Chapter 19
| Unicast Routing
Configuring the Open Shortest Path First Protocol (Version 2)
– 718 –
Routers in a normal area may import or export routing information about
individual nodes. To reduce the amount of routing traffic flooded onto the network,
an area can be configured to export a single summarized route that covers a broad
range of network addresses within the area (page 732). To further reduce the
amount of routes passed between areas, an area can be configured as a stub
(page 725, page 729) or a not-so-stubby area (page 725, page 726).
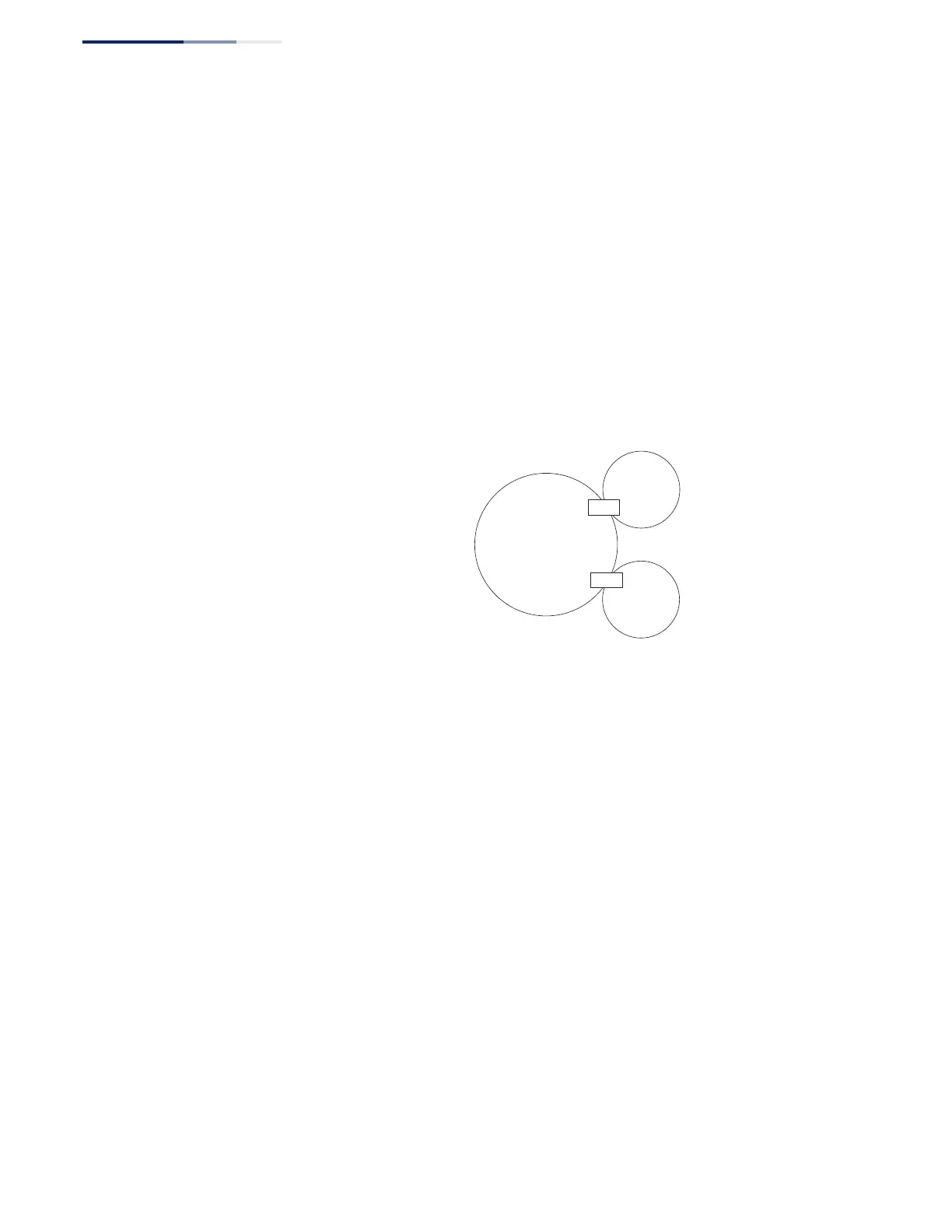
Normal Area – A large OSPF domain should be broken up into several areas to
increase network stability and reduce the amount of routing traffic required
through the use of route summaries that aggregate a range of addresses into a
single route. The backbone or any normal area can pass traffic between other areas,
and are therefore known as transit areas. Each router in an area has identical
routing tables. These tables may include area links, summarized links, or external
links that depict the topology of the autonomous system.
Figure 483: OSPF Areas
Command Usage
◆ Specify an Area ID and the corresponding network address range for each OSPF
broadcast area. Each area identifies a logical group of OSPF routers that actively
exchange Link State Advertisements (LSAs) to ensure that they share an
identical view of the network topology.
◆ Each area must be connected to a backbone area. This area passes routing
information between other areas in the autonomous system. All routers must
be connected to the backbone, either directly, or through a virtual link if a
direct physical connection is not possible.
◆ All areas are created as normal transit areas using the Network Area (Add) page.
A normal area (or transit area) can send and receive external LSAs. If necessary,
an area can be configured as a not-so-stubby area (NSSA) that can import
external route information into its area, or as a stubby area that cannot send or
receive external LSAs.
◆ An area must be assigned a range of subnetwork addresses. This area and the
corresponding address range forms a routing interface, and can be configured
to aggregate LSAs from all of its subnetwork addresses and exchange this
information with other routers in the network as described under “Configuring
Area Ranges (Route Summarization for ABRs)” on page 732.

 Loading...
Loading...











