Working with VSCs
Key concepts
5-3
Key concepts
A VSC (virtual service community) is a collection of configuration settings that define key
operating characteristics of the controller and controlled APs. In most cases, a VSC is used to
define the characteristics of a wireless network and to control how wireless user traffic is
distributed onto the wired network.
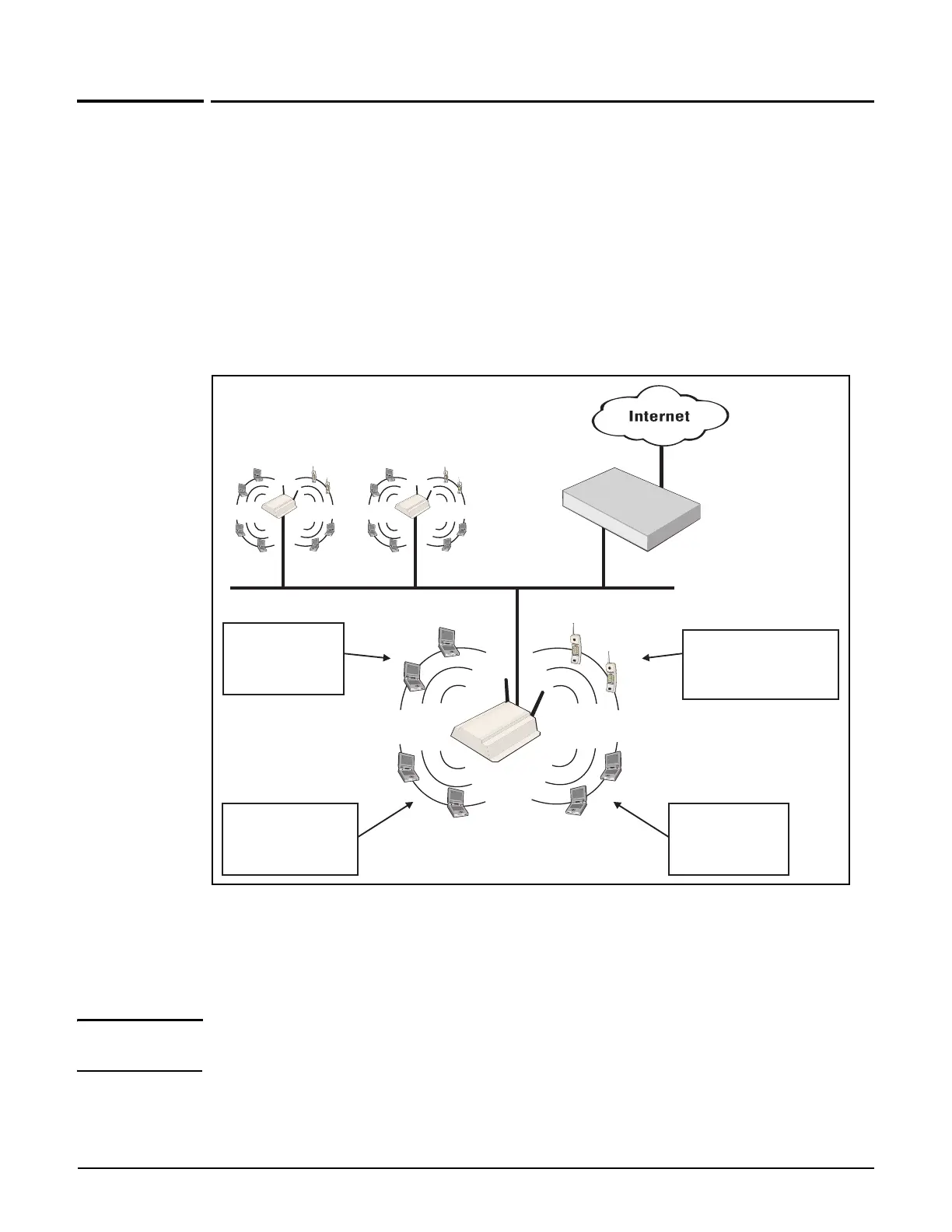
Multiple VSCs can be active at the same time, allowing for great flexibility in the
configuration of services. For example, in the following scenario four VSCs are used to
support different types of wireless users. Each VSC is configured with a different wireless
network name (SSID), and the quality of service (QoS) feature is used to classify user traffic
priority.
Binding VSCs to APs
VSCs are defined on the controller, creating a global pool of services. From this pool, specific
VSCs are then bound to one or more groups (and the APs in the groups), to provide a
homogeneous wireless offering. See Binding VSCs to groups on page 6-23.
Note The MSM760 and MSM765 controllers support up to 64 VSCs. Other controllers support up to
16 VSCs. Controlled APs support a maximum of 16 VSCs.
VSC #2
SSID=Phone
QoS=Very High Priority
VSC #1
SSID=Guest
QoS=Low priority
VSC #3
SSID=Employee
QoS=Normal priority
VSC #4
SSID=Video
QoS=High priority
Backbone Network
Controller
AP
AP AP
#1 #2 #1 #2
#3
#4
#3
#4

 Loading...
Loading...