Working with controlled APs
Discovery of controllers by controlled APs
6-7
2. Discovered controllers send a discovery reply to the AP. If the controller is configured to
require AP authentication, the reply is only sent after the AP is authenticated by the
controller.
3. The controller adds the AP to a group. This will either be the default group (if the AP is
new/unknown) or an existing group (to which the AP was previously assigned).
4. The AP is now managed by the controller, and it can be configured and monitored using
the controller management tool.
Note APs must be connected to the network via Port 1 (or the Uplink port on an MSM317)
for discovery to work.
Unprovisioned APs must obtain an IP address from a DHCP server before discovery
can be initiated. When discovery occurs on a VLAN, the DHCP server must be active
on the VLAN.
Discovery is performed whenever an AP:
Is restarted (or reset to factory defaults)
Loses connectivity with its controller
Is removed and rediscovered using an action on the Controlled APs >> Overview >
Discovered APs page.
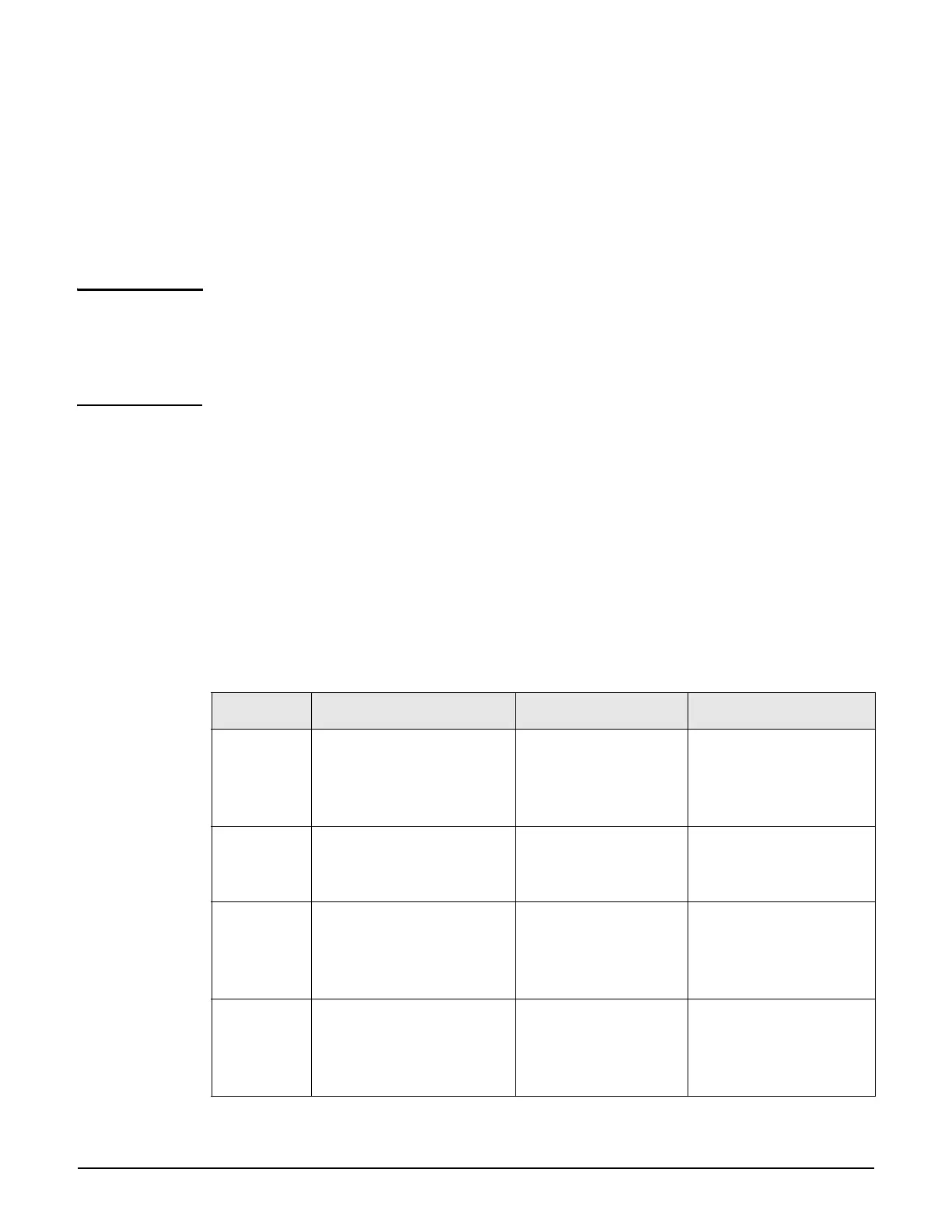
Discovery methods
Four discovery methods are available. The following table summaries their features and
recommended applications.
Method Description Supported by Suggested use
UDP
broadcast
AP issues UDP
broadcasts to discover
controllers on the same
subnet.
Unprovisioned APs Both the controller and
AP reside on the same
subnet.
DHCP AP obtains controller
address from a specially
configured DHCP server.
Unprovisioned APs The AP is on a different
subnet than the
controller.
DNS AP obtains controller
address from a DNS
server using predefined
host names.
Unprovisioned APs
Provisioned APs
The AP is on a different
subnet than the
controller.
Specific IP
addresses
AP connects to a specific
controller using a pre-
configured static IP
address.
Provisioned APs DHCP and DNS are not
used and the AP is on a
different subnet than
the controller.

 Loading...
Loading...