Chapter 12
| Security Measures
Network Access (MAC Address Authentication)
– 299 –
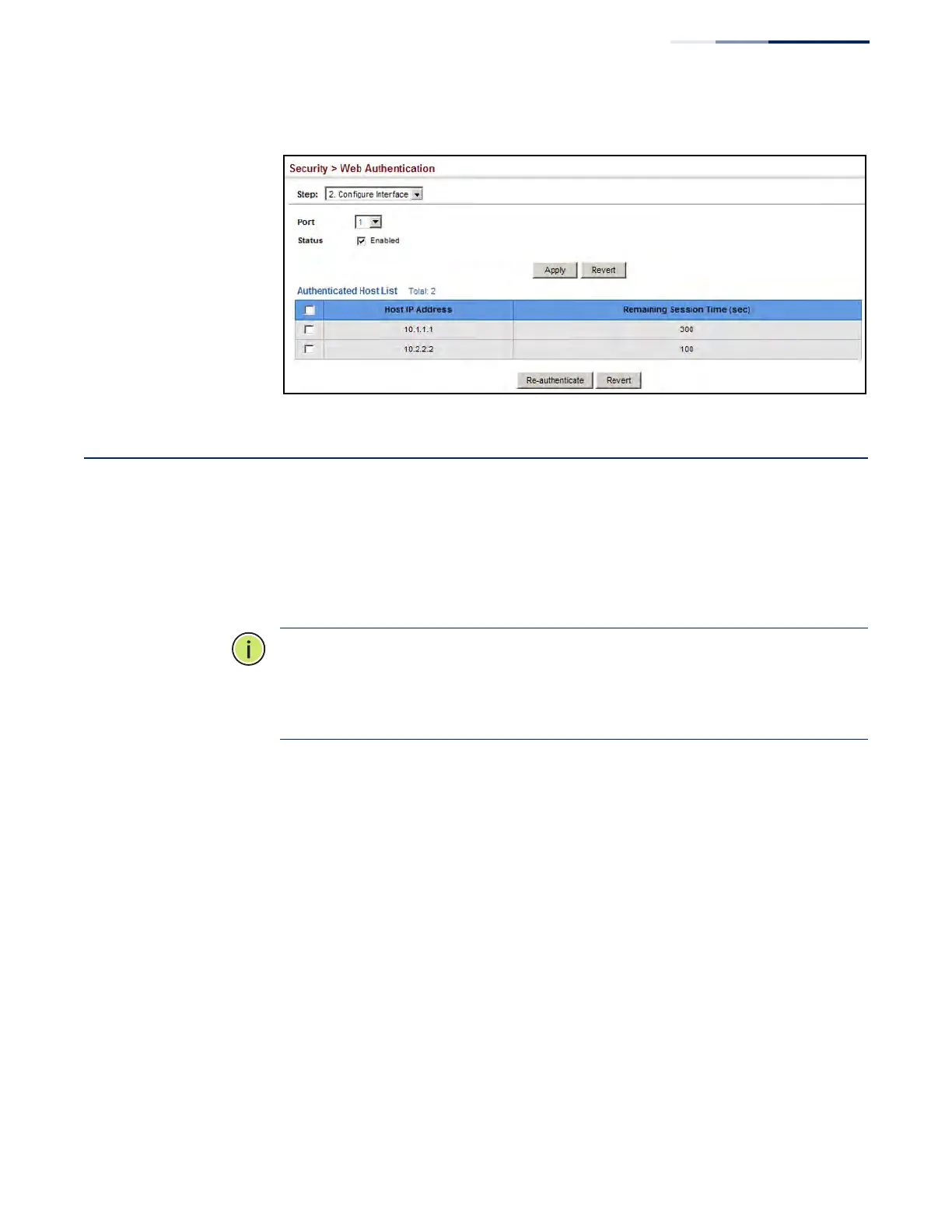
Figure 179: Configuring Interface Settings for Web Authentication
Network Access (MAC Address Authentication)
Some devices connected to switch ports may not be able to support 802.1X
authentication due to hardware or software limitations. This is often true for
devices such as network printers, IP phones, and some wireless access points. The
switch enables network access from these devices to be controlled by
authenticating device MAC addresses with a central RADIUS server.
Note:
RADIUS authentication must be activated and configured properly for the
MAC Address authentication feature to work properly. (See “Configuring
Remote Logon Authentication Servers” on page 280.)
Note:
MAC authentication cannot be configured on trunk ports.
Command Usage
◆ MAC address authentication controls access to the network by authenticating
the MAC address of each host that attempts to connect to a switch port. Traffic
received from a specific MAC address is forwarded by the switch only if the
source MAC address is successfully authenticated by a central RADIUS server.
While authentication for a MAC address is in progress, all traffic is blocked until
authentication is completed. On successful authentication, the RADIUS server
may optionally assign VLAN and quality of service settings for the switch port.
◆ When enabled on a port, the authentication process sends a Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP) request to a configured RADIUS server. The user
name and password are both equal to the MAC address being authenticated.
On the RADIUS server, PAP user name and passwords must be configured in the
MAC address format XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX (all in upper case).
◆ Authenticated MAC addresses are stored as dynamic entries in the switch
secure MAC address table and are removed when the aging time expires. The

 Loading...
Loading...











