Working with VPNs
Overview
16-2
Overview
Virtual private networks (VPNs) create secure tunnels across non-secure infrastructure such
as the Internet or publicly-accessible networks. The controller features virtual private
network (VPN) capabilities that enable it to do the following:
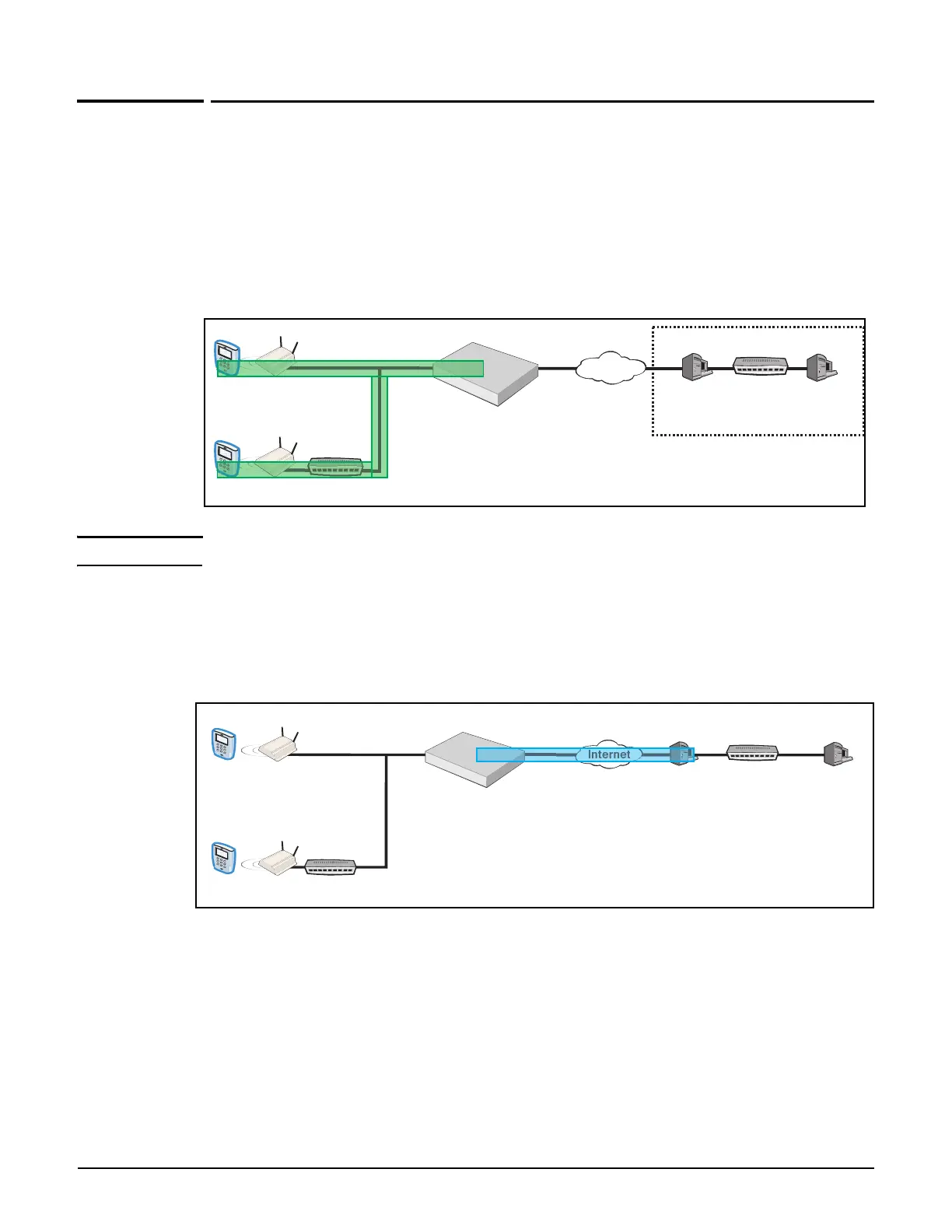
Secure wireless client sessions with a VPN tunnel between wireless clients such as
wireless point-of-sale (POS) terminals and the controller. IPSec, L2TP, and PPTP are all
supported. (VPN tunnel represented in green.)
Note For WPA-capable wireless clients, a better alternative to VPNs, is to extend WPA termination
from the AP to the controller. See Terminate WPA at the controller on page 5-24.
Secure controller communications to VPN servers, including both management and client
traffic. For example, the controller can securely contact a remote RADIUS server for user
authentication. IPsec and PPTP are supported. (VPN tunnel represented in blue.)
Controller
Router
Internet
port
24.1.1.4
Internet
LAN
port
7.1.1.1
VPN Server/
Gateway
(Peer)
3.1.1.2 10.0.0.0
10.0.0.2
Secure
resource
7.1.1.2
AP
Router
5.1.1.0
5.1.1.2
AP
5.1.1.3
Wireless
POS
7.1.1.3
Wireless
POS
Internet
Controller
Router
Internet
port
24.1.1.4
LAN
port
7.1.1.1
VPN Server/
Gateway
(Peer)
3.1.1.2
10.0.0.0
10.0.0.2
Secure
resource
7.1.1.2
7.1.1.2
APWireless
Client
7.1.1.3
5.1.1.2
5.1.1.2
APWireless
Client
5.1.1.3
Router

 Loading...
Loading...