Chapter 14
| Multicast Filtering
MLD Snooping (Snooping and Query for IPv6)
– 571 –
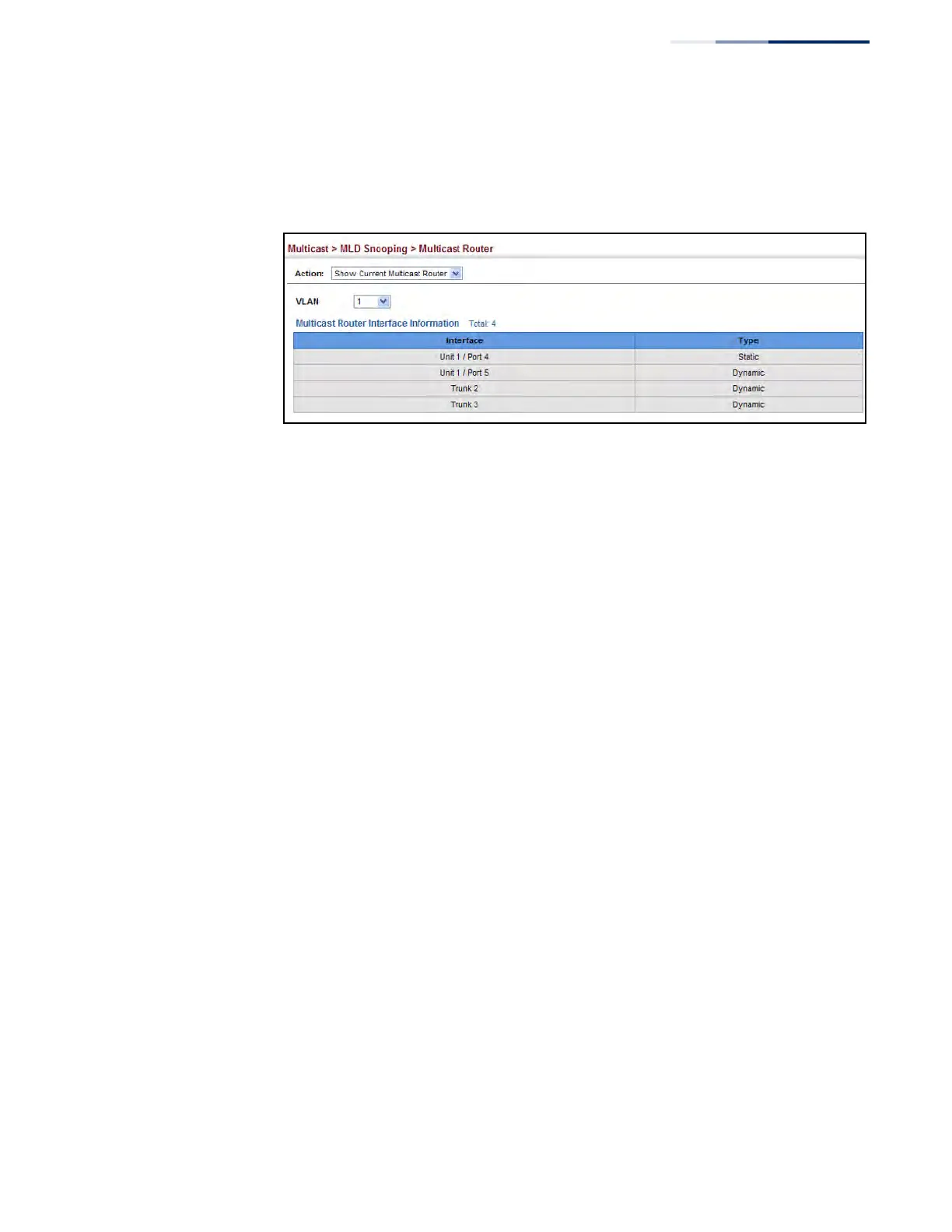
3. Select the VLAN for which to display this information. Ports in the selected
VLAN which are attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch are
displayed.
Figure 360: Showing Current Interfaces Attached an IPv6 Multicast Router
Assigning Interfaces
to IPv6 Multicast
Services
Use the Multicast > MLD Snooping > MLD Member (Add Static Member) page to
statically assign an IPv6 multicast service to an interface.
Multicast filtering can be dynamically configured using MLD snooping and query
messages (see “Configuring MLD Snooping and Query Parameters” on page 567).
However, for certain applications that require tighter control, it may be necessary to
statically configure a multicast service on the switch. First add all the ports attached
to participating hosts to a common VLAN, and then assign the multicast service to
that VLAN group.
Command Usage
◆ Static multicast addresses are never aged out.
◆ When a multicast address is assigned to an interface in a specific VLAN, the
corresponding traffic can only be forwarded to ports within that VLAN.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ VLAN – Specifies the VLAN which is to propagate the multicast service.
(Range: 1-4094)
◆ Multicast IPv6 Address – The IP address for a specific multicast service.
◆ Interface – Activates the Port or Trunk scroll down list.
◆ Port or Trunk – Specifies the interface assigned to a multicast group.
◆ Type (Show Current Member) – Shows if this multicast stream was statically
configured by the user, discovered by MLD Snooping, or is a data stream to
which no other ports are subscribing (i.e., the stream is flooded onto VLAN
instead of being trapped to the CPU for processing, or is being processed by
MVR6).

 Loading...
Loading...











