6.1 Introduction to VPLS
This section describes the principle of PWE3.
With the development of Ethernet technologies, Ethernet has become a leading networking
technology for Local Area Networks (LANs). Moreover, Ethernet is increasingly used for
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) as an access
technology.
Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) is used to connect multiple Ethernet LAN segments through
the Packet Switch Network (PSN) so that the Ethernet LAN segments can operate in an
environment similar to a LAN.
The VPLS is also called Transparent LAN Service (TLS) or Virtual Private Switched Network
service (VPSNS). Different from Point to Point (P2P) services of a common L2VPN, the VPLS
technology enables service providers to offer Ethernet-based multipoint services to customers
through the MPLS backbone network.
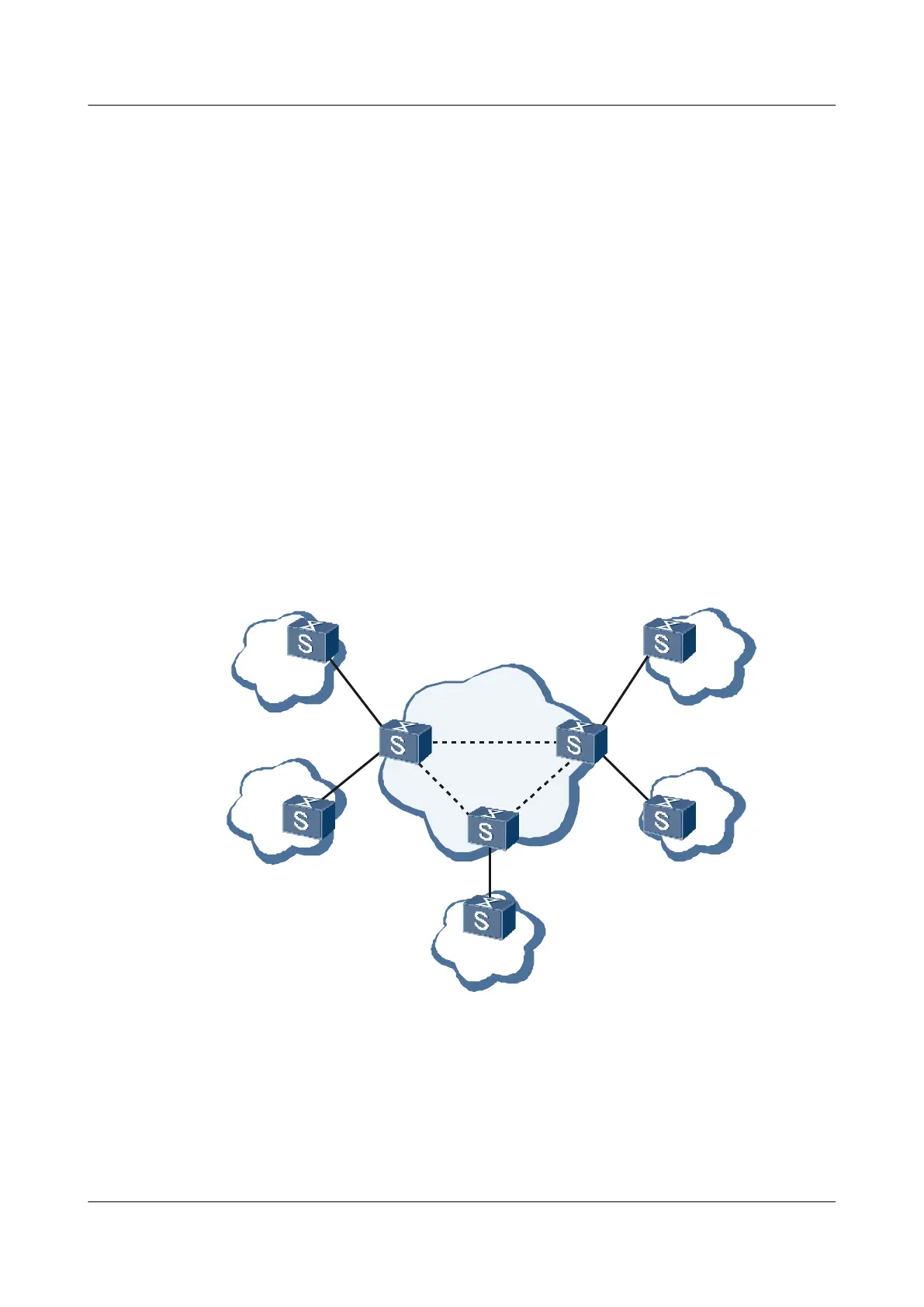
As shown in Figure 6-1, normally, a VPLS contains multiple sites connected to Provider Edge
(PE) devices to implement an emulated LAN.
Figure 6-1 VPLS architecture
VPLS- A
VPLS -B
CE
CE
PE
PE
PE
Emulated
LAN
VPLS- A
CE
VPLS- A
VPLS -B
CE
CE
site1
site2
site3
site4
site5
In a VPLS network, the PSN simulates network bridge devices and forwards packets based on
MAC addresses, or MAC addresses and VLAN tags.
Basic concepts of VPLS are as follows:
l PW
6 VPLS Configuration
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Configuration Guide - VPN
6-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 03 (2009-08-20)

 Loading...
Loading...















