Chapter 14
| Multicast Filtering
Multicast VLAN Registration for IPv4
– 592 –
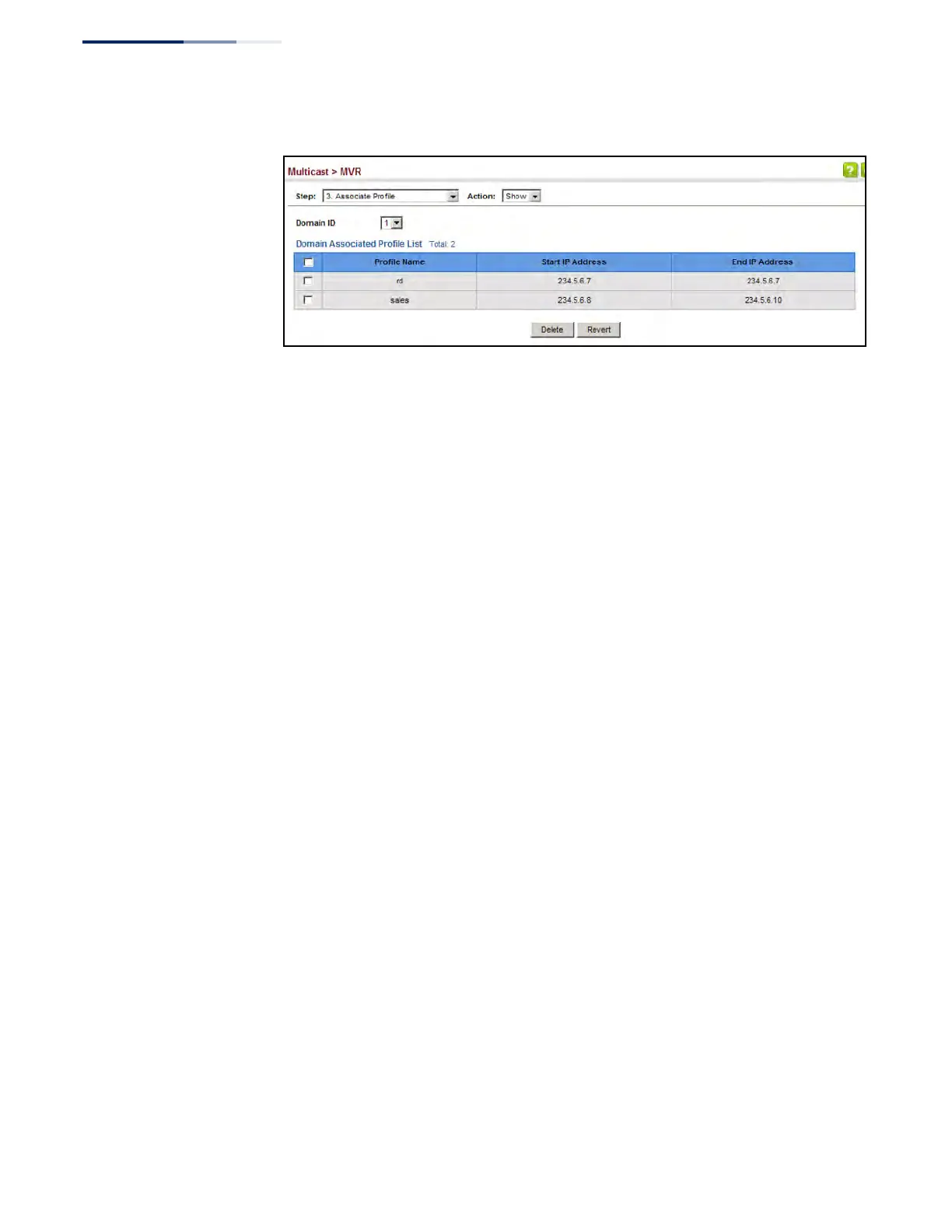
Figure 378: Showing the MVR Group Address Profiles Assigned to a Domain
Configuring MVR
Interface Status
Use the Multicast > MVR (Configure Interface) page to configure each interface that
participates in the MVR protocol as a source port or receiver port. If you are sure
that only one subscriber attached to an interface is receiving multicast services, you
can enable the immediate leave function.
Command Usage
◆ A port configured as an MVR receiver or source port can join or leave multicast
groups configured under MVR. However, note that these ports can also use
IGMP snooping to join or leave any other multicast groups using the standard
rules for multicast filtering.
◆ Receiver ports can belong to different VLANs, but should not be configured as a
member of the MVR VLAN. MVR allows a receiver port to dynamically join or
leave multicast groups sourced through the MVR VLAN. Multicast groups can
also be statically assigned to a receiver port (see “Assigning Static MVR
Multicast Groups to Interfaces” on page 594).
Receiver ports should not be statically configured as a member of the MVR
VLAN. If so configured, its MVR status will be inactive. Also, note that VLAN
membership for MVR receiver ports cannot be set to access mode (see“Adding
Static Members to VLANs” on page 169).
◆ One or more interfaces may be configured as MVR source ports. A source port is
able to both receive and send data for configured MVR groups or for groups
which have been statically assigned (see “Assigning Static MVR Multicast
Groups to Interfaces” on page 594).
All source ports must belong to the MVR VLAN.
Subscribers should not be directly connected to source ports.
◆ Immediate leave applies only to receiver ports. When enabled, the receiver port
is immediately removed from the multicast group identified in the leave
message. When immediate leave is disabled, the switch follows the standard
rules by sending a query message to the receiver port and waiting for a

 Loading...
Loading...











