v With the CLI, log in as an admin user, then open the CLI and issue the
lsnode -r command to determine whether CTDB is active on all nodes.
The system displays information similar to the following:
[yourlogon@yourmachine]$ lsnode -r
EFSSG0015I Refreshing data.
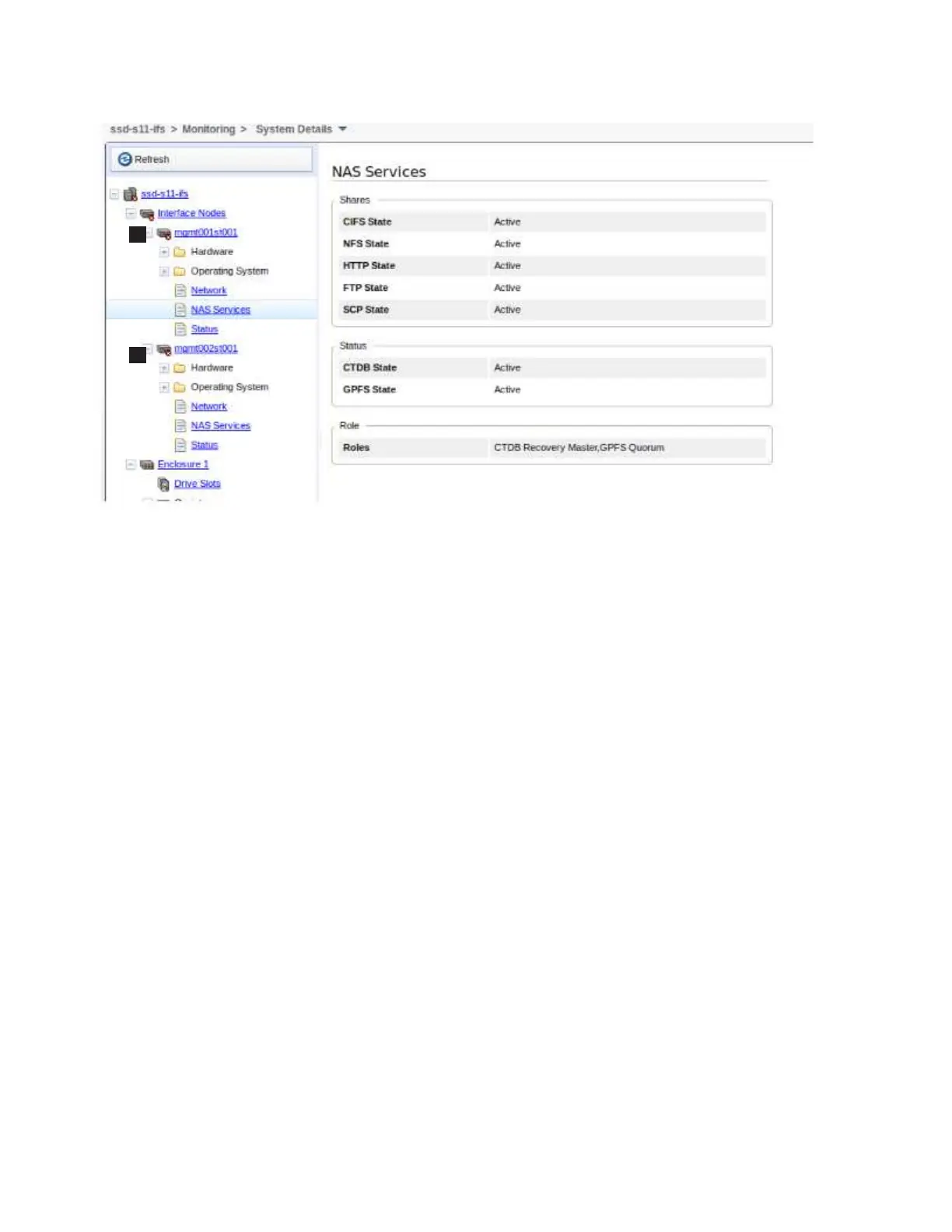
Hostname IP Description Role
mgmt001st001 10.254.8.2 active management node management,interface,storage
mgmt002st001 10.254.8.3 passive management node management,interface,storage
Product version Connection status GPFS status CTDB status Last updated
1.3.0.0-55c OK active active
1.3.0.0-55c OK active unhealthy
EFSSG1000I The command completed successfully.
In the CTDB Status column, “active” indicates a healthy status and “unhealthy”
indicates an error status. A "disconnected" status is displayed when this CTDB
node could not be reached through the network and is currently not
participating in the cluster.
2. If the CTDB status for a file module is not “active”, perform one or more of the
following procedures:
v Review the health status for any potential network problems. A network
failure between a file module and the customer can result in an
“UNHEALTHY” CTDB status. Follow the appropriate error code action plans
to resolve the network problems. Refer to “Checking network interface
availability” on page 195.
v If the network has been examined without any problems being identified,
perform the procedures in “Checking the GPFS file system mount on each
file module” on page 189.
v Refer to the information in "Troubleshooting the System x3650 server" topic
in the IBM Storwize V7000 Unified Information Center to determine if any
additional hardware problems might be causing the “unhealthy” CTDB
status.
Figure 72. Management GUI showing CTDB status for both file modules
188 Storwize V7000 Unified: Problem Determination Guide 2073-720
 Loading...
Loading...











