PLC concepts
4.2 Accessing data
S7-200 SMART
68 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
S (sequence control relay)
S bits are associated with SCRs, which you can use to organize machine or steps into
equivalent program segments. SCRs allow logical segmentation of the control program. You
can access the S memory as bits, bytes, words, or double words.
Table 4- 16 Absolute addressing of S memory
Bit: S
[byte address].[bit address]
S3.1
Byte, Word, or Double Word: S
[size][starting byte address]
SB4,
SW7,
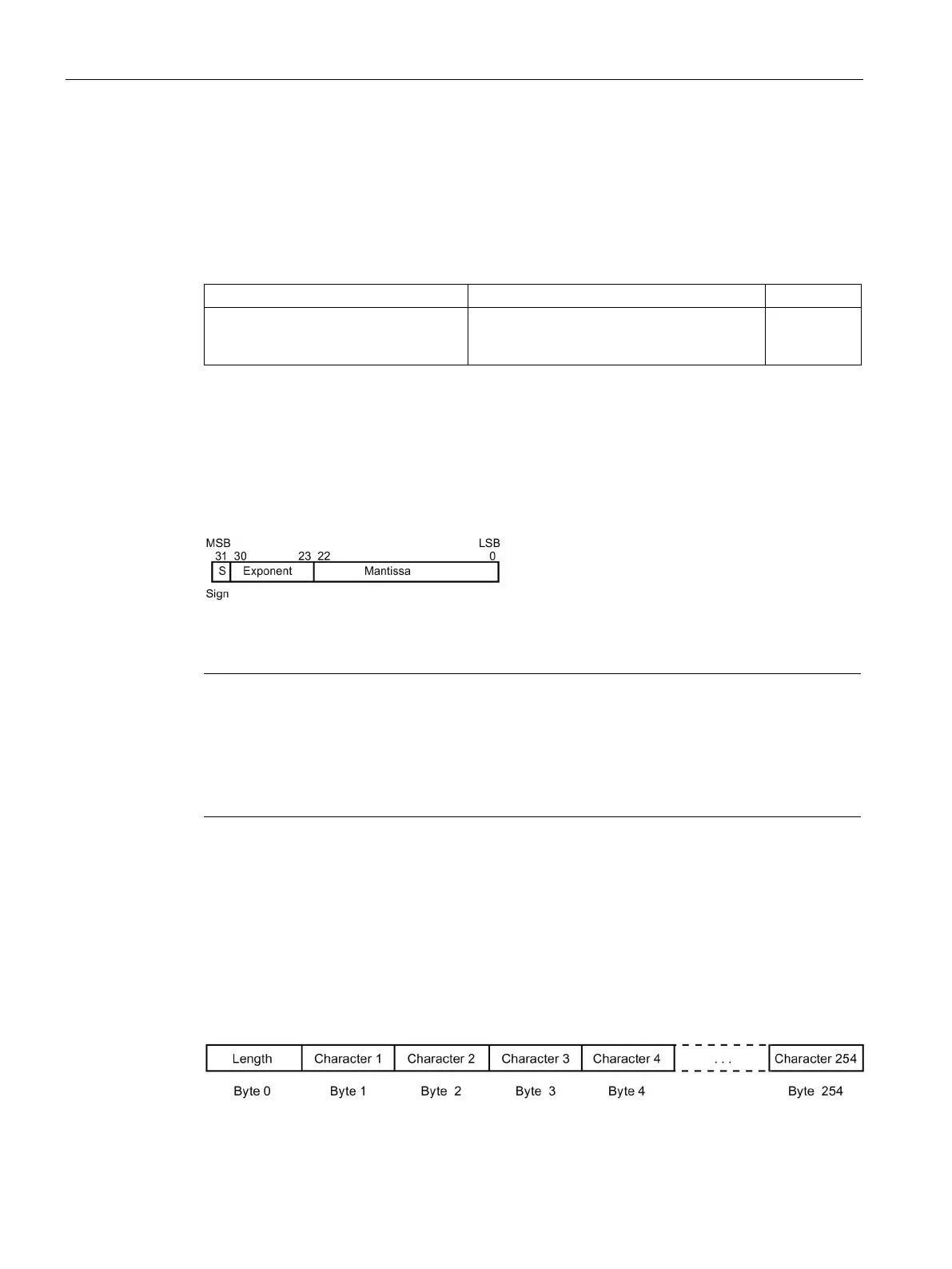
Real (or floating-point) numbers are represented as 32-bit, single-precision numbers, whose
format is described in the ANSI/IEEE 754-1985 standard. Real numbers are accessed in
double-word lengths.
Figure 4-5 Format of a Real number
-point numbers are accurate up to 6 decimal places. Therefore, you can specify a
maximum of 6 decimal places when entering a floating
-point constant.
Calculations that involve a long series of values including very large and very small numbers
can produce inaccurate results. This can oc
cur if the numbers differ by 10 to the power of
x
,
x
> 6. For example: 100 000 000 + 1 = 100 000 000
A string is a sequence of characters, with each character being stored as a byte. The first
byte of the string defines the length of the string, which is the number of characters. The
following figure shows the format for a string. A string can have a length of 0 to 254
characters, plus the length byte, so the maximum length for a string is 255 bytes. A string
constant is limited to 126 bytes.
Figure 4-6 Format for strings

 Loading...
Loading...











