Program instructions
7.18 Subroutine
S7-200 SMART
348 System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
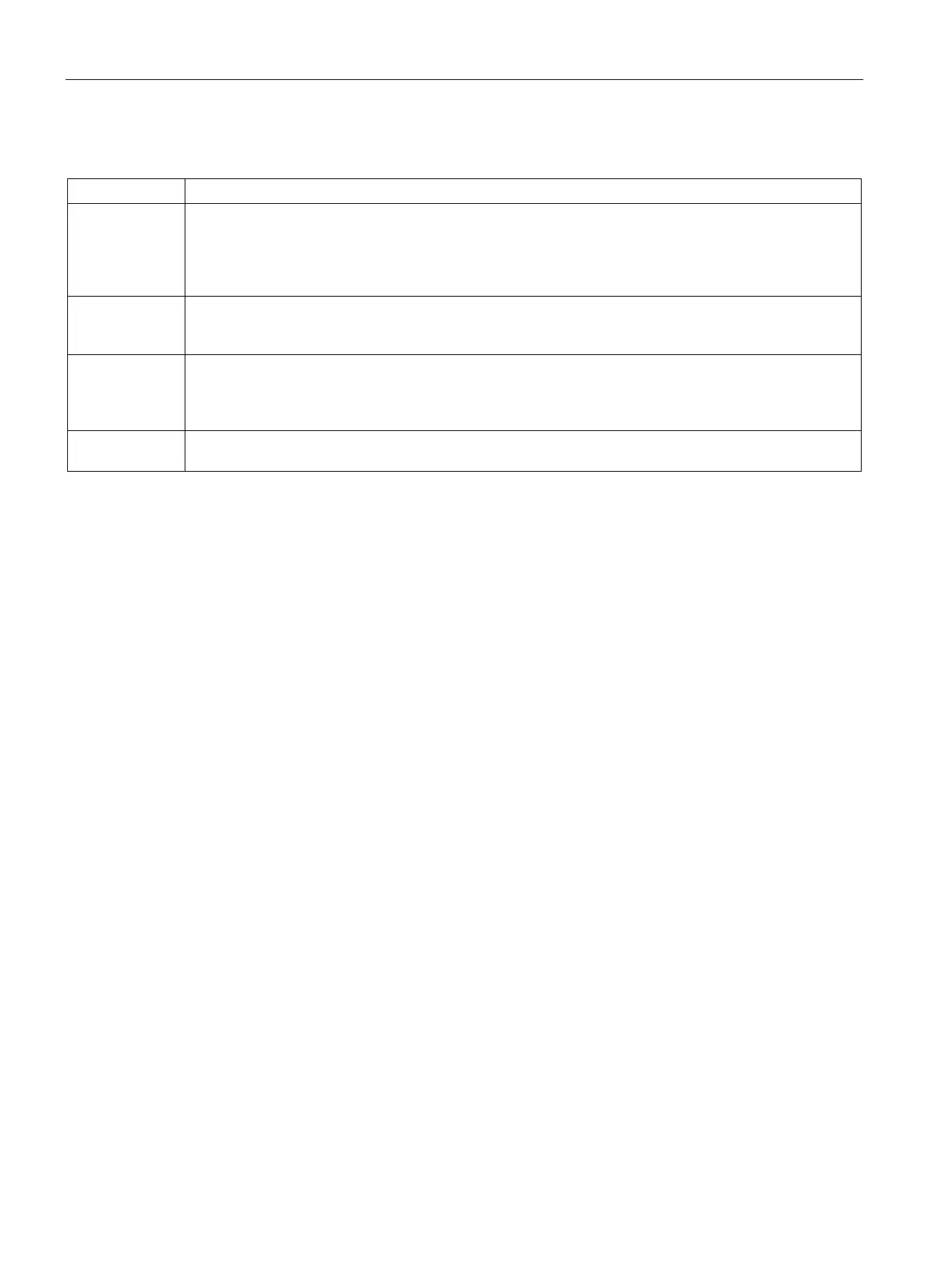
Variable table parameter types for a subroutine
IN Parameters are passed into the subroutine. If the parameter is a direct address (such as VB10), the
value at the specified location is passed into the subroutine. If the parameter is an indirect address (such
as *AC1), the value at the location pointed to is passed into the subroutine. If the parameter is a data
constant (16#1234) or an address (&VB100), the constant or address value is passed into the subrou-
IN_OUT The value at the specified parameter location is passed into the subroutine, and the result value from the
subroutine is returned to the same location. Constants (such as 16#1234) and addresses (such as
&VB100) are not allowed for input/output parameters.
OUT The result value from the subroutine is returned to the specified parameter location. Constants (such as
16#1234) and addresses (such as &VB100) are not allowed as output parameters. Since output param-
eters do not retain the value assigned by the last execution of the subroutine, you must assign values to
outputs each time the subroutine is called.
TEMP Any local memory that is not used for passed parameters can be used for temporary storage within the
Data types allowed for call parameters
● Power Flow: Boolean power flow is allowed only for bit (Boolean) inputs. This declaration
assigns an input parameter to the result of power flow based on a combination of bit logic
instructions. Power flow inputs are similar to the EN input in that they connect to bit logic
(for ex. LAD contacts) and not to a direct/indirect address assignment. Boolean power
flow input(s) must be assigned in the top row(s) of the variable table before any non-
BOOL data type assignment. Only input parameters are allowed to be used this way. The
enable input (EN) and the IN1 inputs in the following example use power flow logic.
● BOOL: This data type is used for single bit inputs and outputs. IN3 in the following
example is a Boolean input assigned to a direct address.
● BYTE, WORD, DWORD: These data types identify an unsigned input or output parameter
of 1, 2, or 4 bytes, respectively.
● INT, DINT: These data types identify signed input or output parameters of 2 or 4 bytes,
respectively.
● REAL: This data type identifies a single precision (4 byte) IEEE floating-point value.
● STRING: This data type is used as a four-byte pointer to a string.

 Loading...
Loading...











