sFlow
Overview
18-2
Overview
sFlow is a technology for monitoring traffic in high speed switched or routed
networks. The standard sFlow monitoring system is comprised of the following:
An sFlow Agent that runs on a network device such as an AP, switch, or router. The
agent uses sampling techniques to capture information about the data traffic flowing
through the device and forwards this information to an sFlow collector.
An sFlow Collector that receives monitoring information from sFlow agents. The
collector stores this information so that a network administrator can analyze it.
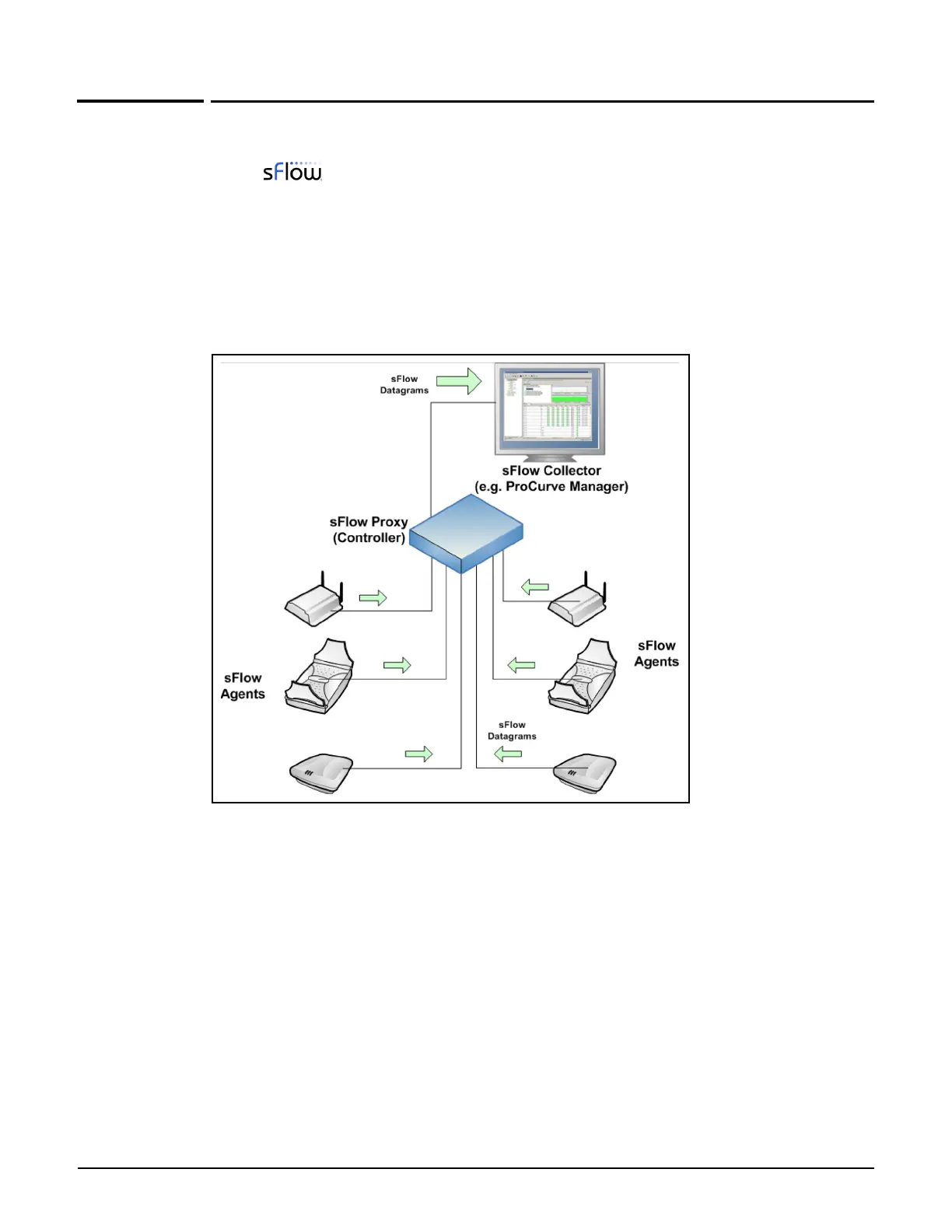
sFlow proxy
In the case of the controller and its controlled APs, the sFlow monitoring system operates
slightly differently. Instead of each AP sending information directly to a collector, the APs
send their information to the controller, which acts as an sFlow proxy. The controller then
forwards the information to one or more collectors.
The collectors are not aware of the APs, as all sFlow information is repackaged by the
controller to indicate that it is the source device. Essentially, the interfaces on the APs appear
as interfaces on the controller. When the controller detects that an AP is missing, it will
answer SNMP SET and GET queries from collectors with an SNMP error message.

 Loading...
Loading...