Program instructions
7.10 Interrupt
S7-200 SMART
284 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
Interrupt routine overview and CPU model event support
Before an interrupt routine can be invoked, an association must be assigned between the
interrupt event and the program segment that you want to execute when the event occurs.
Use the attach interrupt instruction to associate an interrupt event (specified by the interrupt
event number) and the program segment (specified by an interrupt routine number). You can
attach multiple interrupt events to one interrupt routine, but one event cannot be concurrently
attached to multiple interrupt routines.
When you attach an event and interrupt routine, new occurrences of this event will cause
execution of the attached interrupt routine only if the global ENI (enable interrupts)
instruction was executed and interrupt event processing is active. Otherwise, the event is
added to the interrupt event queue. If you disable all interrupts using the global DISI (disable
interrupts) instruction, each occurrence of the interrupt event is queued until interrupts are
re-enabled, using the global ENI (enable interrupt) instruction, or the interrupt queue
overflows.
You can disable individual interrupt events by breaking the association between the interrupt
event and the interrupt routine with the detach Interrupt instruction. The detach interrupt
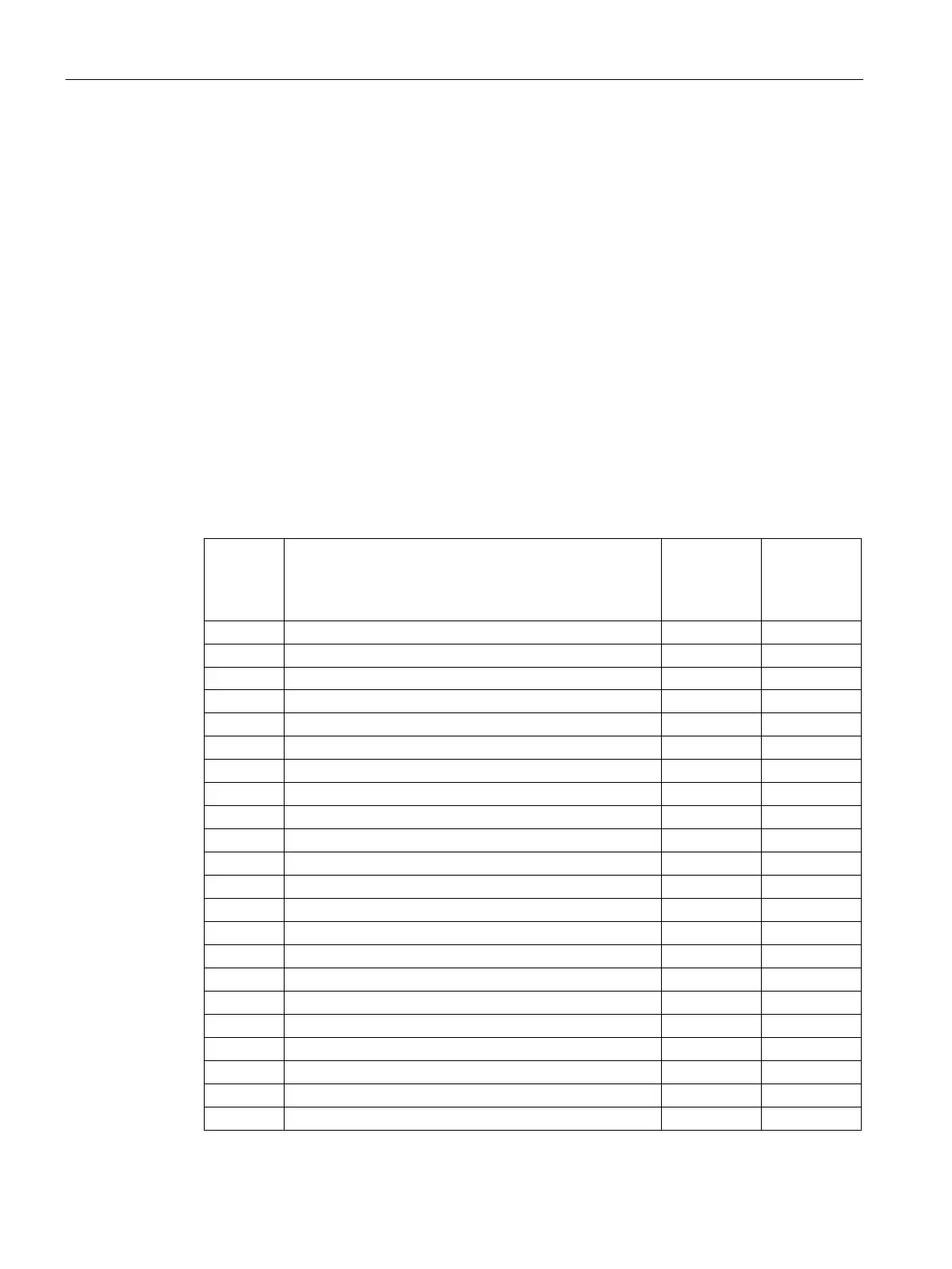
instruction returns the interrupt to an inactive or ignored state. The following table lists the
different types of interrupt events.
SR20/ST20
SR30/ST30
SR40/ST40
SR60/ST60
1 Falling edge I0.0 Y Y
Timed interrupt 0 (SMB34 controls the time interval)
Timed interrupt 1 (SMB35 controls the time interval)
HSC0 CV=PV (current value = preset value)
HSC1 CV=PV (current value = preset value)
HSC2 CV=PV (current value = preset value)
PLS0 PTO pulse count complete interrupt
PLS1 PTO pulse count complete interrupt
Timer T32 CT=PT (current time = preset time)
Timer T96 CT=PT (current time = preset time)

 Loading...
Loading...











