Open loop motion control
12.9 Monitoring the Axis of Motion
S7-200 SMART
System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
537
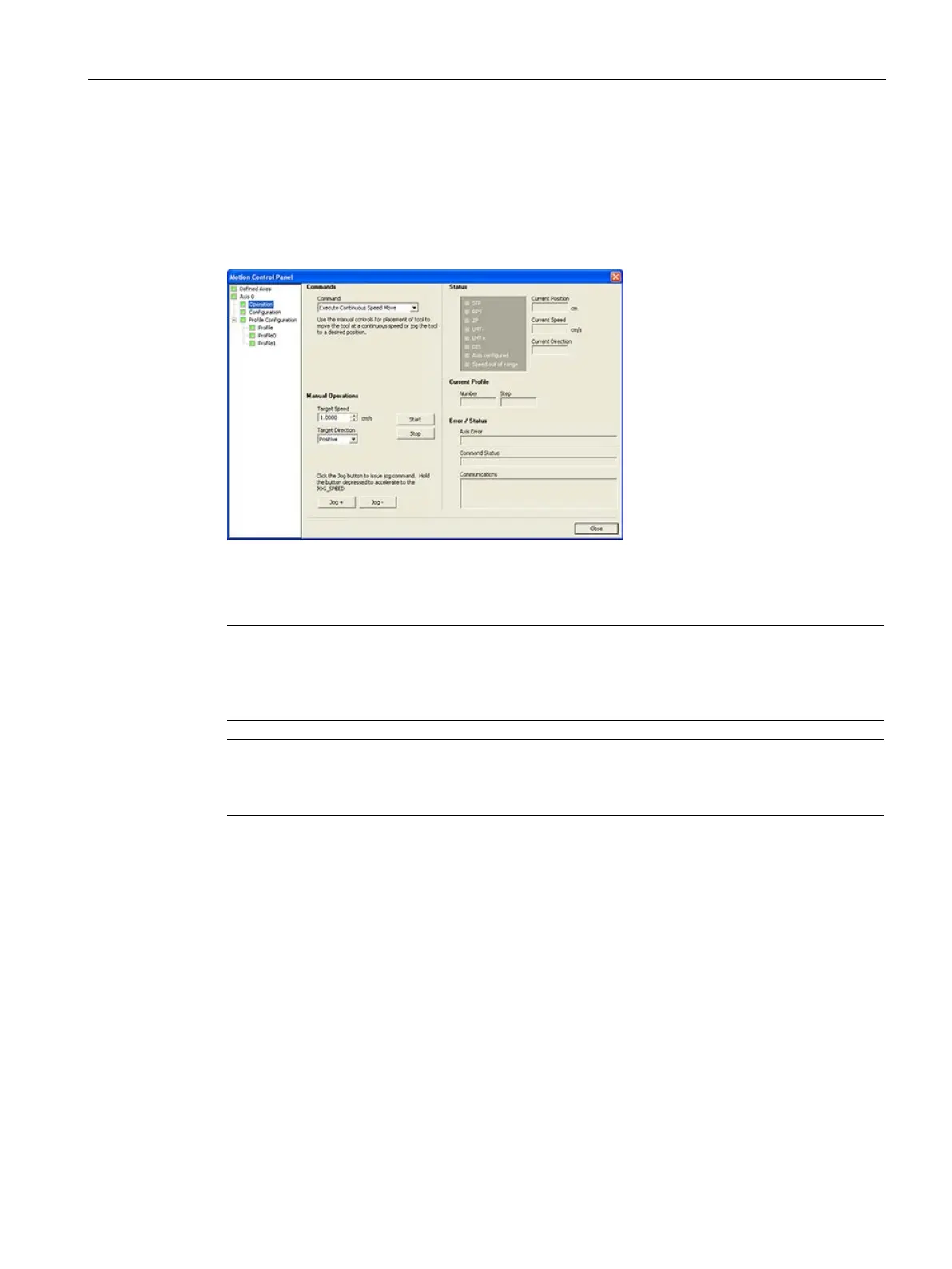
Displaying and controlling the operation of the Axis of Motion
In the Operation node, you can interact with the operations of the Axis of Motion. The control
panel displays the current speed, the current position, and the current direction of the Axis of
Motion. You can also see the status of the input and output LEDs (excluding the Pulse
LEDs).
The control panel allows you to interact with the Axis of Motion by changing the speed and
direction, by stopping and starting the motion, and by jogging the tool (if the CPU is
stopped).
Note
You cannot execute a motion command while the CPU is
running. The CPU must be in
STOP mode in order to change the speed and direction, stop and start the motion, and use
the jog tool.
Note
Exiting the Motion control panel or a loss of communications while a motion command is
active causes the axis to
stop its motion after a 5 second timeout.

 Loading...
Loading...











