Calculation of motor-shaft conversion torque and effective torque
• Calculation of acceleration torque (TA)
Motor
JL
JM
TA
JL
JM
η
tA
N
: Acceleration torque [N·m]
:
Motor-shaft conversion load inertia [kg·m
2
]
: Motor-rotor inertia [kg·m
2
]
: Efficiency of transfer part (η≤1)
: Acceleration time [s]
: Motor rotation speed [r/min]
Speed (rotation speed)
Time
N
tA
• Calculation of motor-shaft conversion load torque (TL)
F
D
TW
TW [N·m]=F· × 10
–
3
D
2
(Generally, the friction force can be calculated as:
F=
Mg [N], where
: Coefficient of friction
: Mass of motion part [kg]
: Acceleration of gravity (g≈9.8 [m/s
2
])
Motor
Z
2
TL
Z1
TL [N·m]=TW ·
G
TL
TW
Z1
Z
2
G
: Motor-shaft conversion load torque [N·m]
:
Load torque (Load-shaft conversion) [N·m]
: Number of motor-side gear teeth
: Number of load-side gear teeth
:
Gear ratio (Speed reduction ratio) =Z1/Z2
TW
F
D
: Load torque (Load-shaft conversion) [N·m]
: External force [N]
: Diameter of cylinder [mm]
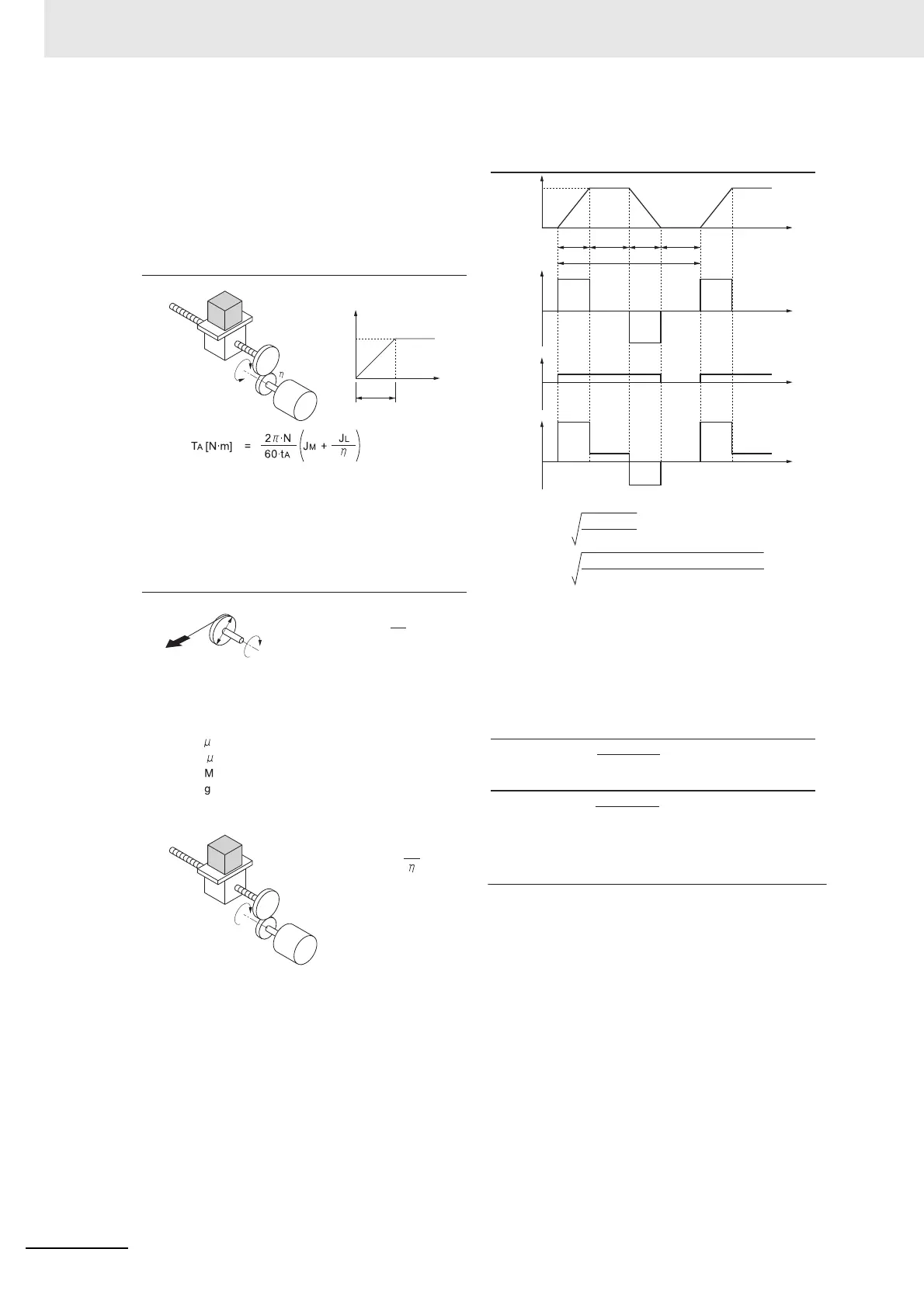
• Calculation of combined torque and effective torque
[r/min]
Time
Rotation
speed
Load
torque
Combined
torque
Acceleration/
Deceleration torque
[N·m]
[N·m]
[N·m]
Time
t1 t 2 t3 t4
0
Time
0
TA
Time
0
T1
TL
T2
T3
T4
· Effective torque TRMS [N·m]
=
∑(Ti
2
· ti)
∑t
i
=
T1
2
· t1 + T 2
2
· t2 + T3
2
· t3 + T4
2
· t4
t
1 + t 2 + t3 + t4
· Maximum torque MAX [N·m] =T
T
1 =TA +TL
Motor selection
• Motor capacity conversion to effective torque
]nim/r[
N: Maximum rotation speed
• Motor capacity required for maximum torque output
]nim/r
[
N: Maximum rotation speed
Motor capacity [kW]
= ×10
–
3
2π ·T RMS·N
60
Motor capacity [kW]
=
–
3
2π ·T MAX ·N
60×1.5
N
1 cycle1 cycle
Inverter Capacity Selection
Rated motor current
≤
Rated output current of inverter
Max. continuous torque output time for application ≤ 1 min
Calculate the acceleration torque from the motor-shaft conver-
sion load inertia, the motor-rotor inertia, and the acceleration.
Then, calculate the load torque from the external force (gravity
and tension) and friction force applied to the load. Finally,
combine these calculation results to calculate the torque
required for the motor.
Based on the above calculation results, select the motor capacity
by using the following formulae.
Select the larger of the two calculated values as the motor capacity.
Also, when selecting a motor, take into consideration the errors in
calculation and modeling. Select a motor whose capacity is at least
approximately 20% larger.
* The above calculation formulae assume that the maximum
motor toque is 150% of the rated torque.
Select an inverter that can be used with the motor you
selected based on the result of motor capacity selection.
Basically, select an inverter which fits the maximum
applicable motor capacity of the selected motor.
After selecting an inverter, check if it meets the both of the
following conditions. If not, select an inverter that has a
one class larger capacity and check again.
×10
Note 1. In the light load mode, the overload capacity of the inverter is 150%
of the rated torque for 5 seconds. Use the 5-seconds rating when
determining the maximum continuous torque.
2. If you want to use 0-Hz sensorless vector control, need a holding
torque at a rotation speed of 0 (r/min), or frequently require 150% of
the rated torque or more, use an inverter with a one class larger
capacity than the one selected by the above method.
1 cycle

 Loading...
Loading...











