Open loop motion control
12.1 Using the PWM output
S7-200 SMART
482 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
PWM provides a fixed cycle time output with a variable duty cycle. The PWM output runs
continuously after being started at the specified frequency (cycle time). The pulse width is
varied as required to affect the desired control. Duty cycle can be expressed as a
percentage of the cycle time or as a time value corresponding to pulse width. The pulse
width can vary from 0% (no pulse, always off) to 100% (no pulse, always on). See the
following figure.
Since the PWM output can be varied from 0% to 100%, it provides a digital output that in
many ways is analogous to an analog output. For example the PWM output can be used to
control the speed of a motor from stop to full speed or it can be used to control the position
of a valve from closed to full open.
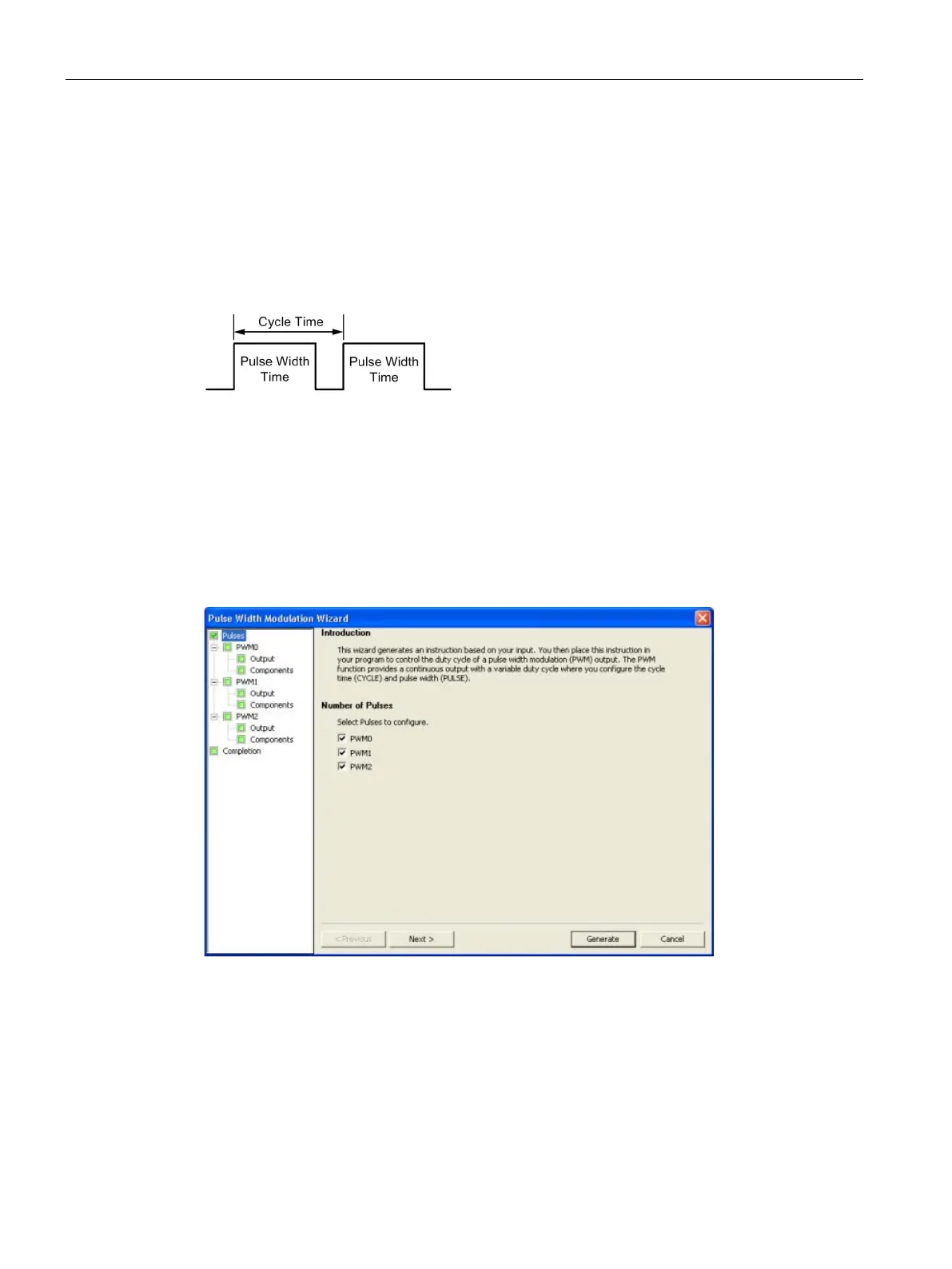
Configuring the PWM output
To configure one of the built-in outputs for PWM control, use the PWM wizard.

 Loading...
Loading...











