Chapter 20
| Multicast Routing
Configuring PIMv6 for IPv6
– 783 –
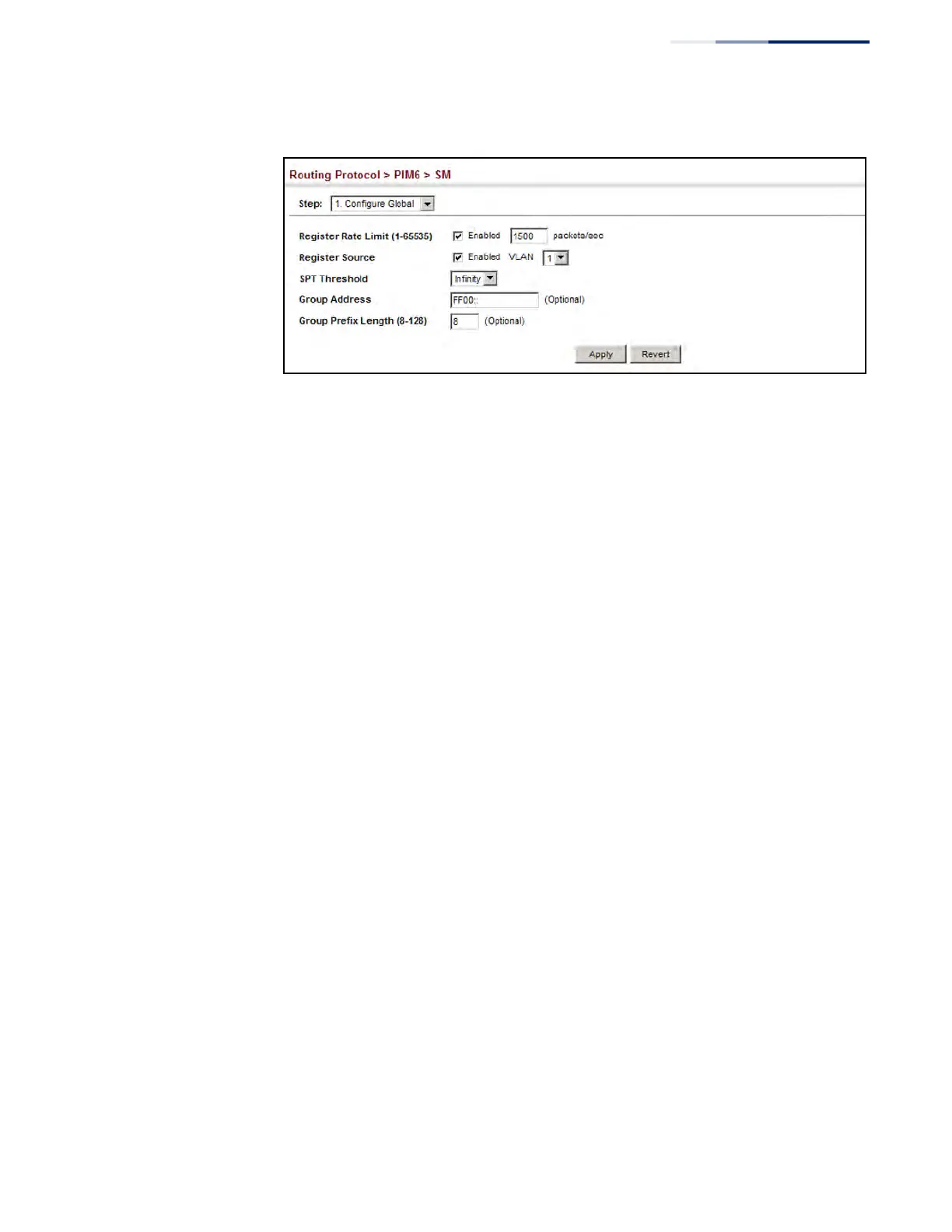
Figure 538: Configuring Global Settings for PIM6-SM
Configuring a PIM6
BSR Candidate
Use the Routing Protocol > PIM6 > SM (BSR Candidate) page to configure the
switch as a Bootstrap Router (BSR) candidate.
Command Usage
◆ When this router is configured as a BSR candidate, it starts sending bootstrap
messages to all of its PIM6-SM neighbors. The primary IP address of the
designated VLAN is sent as the candidate’s BSR address. Each neighbor
receiving the bootstrap message compares the BSR address with the address
from previous messages. If the current address is the same or a higher address,
it accepts the bootstrap message and forwards it. Otherwise, it drops the
message.
◆ This router will continue to be the BSR until it receives a bootstrap message
from another candidate with a higher priority (or a higher IP address if the
priorities are the same).
◆ To improve failover recovery, it is advisable to select at least two core routers in
diverse locations, each to serve as both a candidate BSR and candidate RP. It is
also preferable to set up one of these routers as both the primary BSR and RP.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ BSR Candidate Status – Configures the switch as a Bootstrap Router (BSR)
candidate. (Default: Disabled)
◆ VLAN ID – Identifier of configured VLAN interface. (Range: 1-4094)
◆ Hash Mask Length – Hash mask length (in bits) used for RP selection (see
“Configuring a PIM6 Static Rendezvous Point” on page 784 and “Configuring a
PIM6 RP Candidate” on page 786). The portion of the hash specified by the
mask length is ANDed with the group address. Therefore, when the hash
function is executed on any BSR, all groups with the same seed hash will be
mapped to the same RP. If the mask length is less than 32, then only the first

 Loading...
Loading...











