PLC concepts
4.2 Accessing data
S7-200 SMART
70 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
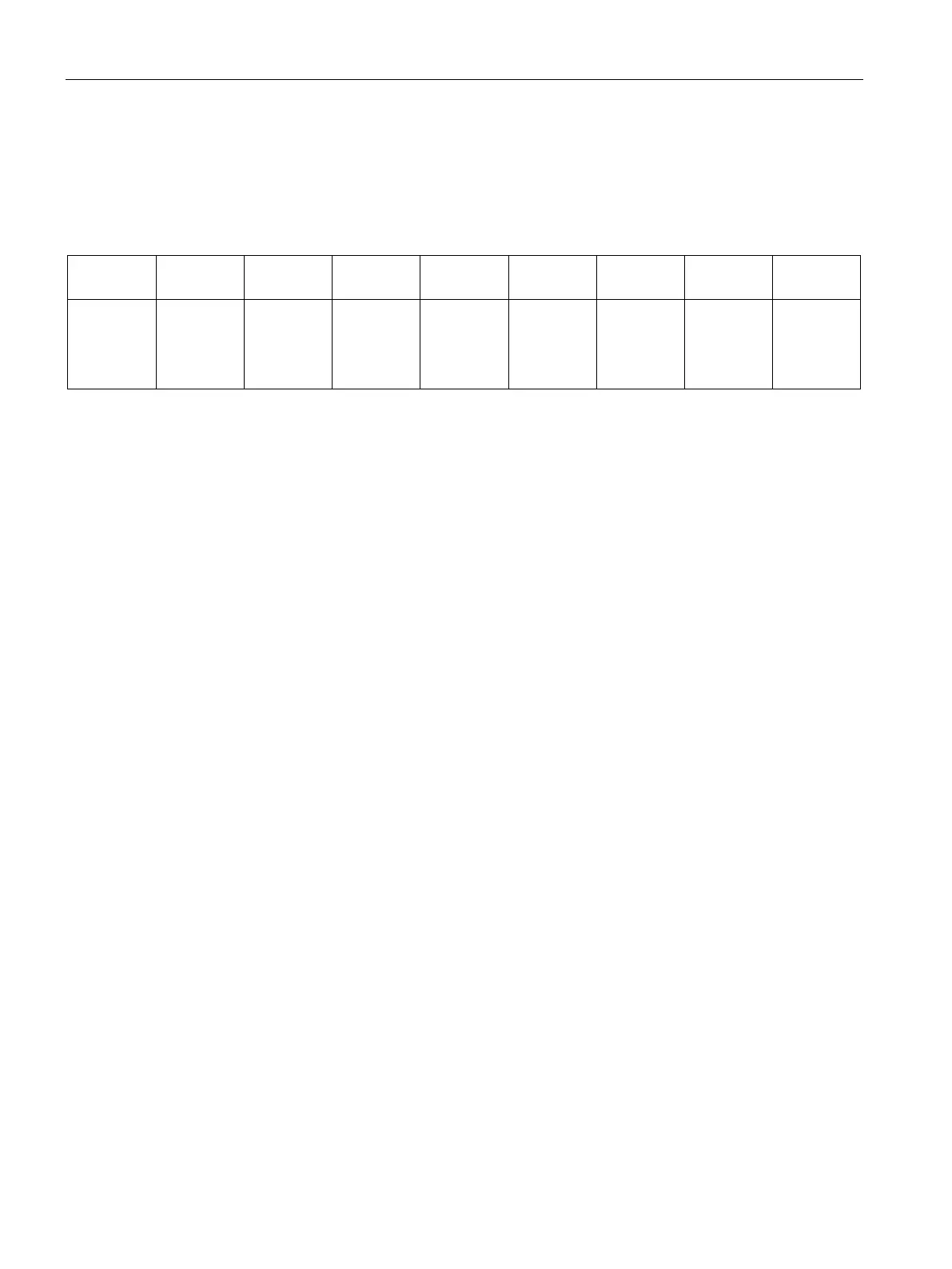
The following table provides an example of the fixed mapping convention (established by
STEP 7 Micro/WIN SMART and downloaded as part of the I/O configuration, in the system
block).
Table 4- 18 CPU mapping convention
Starting
address
I0.0
Q0.0
I7.0
Q7.0
AI12
I8.0
Q8.0
AI16
I12.0
Q12.0
AI32
I16.0
Q16.0
AI48
I20.0
Q20.0
AI64
I24.0
Q24.0
AI80
I28.0
Q28.0
AI96
Using pointers for indirect addressing
Indirect addressing uses a pointer to access data in memory. Pointers are double word
memory locations that contain the address of another memory location. You can only use
V memory locations, L memory locations, or accumulator registers (AC1, AC2, AC3) as
pointers. To create a pointer, you must use the Move Double Word instruction to move the
address of the indirectly addressed memory location to the pointer location. Pointers can
also be passed to a subroutine as a parameter.
An S7-200 SMART CPU allows pointers to access the following memory areas: I, Q, V, M, S,
AI, AQ, SM, T (current value only), and C (current value only). You cannot use indirect
addressing to access an individual bit or to access HC, L or accumulator memory areas.
To indirectly access the data in a memory address, you create a pointer to that location by
entering an ampersand character (&) and the first byte of the memory location to be
addressed. The input operand of the instruction must be preceded with an ampersand (&) to
signify that the address of a memory location, instead of its contents, is to be moved into the
location identified in the output operand of the instruction (the pointer).
 Loading...
Loading...











