Chapter 5
| VLAN Configuration
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
– 182 –
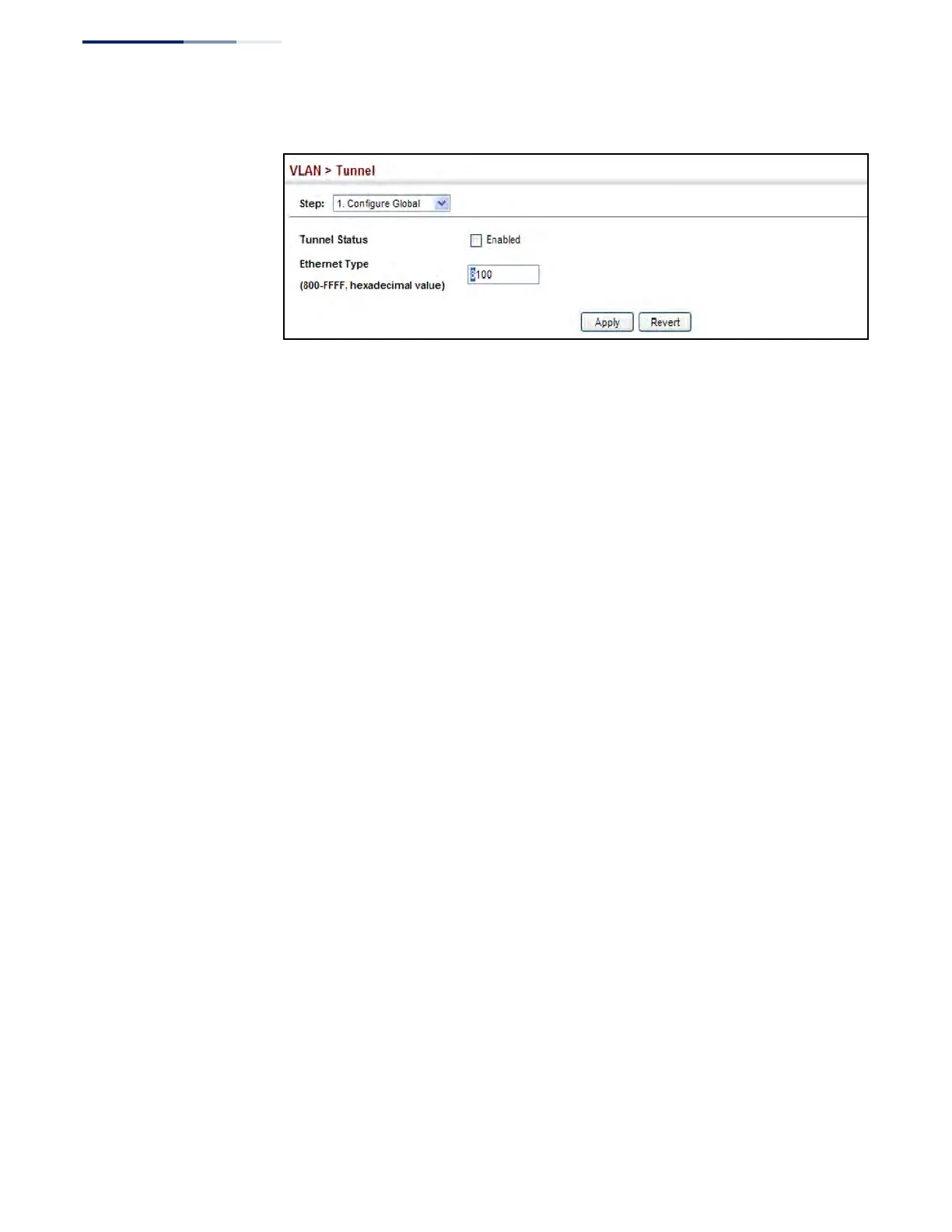
Figure 82: Enabling QinQ Tunneling
Creating
CVLAN to SPVLAN
Mapping Entries
Use the VLAN > Tunnel (Configure Service) page to create a CVLAN to SPVLAN
mapping entry.
Command Usage
◆ The inner VLAN tag of a customer packet entering the edge router of a service
provider’s network is mapped to an outer tag indicating the service provider
VLAN that will carry this traffic across the 802.1Q tunnel. By default, the outer
tag is based on the default VID of the edge router’s ingress port. This process is
performed in a transparent manner as described under “IEEE 802.1Q
Tunneling” on page 177.
◆ When priority bits are found in the inner tag, these are also copied to the outer
tag. This allows the service provider to differentiate service based on the
indicated priority and appropriate methods of queue management at
intermediate nodes across the tunnel.
◆ Rather than relying on standard service paths and priority queuing, QinQ VLAN
mapping can be used to further enhance service by defining a set of
differentiated service pathways to follow across the service provider’s network
for traffic arriving from specified inbound customer VLANs.
◆ Note that all customer interfaces should be configured as access interfaces
(that is, a user-to-network interface) and service provider interfaces as uplink
interfaces (that is, a network-to-network interface). Use the Configure Interface
page described in the next section to set an interface to access or uplink mode.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ Port – Port identifier. (Range: 1-28/52)
◆ Customer VLAN ID – VLAN ID for the inner VLAN tag. (Range: 1-4094)
◆ Service VLAN ID – VLAN ID for the outer VLAN tag. (Range: 1-4094)

 Loading...
Loading...











