3.1 Introduction to BGP/MPLS IP VPN
This section describes the principle and concepts of BGP/MPLS IP VPN.
BGP/MPLS IP VPN is a PE-based L3VPN technology which is a solution of the Provider
Provisioned VPN (PPVPN). BGP/MPLS IP VPN advertises VPN routes on the backbone
network of the ISP by using BGP and forwards VPN packets through MPLS.
The networking of BGP/MPLS IP VPN is flexible and extensible. The BGP/MPLS IP VPN
supports MPLS QoS and MPLS TE, and thus it is used widely.
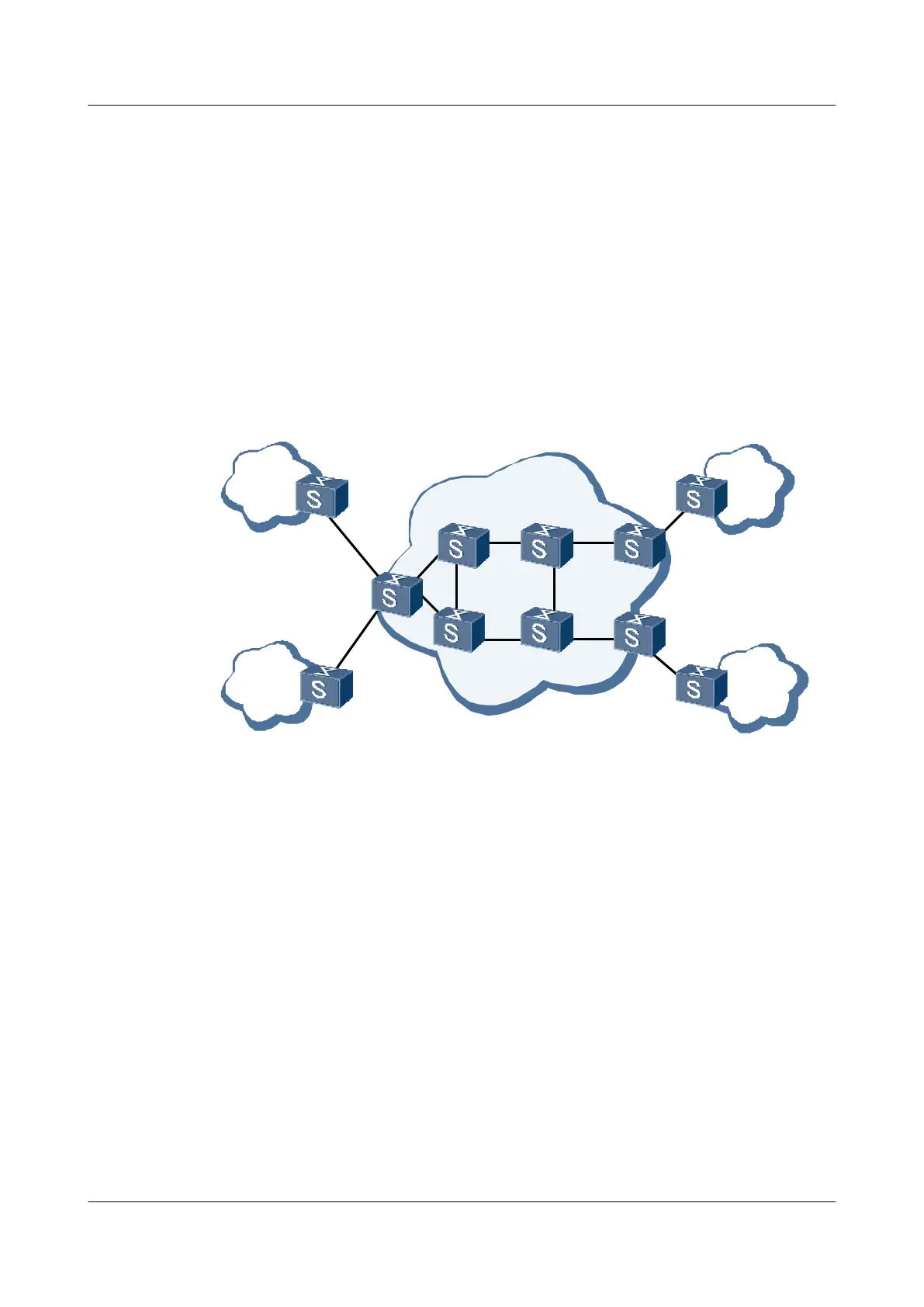
Figure 3-1 shows the model of the BGP/MPLS IP VPN.
Figure 3-1 BGP/MPLS IP VPN model
Site
VPN 1
CE CE
PE
PE
Service provider's
backbone
P P
P
CE
PE
Site
VPN 2
CE
P
Site
VPN 1
Site
VPN 2
The model of the BGP/MPLS IP VPN consists of CE, PE, and P.
l Customer edge (CE) device: It is an edge device on the user network. A CE provides
interfaces that are directly connected to the SP network. A CE can be a router, a switch, or
a host. In most situations, a CE neither senses a VPN nor supports MPLS.
l Provider edge (PE) device: It is an edge device on the SP network. A PE is directly
connected to a CE. On an MPLS network, PEs process all VPN services.
l Provider (P) device: It is a backbone device on the SP network. A P is not directly connected
to a CE. The P only forwards MPLS packets, without maintaining information about a
VPN.
l Site: It is a group of IP systems. Sites have IP connectivity between each other and this
connectivity is realized without the service provider network. A site is connected to the ISP
network through the CE. Generally, a site may contain many CEs, but a CE belongs only
to a single site.
3.2 BGP/MPLS IP VPN Supported by the S9300
This section describes the BGP/MPLS IP VPN features supported by the S9300.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Configuration Guide - VPN 3 BGP/MPLS IP VPN Configuration
Issue 03 (2009-08-20) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-3

 Loading...
Loading...















