Chapter 17
| General IP Routing
Equal-cost Multipath Routing
– 684 –
Parameters
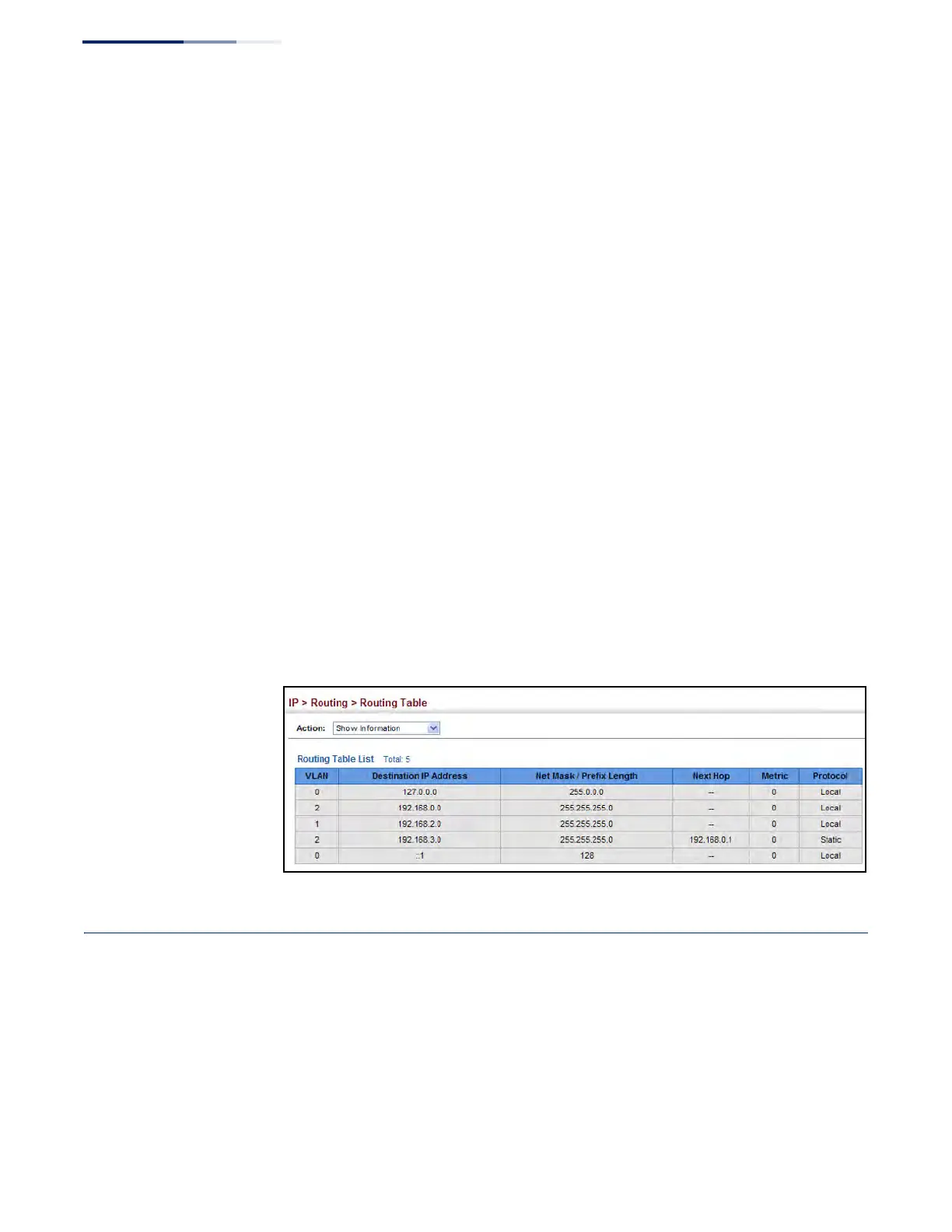
These parameters are displayed:
◆ VLAN – VLAN identifier (i.e., configured as a valid IP subnet).
◆ Destination IP Address – IP address of the destination network, subnetwork,
or host. Note that the address 0.0.0.0 indicates the default gateway for this
router.
◆ Net Mask / Prefix Length – Network mask for the associated IP subnet. This
mask identifies the host address bits used for routing to specific subnets.
◆ Next Hop – The IP address of the next hop (or gateway) in this route.
◆ Metric – Cost for this interface.
◆ Protocol – The protocol which generated this route information.
(Options: Local, Static, RIP, OSPF, Others)
Web Interface
To display the routing table:
1. Click IP, Routing, Routing Table.
2. Select Show Information from the Action List.
Figure 451: Displaying the Routing Table
Equal-cost Multipath Routing
Use the IP > Routing > Routing Table (Configure ECMP Number) page to configure
the maximum number of equal-cost paths that can transmit traffic to the same
destination. The Equal-cost Multipath routing algorithm is a technique that
supports load sharing over multiple equal-cost paths for data passing to the same
destination. Whenever multiple paths with equal path cost to the same destination
are found in the routing table, the ECMP algorithm first checks if the cost is lower
than that of any other entries in the routing table. If the cost is the lowest in the
table, the switch will use up to eight of the paths with equal lowest cost to balance
 Loading...
Loading...











