Program instructions
7.9 PID
S7-200 SMART
System Manual, 09/2015, A5E03822230-AC
281
The default state of the PID history bits is "set" and that state is established at startup and on
every STOP-to-RUN mode transition of the controller. If power flows to the PID box the first
time that it is executed after entering RUN mode, then no power-flow transition is detected
and the bumpless mode change actions are not performed.
Alarm checking and special operations
The PID instruction is a simple but powerful instruction that performs the PID calculation. If
other processing is required such as alarm checking or special calculations on loop
variables, these must be implemented using the basic instructions supported by the CPU.
When it is time to compile, the CPU will generate a compile error (range error) and the
compilation will fail if the loop table start address or PID loop number operands specified in
the instruction are out of range.
Certain loop table input values are not range checked by the PID instruction. You must take
care to ensure that the process variable and setpoint (as well as the bias and previous
process variable if used as inputs) are real numbers between 0.0 and 1.0.
If any error is encountered while performing the mathematical operations of the PID
calculation, then SM1.1 (overflow or illegal value) is set and execution of the PID instruction
is terminated. (Update of the output values in the loop table could be incomplete, so you
should disregard these values and correct the input value causing the mathematical error
before the next execution of the loop's PID instruction.)
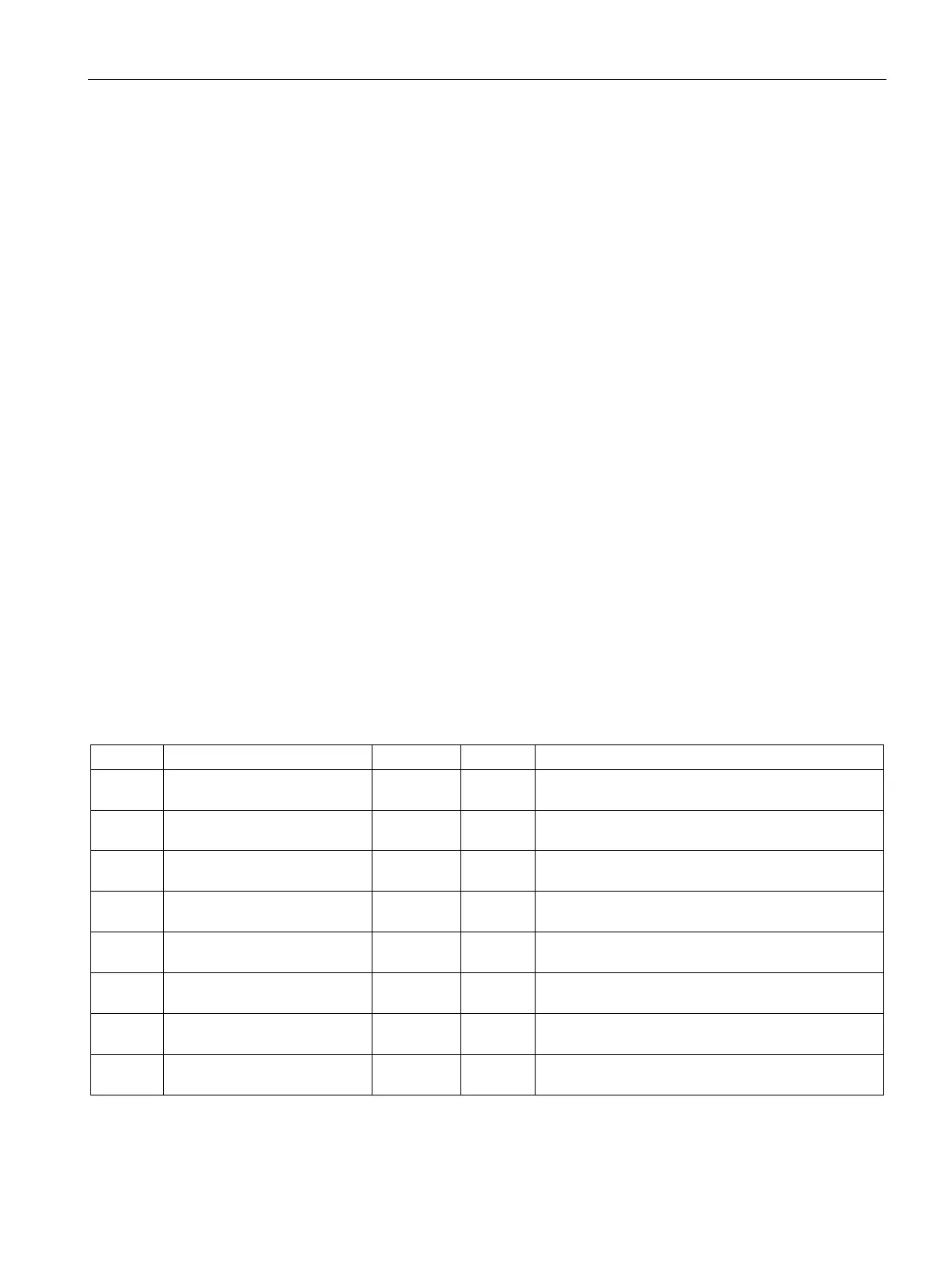
The loop table is 80 bytes long and has the format shown in the following table.
0 Process variable (PV
n
) REAL In Contains the process variable, which must be scaled
4 Setpoint (SP
n
) REAL In Contains the setpoint, which must be scaled be-
tween 0.0 and 1.0.
8 Output (M
n
) REAL In/Out Contains the calculated output, scaled between 0.0
12 Gain (K
C
) REAL In Contains the gain, which is a proportional constant.
Can be a positive or negative number.
16 Sample time (T
S
) REAL In Contains the sample time, in seconds. Must be a
20 Integral time or reset (T
I
) REAL In Contains the integral time or reset, in minutes. Must
24 Derivative time or rate (T
D
) REAL In Contains the derivative time or rate, in minutes. Must
28 Bias (MX) REAL In/Out Contains the bias or integral sum value between 0.0

 Loading...
Loading...











