Program instructions
7.18 Subroutine
S7-200 SMART
346 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
CALL (subroutine) and RET (conditional return)
To add a new subroutine, select the
ribbon strip then
and
command. STEP 7-Micro/WIN SMART automatically adds an unconditional return from each
subroutine. You can also add conditional return CRET instructions within the subroutine.
From the main program, you can nest subroutines (place a subroutine call within a
subroutine) to a depth of eight.
From an interrupt routine, you can nest subroutines to a depth of four.
Note
Recursion (a subroutine that calls itself) is not prohibited, but you should use caution when
using recursion
with subroutines.
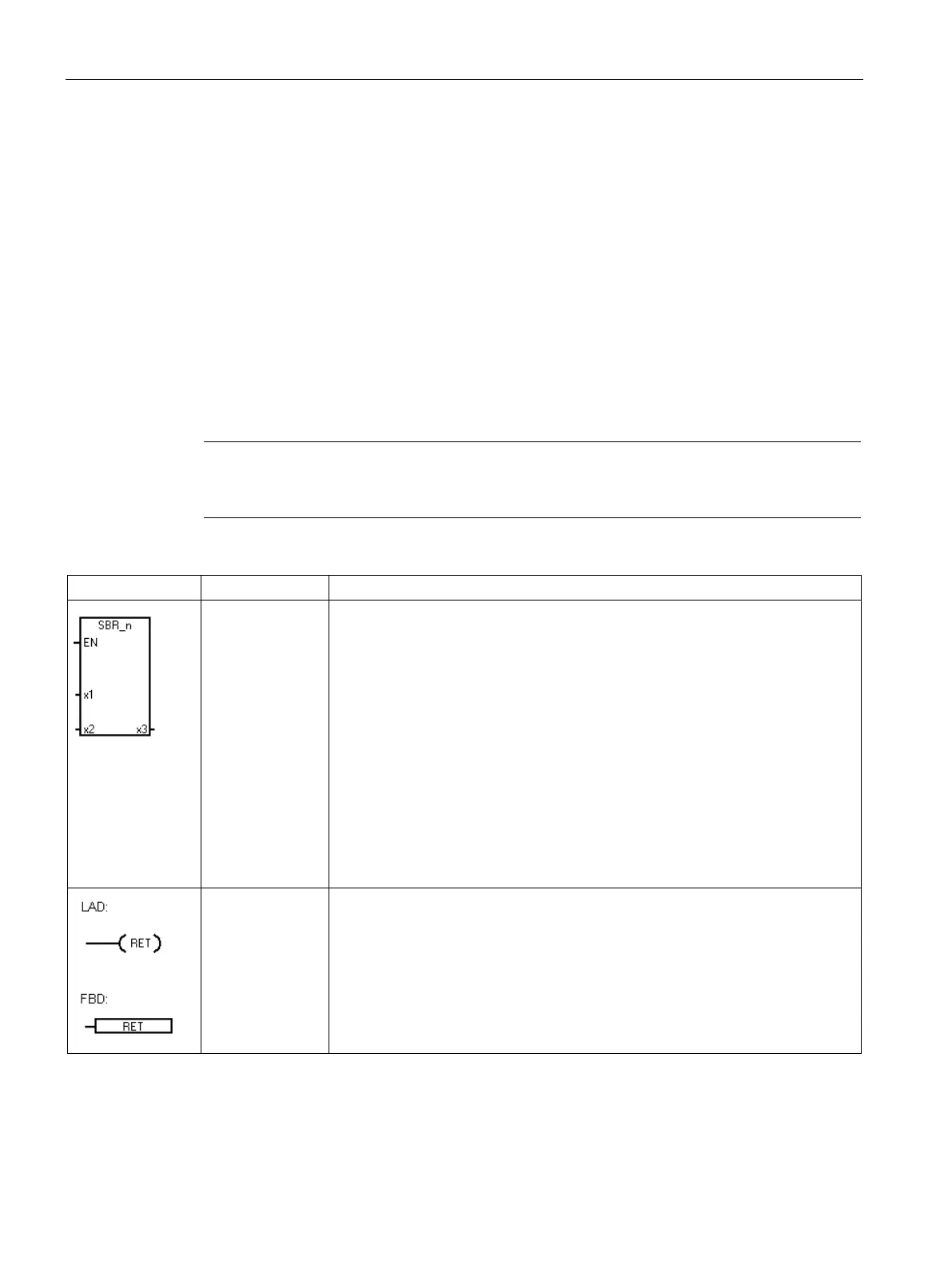
x1, x2, x3
The Call subroutine instruction transfers control to subroutine SBR_n. You can
use a Call subroutine instruction with or without parameters. After the subroutine
completes its execution, control returns to the instruction that follows the Call
subroutine.
The call parameters x1 (IN), x2 (IN_OUT), and x3 (OUT) represent three call
parameters passed in, in and out, or out of the subroutine. The call parameters
are optional. You may use from 0 to 16 call parameters.
When a subroutine is called, the entire logic stack is saved, the top of stack is set
to one, all other stack locations are set to zero, and control is transferred to the
called subroutine. When this subroutine is completed, the stack is restored with
the values saved at the point of call, and control is returned to the calling routine.
Accumulators are common to subroutines and the calling routine. No save or
restore operation is performed on accumulators due to subroutine use.
When a subroutine is called more than once in the same cycle, the edge up, edge
down, timer and counter instructions should not be used.
The Conditional Return from Subroutine instruction (CRET) terminates the sub-
routine based upon the preceding logic.

 Loading...
Loading...











