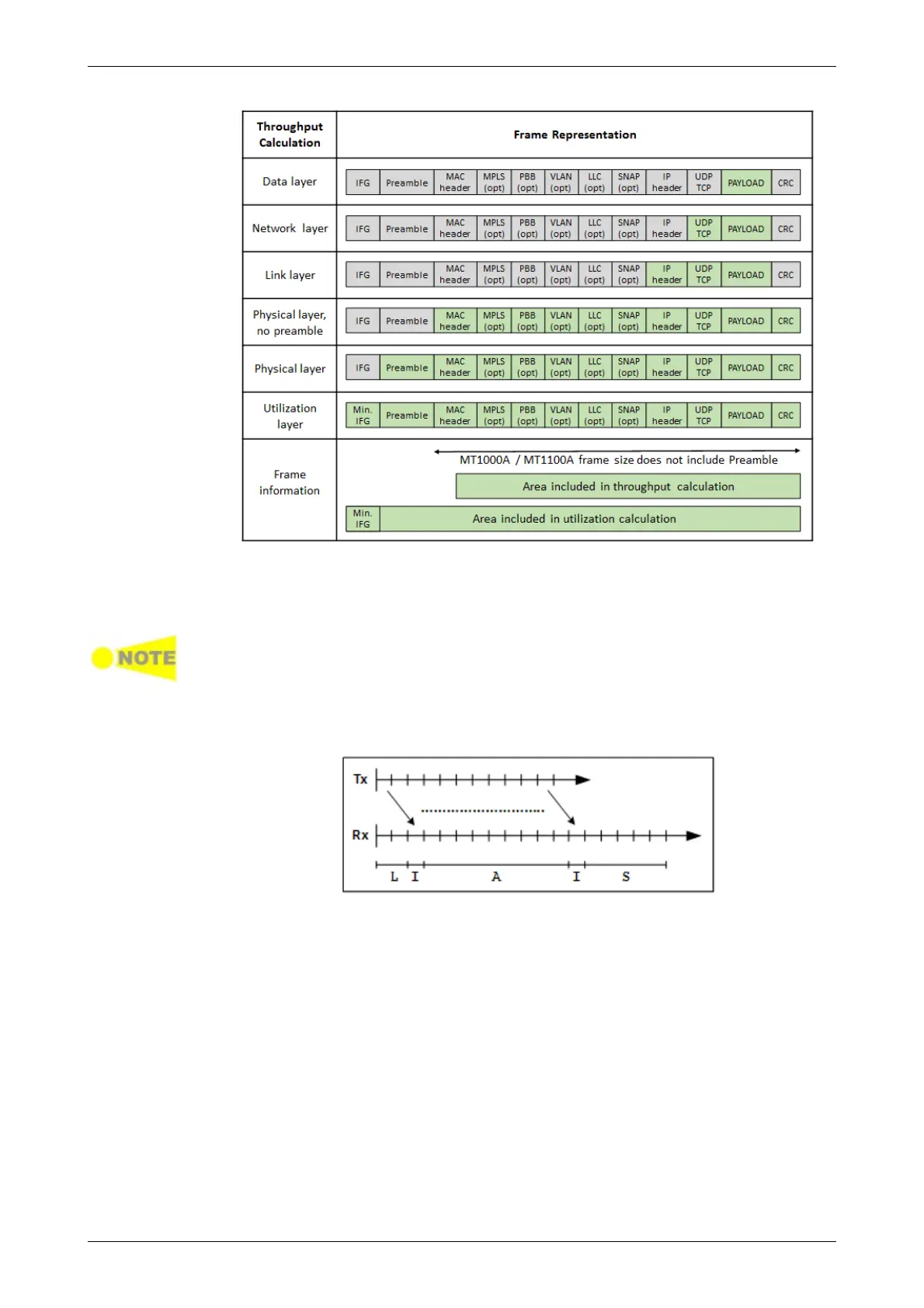
Each calculation is done on a one second base. It is possible either to
register the maximum throughput (actually showing only the second with the
highest throughput), or to register an average throughput per second taken
over a selected part of the test period.
The calculation depends on the setting of the transmitted frame contents. Even
in cases where the transmitter is not used, the calculation will be based on this
setting.
The part of the test from which the average throughput is calculated, is
selected in a way to avoid influence from latency and missing frames. The
drawing below illustrates this.
The Tx graph shows the transmitted periods, and the Rx graph shows the
received periods. Due to latency the receiver will first see the transmitted
frames some time later than when transmitter actually sent the frames (the
L-period). This is also why the receiver may have more periods than the
transmitter, in order to await delayed frames. However the receiver will
maximum wait for 10 extra periods (seconds) before it times out, as frames
may actually physically be lost somewhere in the network.
The average calculation is triggered when the receiver actually sees the first
frame. The frames in this first I-period are ignored. Then the average
calculation is started and runs over the next duration-2 A-periods. Frames in
the last I-period are also ignored. Frames in the remaining S-periods have no
influence on the average calculation.
6.10 RFC 6349
 Loading...
Loading...