Chapter 17
| General IP Routing
Address Resolution Protocol
– 678 –
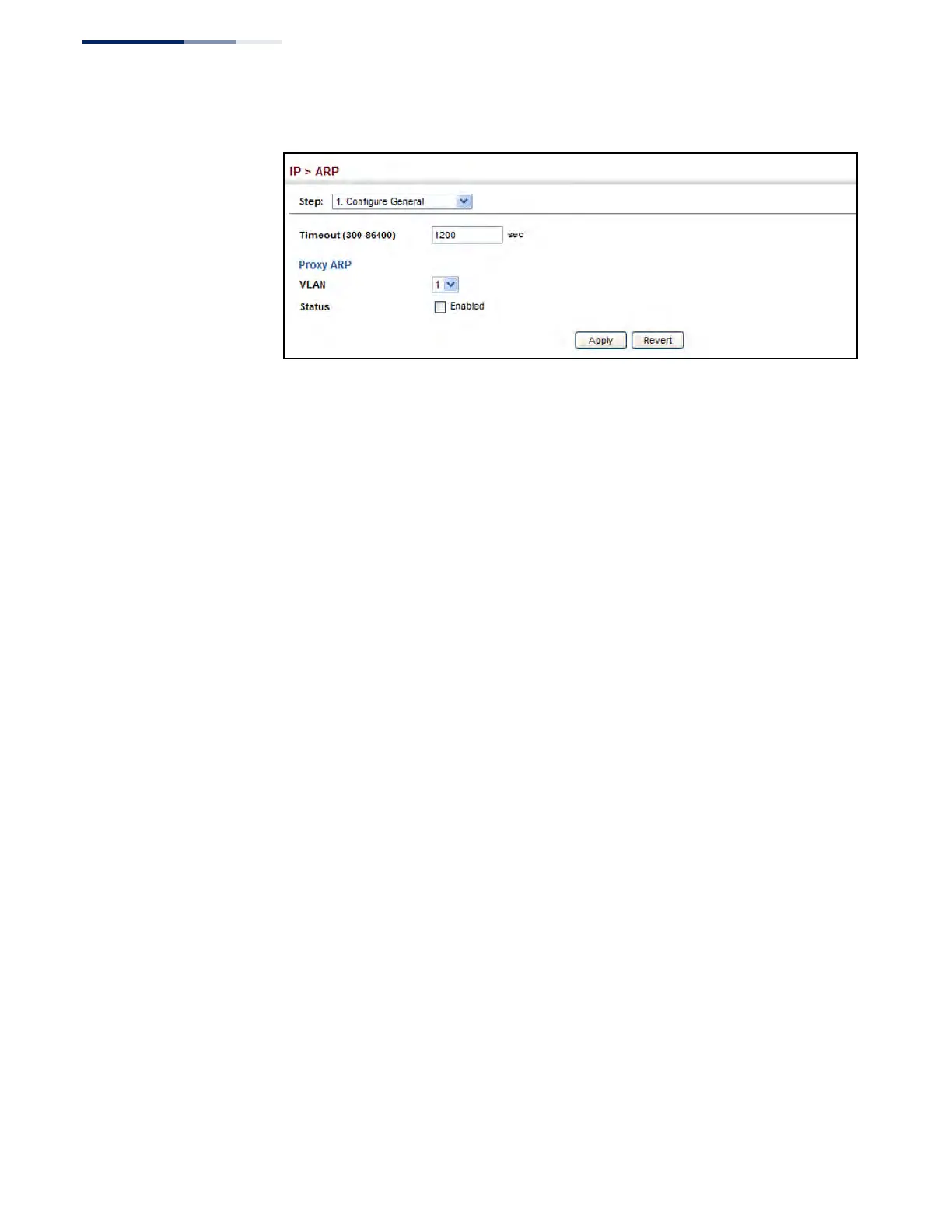
Figure 444: Configuring General Settings for ARP
Configuring
Static ARP Addresses
For devices that do not respond to ARP requests or do not respond in a timely
manner, traffic will be dropped because the IP address cannot be mapped to a
physical address. If this occurs, use the IP > ARP (Configure Static Address – Add)
page to manually map an IP address to the corresponding physical address in the
ARP cache.
Command Usage
◆ The ARP cache is used to map 32-bit IP addresses into 48-bit hardware (that is,
Media Access Control) addresses. This cache includes entries for hosts and
other routers on local network interfaces defined on this router.
◆ You can define up to 128 static entries in the ARP cache.
◆ A static entry may need to be used if there is no response to an ARP broadcast
message. For example, some applications may not respond to ARP requests or
the response arrives too late, causing network operations to time out.
◆ Static entries will not be aged out or deleted when power is reset. You can only
remove a static entry via the configuration interface.
◆ Static entries are only displayed on the Show page for VLANs that are up. In
other words, static entries are only displayed when configured for the IP subnet
of an existing VLAN, and that VLAN is linked up.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ IP Address – IP address statically mapped to a physical MAC address. (Valid IP
addresses consist of four numbers, 0 to 255, separated by periods.)
◆ MAC Address – MAC address statically mapped to the corresponding IP
address. (Valid MAC addresses are hexadecimal numbers in the format: xx-xx-
xx-xx-xx-xx)

 Loading...
Loading...











