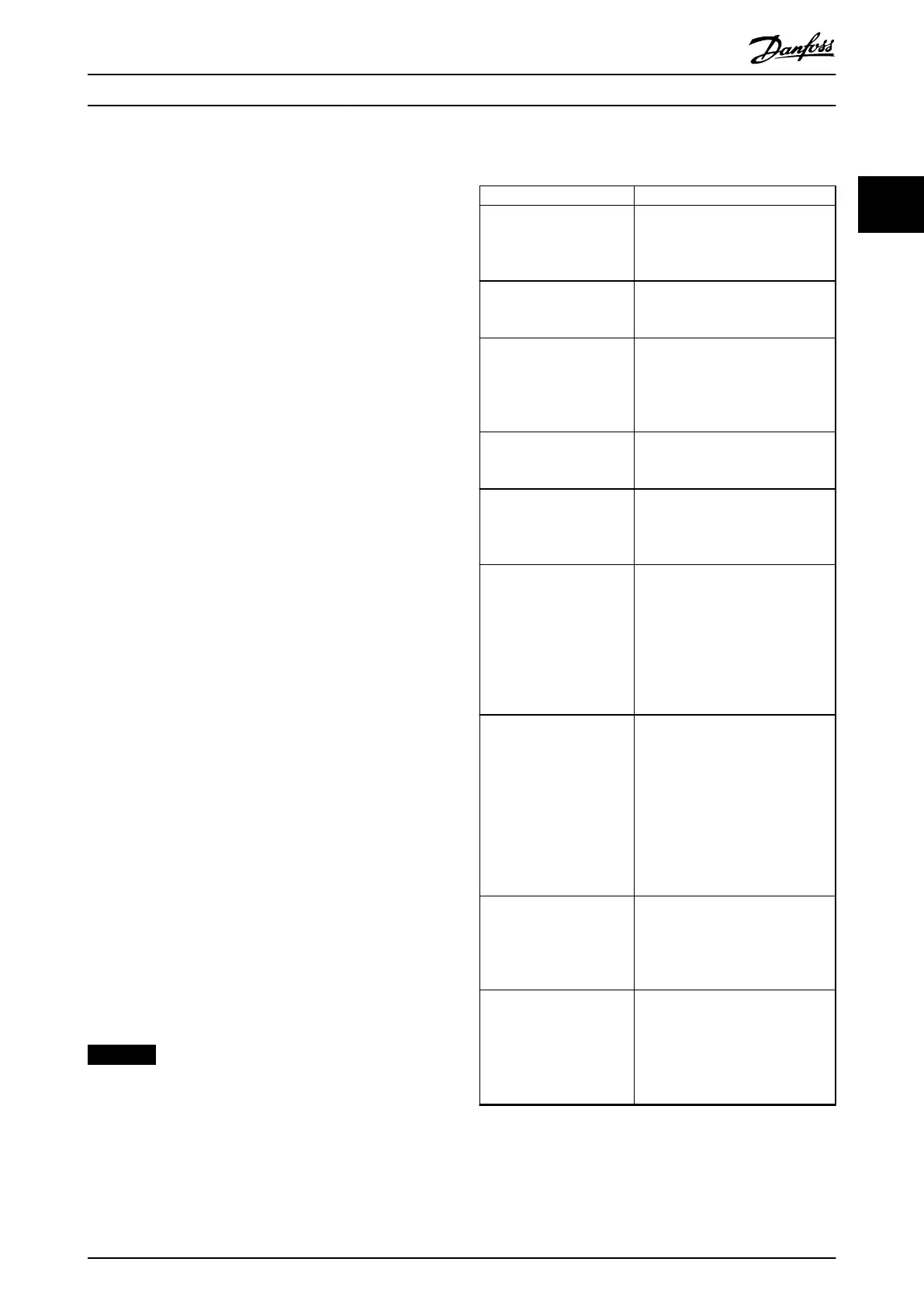
Terminology
Name Description
CAM prole Consists of 1 CAM and 1 CAM
conguration. A valid CAM prole is
automatically stored in the servo
drive (maximum 8 CAM proles).
CAM XML le (basic CAM or advanced
CAM) containing the data points or
the nodes and segments.
CAM conguration Contains the following information:
- Cyclic/non-cyclic
- Master absolute/relative
- Slave absolute/relative
Basic CAM List of data points that describe the
relationship between the slave
position and the master position.
Advanced CAM Describes the relationship between
the slave and the master based on
nodes, segments, actions, and exit
conditions.
CAM prole activation
request (Handshaking)
Handshaking procedure with
Controlword and Statusword to
activate a valid CAM prole. This
does not necessarily mean that the
prole starts immediately. This
depends on the CAM conguration,
time of CAM activation request, and
so on.
Change CAM immediate/
delayed
In the Controlword there are 2
options for changing the CAM:
- Immediate: Abort the currently
running CAM and immediately
change to the new CAM.
- Delayed: The currently running
CAM prole nishes rst before
the CAM is activated (see
Illustration 2.37).
CAM prole activation All setpoints of the CAM prole are
calculated and the servo drive is
able to run the CAM prole. This
mainly contains the calculations for
blending.
Full CAM A basic CAM that is dened with
the 1
st
data point at guide value 0
and last data point at guide value
1. The CAM is dened over the
whole guide value cycle. Not
applicable for advanced CAM.
Servo Drive Operation Programming Guide
MG36D102 Danfoss A/S © 01/2017 All rights reserved. 39
2 2

 Loading...
Loading...
















