Open loop motion control
12.9 Monitoring the Axis of Motion
S7-200 SMART
System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
535
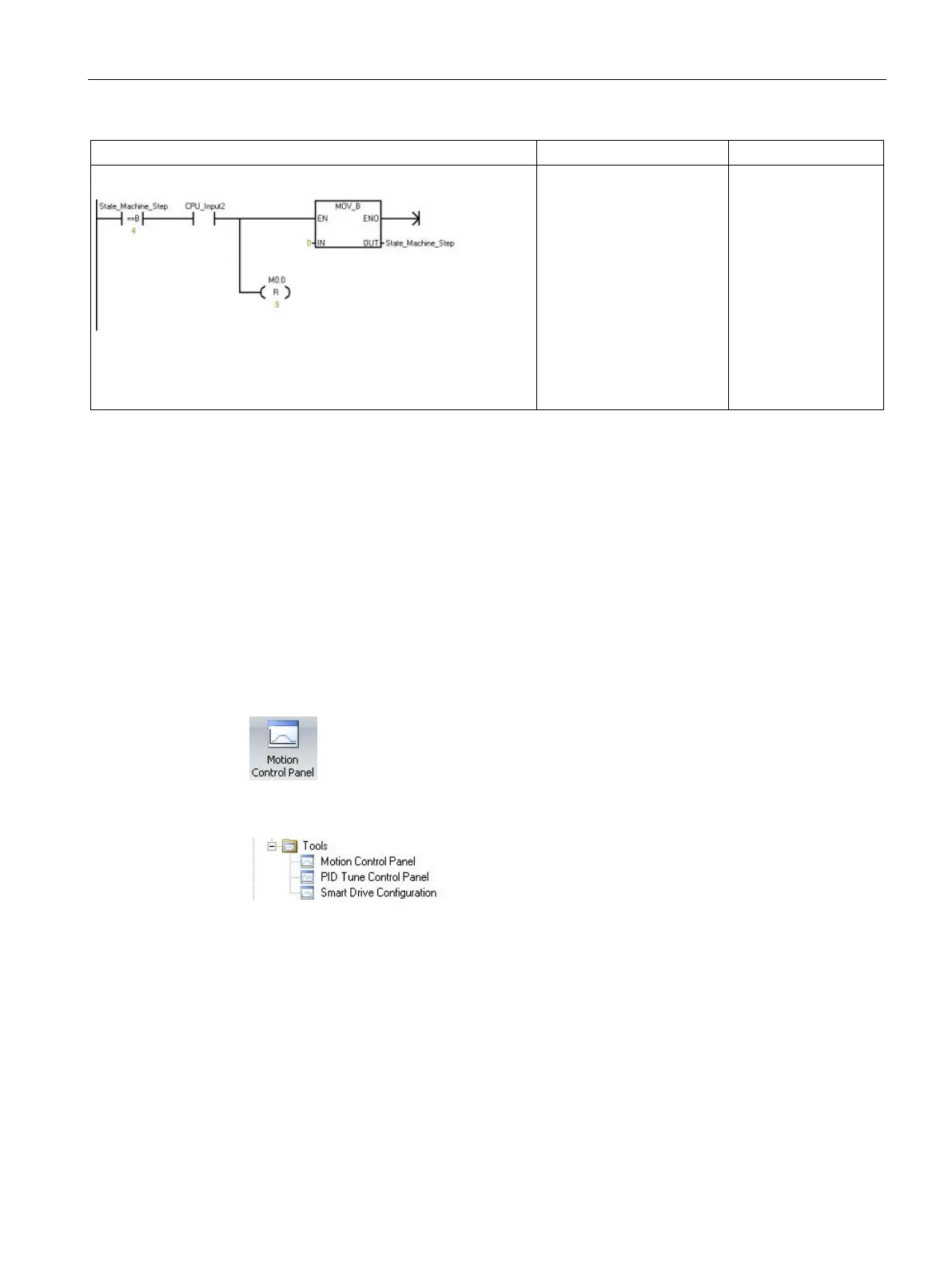
Network 14
If the State Machine is in
Step 4, you must
acknowledge the error by
toggling Input I0.2. This
action resets the state to
Step 0.
Symbol and Address:
1
• CPU_Input2 = I0.2
• State_Machine_Step =
VB1500
State_Machine_
Step, 4
A CPU_Input2
MOVB 0,
State_Machine_
Step
R M0.0, 9
1
The program addresses shown are example addresses. Your program addresses could vary.
Monitoring the Axis of Motion
To aid you in the development of your motion control solution, STEP 7-Micro/WIN SMART
provides the Motion control panel.
Opening the Motion control panel
To open the Motion control panel, use one of the following methods:
● Click the "Motion Control Panel" button from the Tools area of the Tools menu ribbon
strip.
● Open the Tools folder in the project tree, select the "Motion Control Panel" node and
press Enter; or double-click the "Motion Control Panel" node.
 Loading...
Loading...











