7.21.1 DC braking
DC braking is used for applications where the motor must be actively stopped; however, neither
converter energy recovery nor a braking resistor is required for this function. DC braking is not
possible with a permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Typical applications for DC braking include:
• Centrifuges
• Saws
• Grinding machines
• Conveyor belts
DC braking is not permissible in applications involving suspended loads, e.g. lifting
equipment/cranes and vertical conveyors.
Function
NOTICE
Motor overheating as a result of DC braking
The motor will overheat if you use DC braking too frequently or use it for too long. This may
damage the motor.
• Monitor the motor temperature.
• Allow the motor to adequately cool down between braking operations.
• If necessary, select another motor braking method.
With DC braking, the converter outputs an internal OFF2 command for the time that it takes
to de-energize the motor p0347 - and then impresses the braking current for the duration of
the DC braking.
The DC-braking function is possible only for asynchronous motors.
4 dierent events initiate DC braking:
DC braking when falling below a starting speed
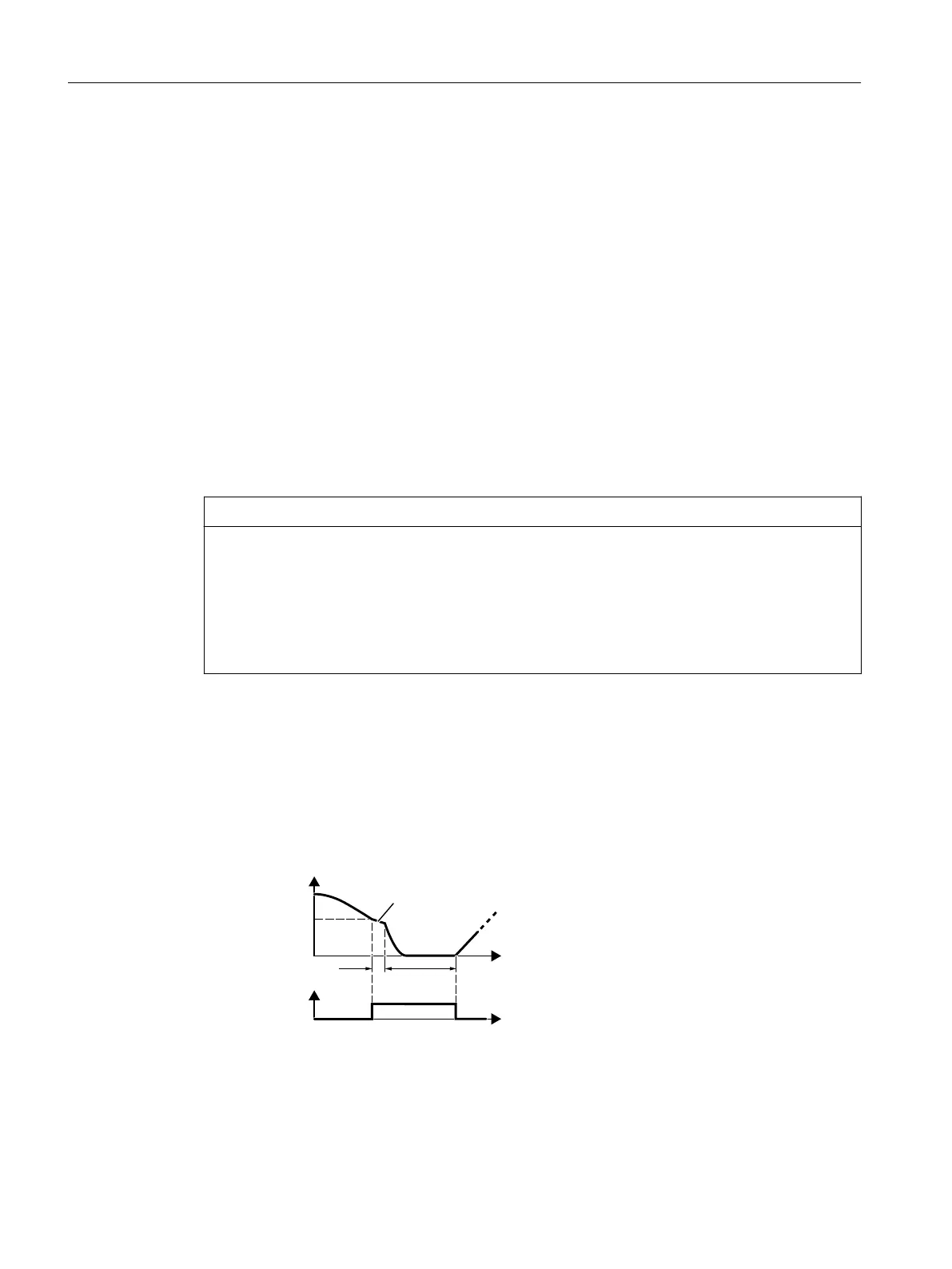
'&EUDNLQJ
DFWLYH
2))
6WDUWVSHHG
7LPHLQWHUYDO
Q
S
W
W
Requirement:
p1230 = 1 and p1231 = 14
Function:
1. The motor speed has fallen below the start‐
ing speed.
2. The converter activates the DC braking as
soon as the motor speed falls below the
starting speed.
Advanced commissioning
7.21Electrically braking the motor
SINAMICS G115D Wall Mounted distributed drive
310 Operating Instructions, 07/2023, FW V4.7 SP14, A5E52808211A AA

 Loading...
Loading...











