Open loop motion control
12.11 Understanding the RP Seek modes of the Axis of Motion
S7-200 SMART
564 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
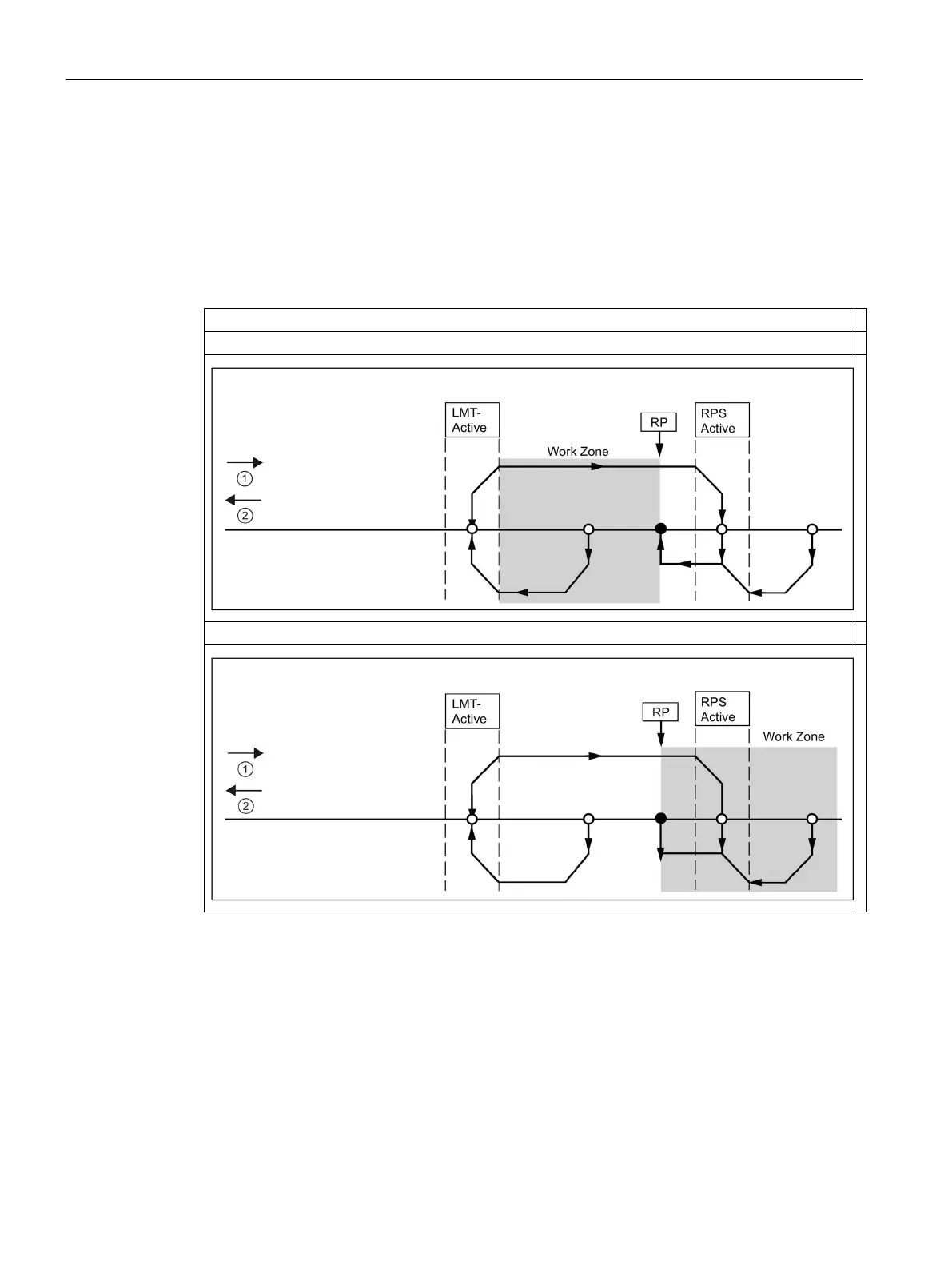
Selecting the work zone location to eliminate backlash
The following figure shows the work zone in relationship to the reference point (RP), the RPS
Active zone, and the limit switches (LMT+ and LMT-) for an approach direction that
eliminates the backlash. The second part of the illustration places the work zone so that the
backlash is not eliminated. The following figure shows RP seek mode 3. A similar placement
of the work zone is possible, although not recommended, for each of the search sequences
for each of the other RP seek modes.
Selecting the work zone location to eliminate backlash
Backlash is eliminated: RP seek direction: negative and RP approach direction: negative
Backlash is not eliminated: RP seek direction: negative and RP approach direction: negative
: Positive motion

 Loading...
Loading...











