Working with VSCs
Quality of service (QoS)
5-43
Downstream traffic marking
This table describes the marking applied to traffic received from the wired network by an AP
and then sent to connected wireless client stations.
Note Although the WMM specification refers to 802.1D and not 802.1p, this guide uses the term
802.1p because it is more widely recognized. (The updated IEEE 802.1D: ISO/IEC 15802-3
(MAC Bridges) standard covers all parts of the Traffic Class Expediting and Dynamic
Multicast Filtering described in the IEEE 802.1p standard.)
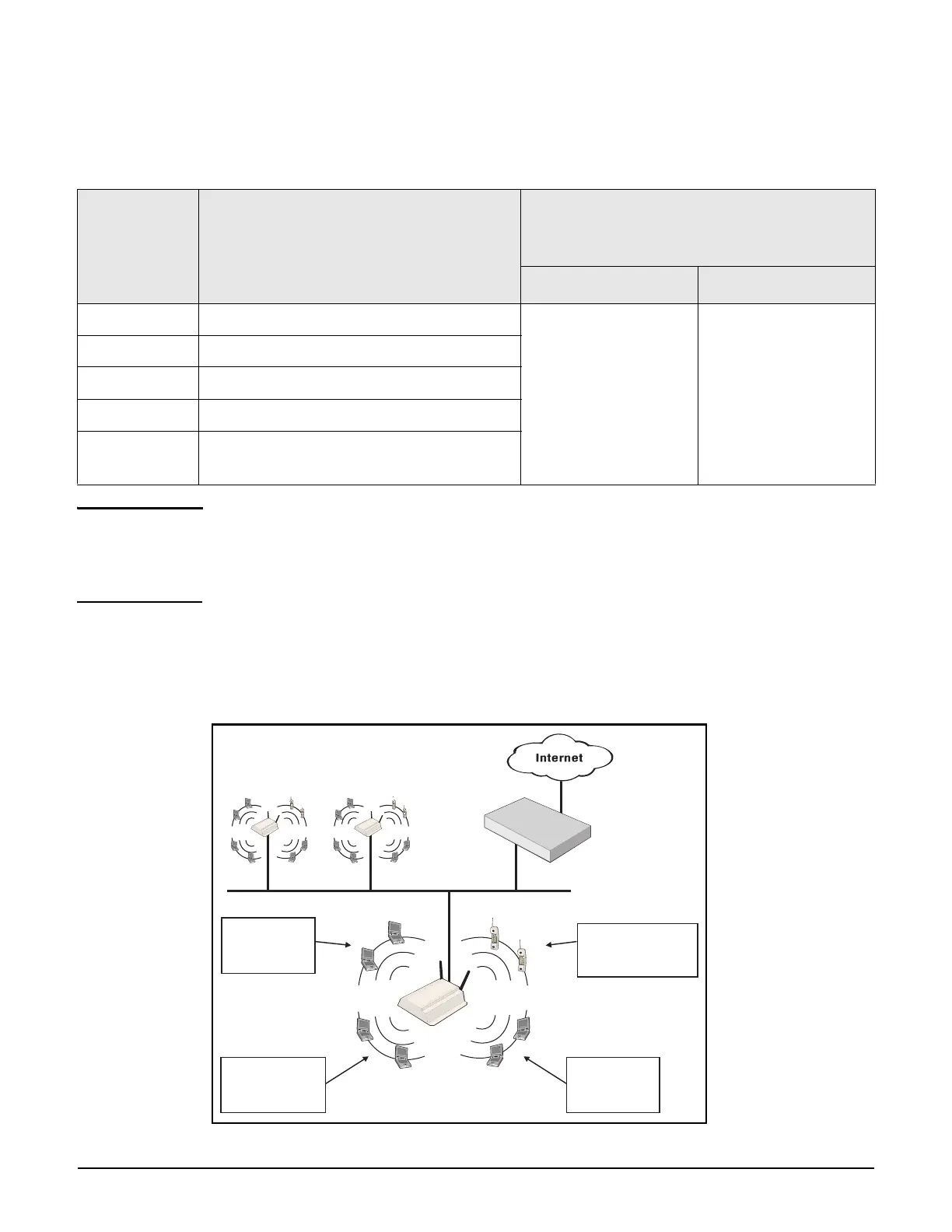
QoS example
In this example, a single controller provides voice and data wireless support with different
quality of service settings for guests and employees.
Mechanism
INCOMING
TRAFFIC
Traffic received from wired network
OUTGOING TRAFFIC
Wireless traffic sent from the
controller to client stations
WMM Client Non-WMM Client
802.1p 802.1p WMM + HPQ (WMM
marking done
according to the rules
for the mechanism.)
HPQ (hardware
priority queueing)
DiffServ DiffServ
TOS TOS
VSC-based All traffic on the VSC.
IP QoS All traffic that matches the ports/protocols
specified in the selected IP QoS profiles.
VSC #2
SSID=Phone
QoS=Very High Priority
VSC #1
SSID=Guest
QoS=Low priority
VSC #3
SSID=Employee
QoS=Normal priority
VSC #4
SSID=Video
QoS=High priority
Backbone Network
Controller
AP
AP AP
#1 #2 #1 #2
#3
#4
#3
#4

 Loading...
Loading...