Network configuration
Network address translation (NAT)
3-30
Network address translation (NAT)
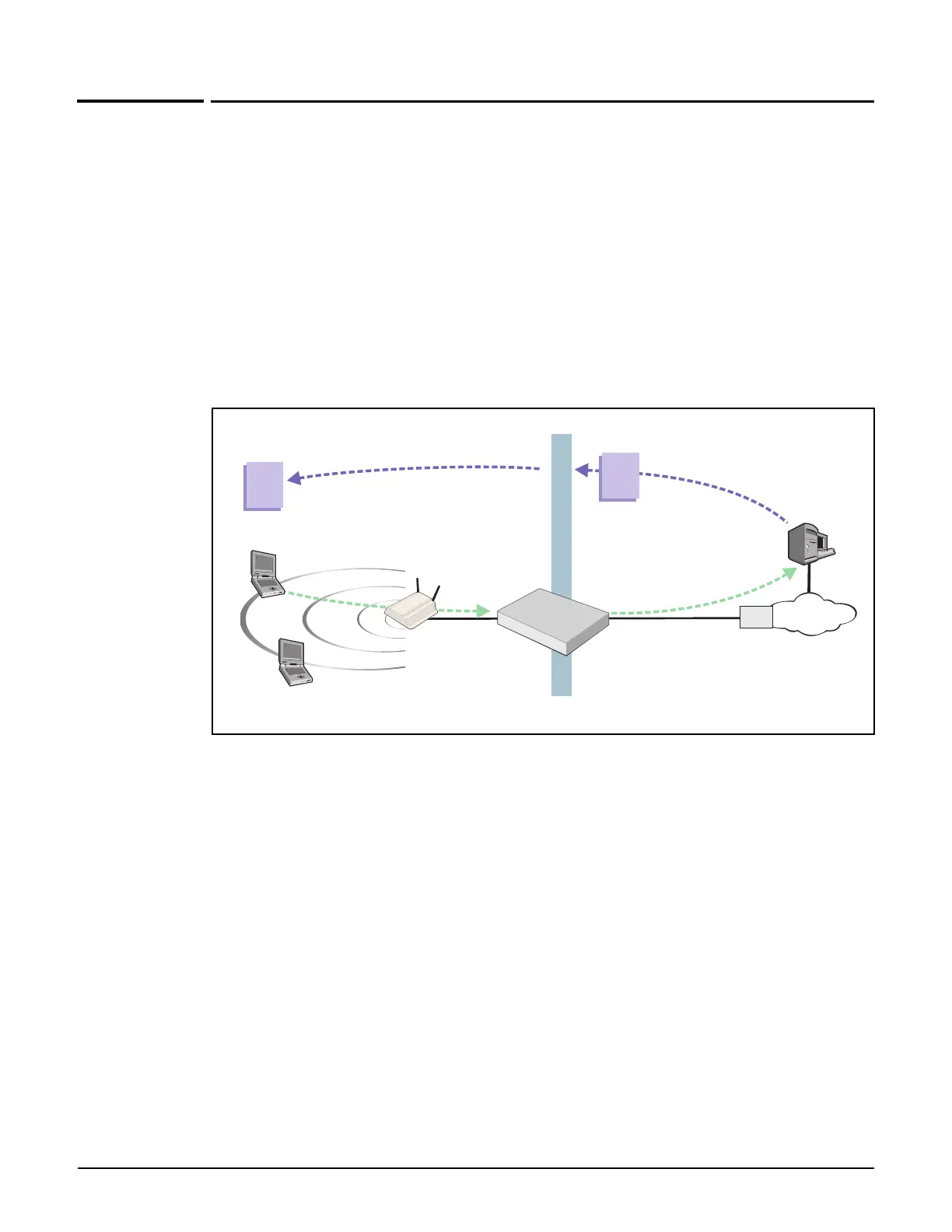
Network address translation is an address mapping service that enables one set of IP
addresses to be used on an internal network, and a second set to be used on an external
network. NAT handles the mapping between the two sets of addresses.
Generally NAT is used to map all addresses on an internal network to a single address for use
on an external network like the Internet. The main benefits are that NAT:
Enables several devices to share a single connection
Effectively hides the IP addresses of all devices on the internal network from the external
network.
This is illustrated as follows:
NAT can be useful in conjunction with virtual private network (VPN) connections. When two
networks are connected through a VPN tunnel, it may be desirable to obscure the address of
local computers for security reasons.
NAT security and static mappings
One of the benefits of NAT is that it effectively hides the IP addresses of all devices on the
internal network an external network. In some cases, however, it is useful to make a
computer on the internal network accessible externally. For example, a Web server or FTP
server.
Static NAT mapping addresses this problem. Static NAT mapping enables you to route
specific incoming traffic to an IP address on the internal network. For example, to support a
Web server, you can define a static NAT mapping to route traffic on TCP port 80 to an internal
computer running a Web server.
Internet
Web
server
Web Page
Web Page
192.168.1.2
NAT
192.168.1.3
ISP
addressed to
192.168.1.2
addressed to
202.125.11.26
Internal addresses are invisible
to computers on the Internet.
All traffic uses the same
external IP address
assigned by the ISP.
202.125.11.26
HTTP request
AP
Controller

 Loading...
Loading...