Communication
8.6 RS485
S7-200 SMART
System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
401
Determining the distances, transmission rates, and cable lengths for your network
As shown in the following table, the maximum length of a network segment is determined by
two factors: isolation (using an RS485 repeater) and baud rate.
Isolation is required when you connect devices at different ground potentials. Different
ground potentials can exist when grounds are physically separated by a long distance. Even
over short distances, load currents of heavy machinery can cause a difference in ground
potential.
Table 8- 16 Maximum length for a network cable
3 Mbaud to 12 Mbaud Not supported 100 m
1
The maximum distance allowed without using an isolator or repeater is 50 m. You measure this
distance from the first node to the last node in the segment.
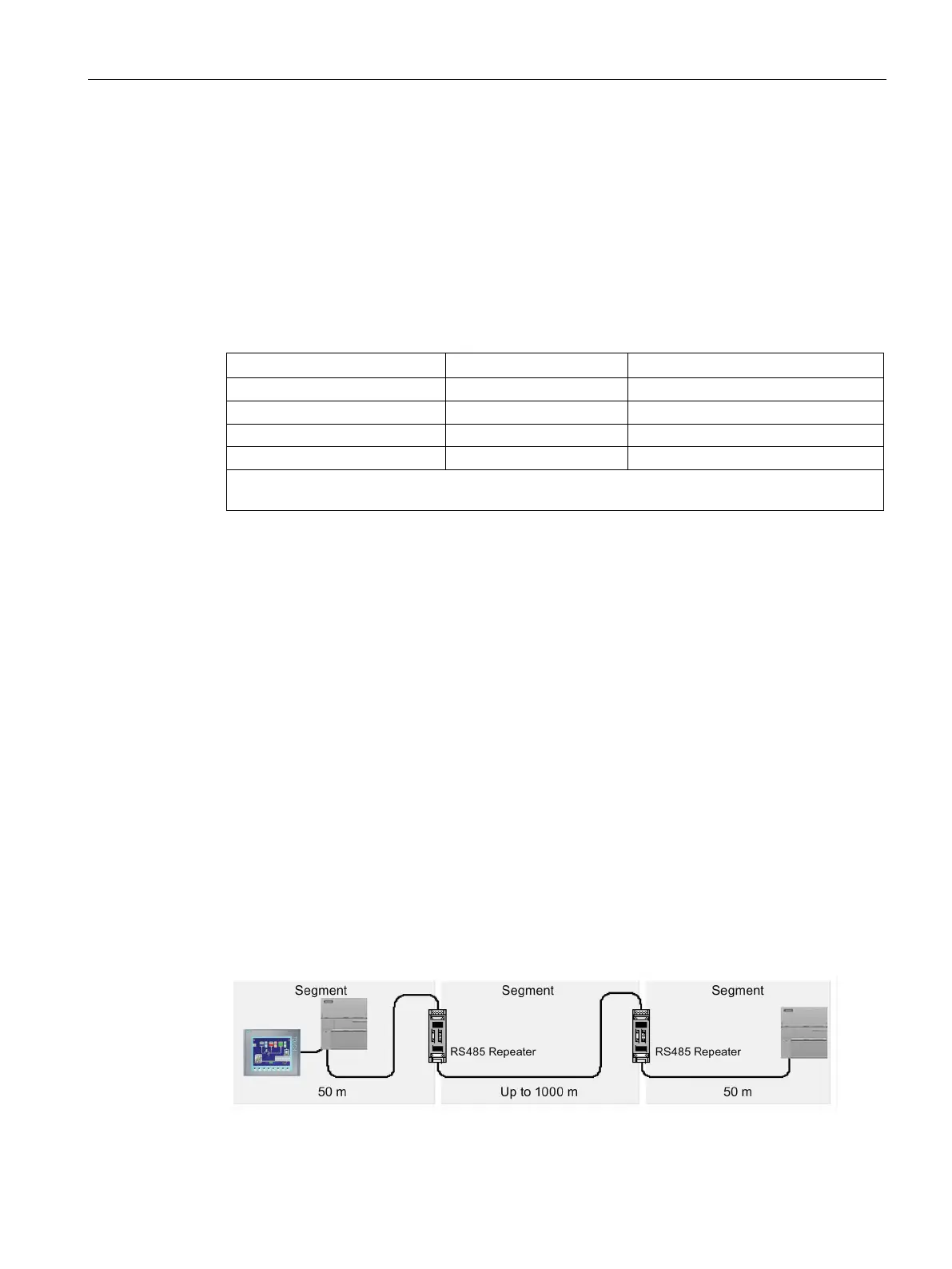
An RS485 repeater provides bias and termination for the network segment. You can use a
repeater for the following purposes:
●
To increase the length of a network
Adding a repeater to your network allows you to extend the network another 50 m. If you
connect two repeaters with no other nodes in between, (as shown in the figure below),
you can extend the network to the maximum cable length for the baud rate. You can use
up to 9 repeaters in series on a network, but the total length of the network must not
exceed 9600 m.
●
To add devices to a network
Each segment can have a maximum of 32 devices connected up to 50 m at 9600 baud.
Using a repeater allows you to add another segment (32 devices) to the network.
●
To electrically isolate different network segments
Isolating the network improves the quality of the transmission by separating the network
segments which may be at different ground potentials.
A repeater on your network counts as one of the nodes on a segment, even though it is not
assigned a network address. The following is a sample network with repeaters.

 Loading...
Loading...











