Chapter 17
| General IP Routing
Configuring Static Routes
– 681 –
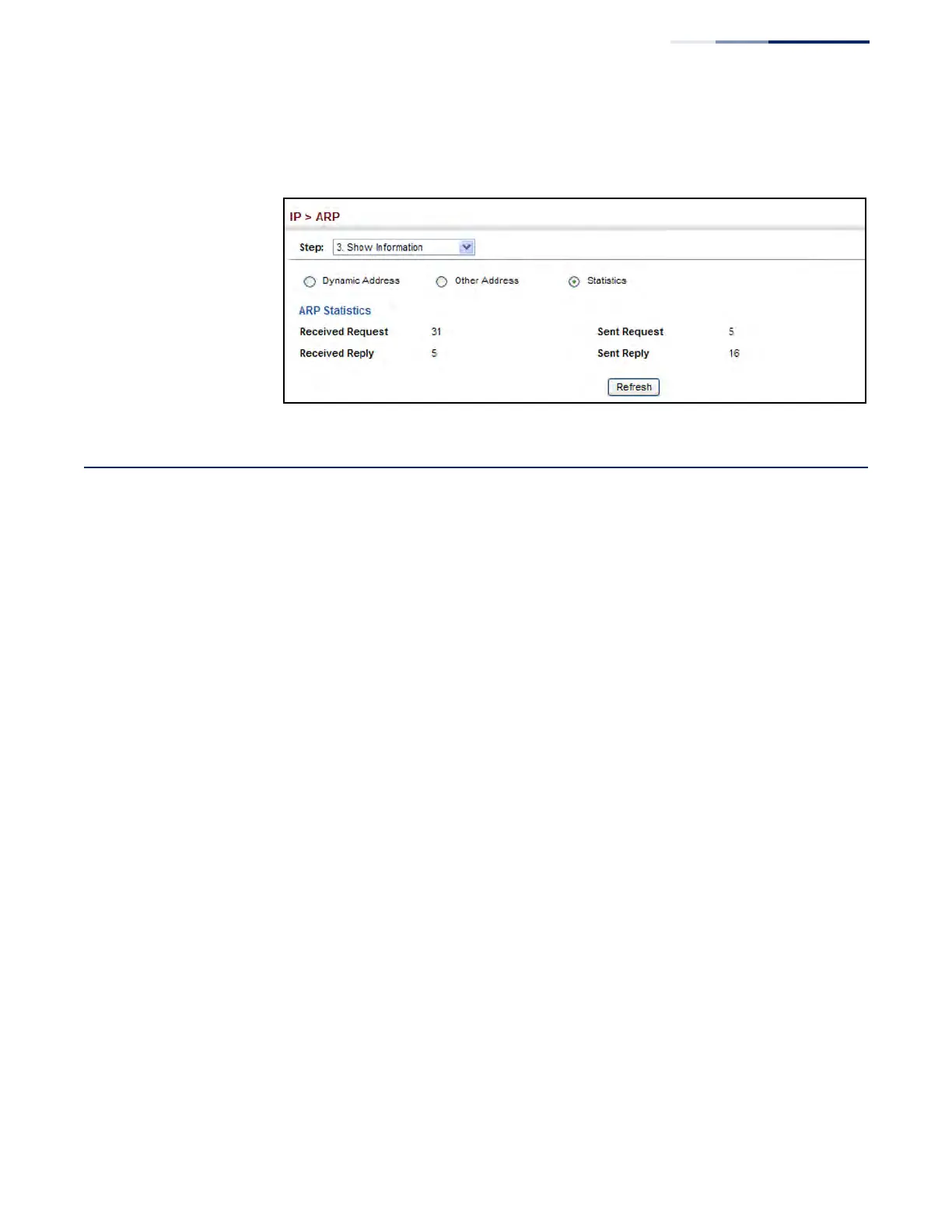
3. Click Statistics.
Figure 448: Displaying ARP Statistics
Configuring Static Routes
This router can dynamically configure routes to other network segments using
dynamic routing protocols (i.e., RIP, OSPF, BGP). However, you can also manually
enter static routes in the routing table using the IP > Routing > Static Routes (Add)
page. Static routes may be required to access network segments where dynamic
routing is not supported, or can be set to force the use of a specific route to a
subnet, rather than using dynamic routing. Static routes do not automatically
change in response to changes in network topology, so you should only configure
a small number of stable routes to ensure network accessibility.
Command Usage
◆ Up to 512 static routes can be configured.
◆ Up to eight equal-cost multipaths (ECMP) can be configured for static routing
(see “Equal-cost Multipath Routing” on page 684).
◆ If an administrative distance is defined for a static route, and the same
destination can be reached through a dynamic route at a lower administration
distance, then the dynamic route will be used.
◆ If both static and dynamic paths have the same lowest cost, the first route
stored in the routing table, either statically configured or dynamically learned
via a routing protocol, will be used.
◆ Static routes are included in RIP and OSPF updates periodically sent by the
router if this feature is enabled (see page 707 or 734, respectively).
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ Destination IP Address – IP address of the destination network, subnetwork,
or host.

 Loading...
Loading...











