Group 12 Appendix - Encoder Guidelines Page 389
JET3up Release R1.06
12.3 Encoder guidelines and “hot-plugging” of external devices
Encoders (also called incremental encoder) are used for the dynamic capture of angles
of shafts or to measure distances and speed information.
They are based on a technology which converts mechanical movements like rotation or
linear movement to electrical digital signals. In combination with measurement wheels
or gear racks, encoders can be also used to measure linear movements as e.g.
distances.
Types of encoders:
Regarding the different internal technology of the encoders, they are distinguished into
two different principles:
Incremental encoders:
supply simple “endless” square wave signals
supply digital signals on several data output lines
(parallel signal output) ⇒ this encoder type
cannot be used!!!
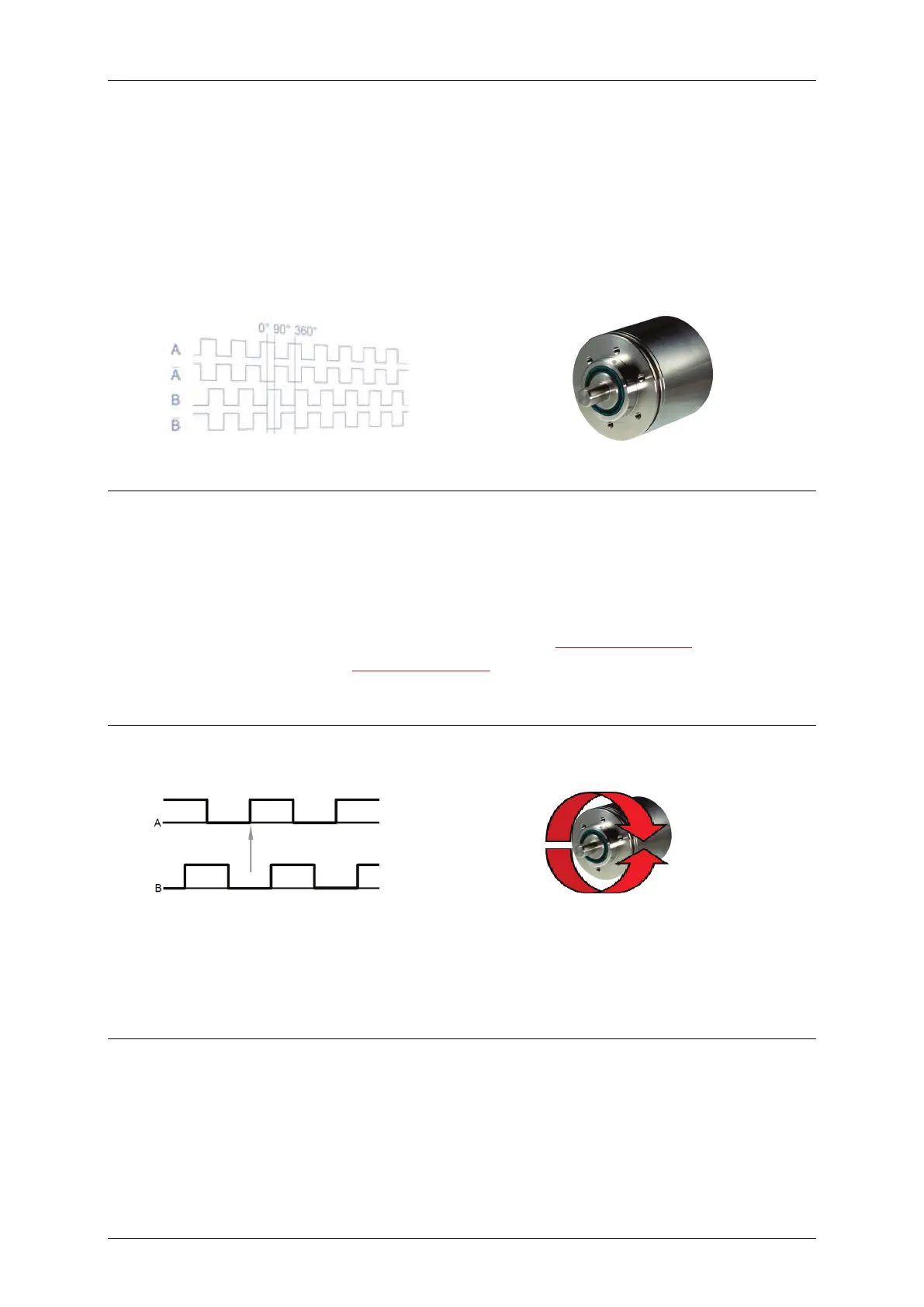
Direction of rotation:
Typically encoders are supplying two output signals which are shifted 90°.
Just with this two shifted signals a so-called „direction detection“ can be realized. Due
to the analysis of the phase position of signal „A“ and the phase position of signal “B”
the electronic can detect if the encoder turns forward or backwards.
Control of print width:
With the help of the encoder signals the printer gets information about the distance and
the speed of the current production and is therefore able to regulate an accurate print
width of the printout.
Just due the permanent and current measurement of the encoder, a steady print width
can be ensured even at varying speeds of the production line.

 Loading...
Loading...