Chapter 17
| General IP Routing
IP Routing and Switching
– 670 –
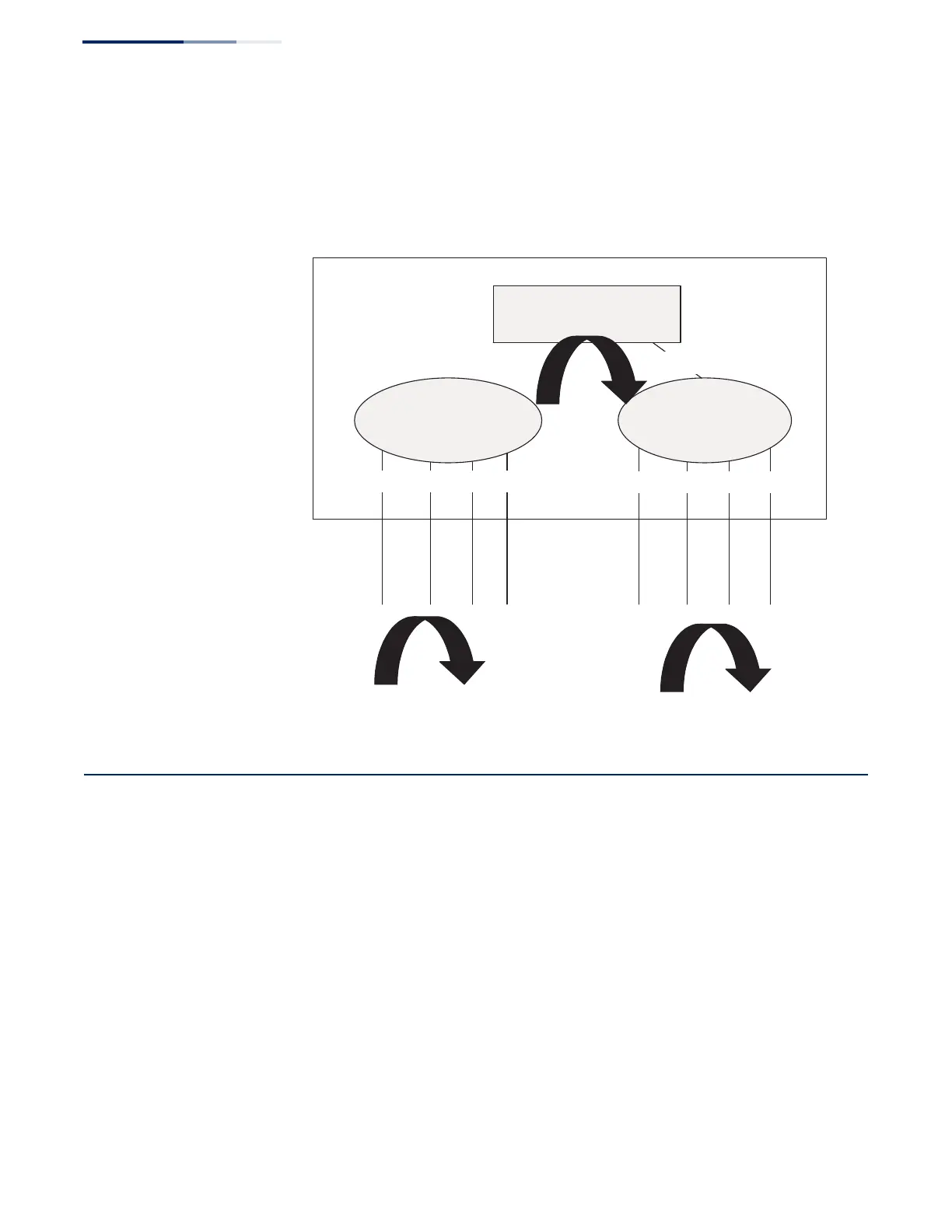
Each VLAN represents a virtual interface to Layer 3. You just need to provide the
network address for each virtual interface, and the traffic between different
subnetworks will be routed by Layer 3 switching.
Figure 440: Virtual Interfaces and Layer 3 Routing
IP Routing and Switching
IP Switching (or packet forwarding) encompasses tasks required to forward packets
for both Layer 2 and Layer 3, as well as traditional routing. These functions include:
◆ Layer 2 forwarding (switching) based on the Layer 2 destination MAC address
◆ Layer 3 forwarding (routing):
■
Based on the Layer 3 destination address
■
Replacing destination/source MAC addresses for each hop
■
Incrementing the hop count
■
Decrementing the time-to-live
■
Verifying and recalculating the Layer 3 checksum
If the destination node is on the same subnetwork as the source network, then the
packet can be transmitted directly without the help of a router. However, if the MAC
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
Inter-subnet traffic (Layer 3 switching)
Routing
Unt
Untagged
Unt
Untagged
Tagged or Untagged
Tagged or Untagged
Tagged or Untagged
Tagged or Untagged
Intra-subnet traffic (Layer 2 switching)

 Loading...
Loading...











