Working with VSCs
Using multiple VSCs
5-36
Using multiple VSCs
When multiple VSCs are defined, it is important to know how user traffic is matched to a VSC
definition. When VSCs have access control enabled, incoming traffic is handled on the
controller as follows:
About the default VSC
The default VSC is automatically created by the controller. It is identified with the label
(Default) in the VSC list. Initially, this VSC is named HP and has the following properties:
Wireless network name: HP
Use Controller for Authentication is enabled. (If you disable this option, the
controller will not provide user authentication services for 802.1X, WPA, or WPA2.)
Use Controller for Access control is enabled. (If you disable this option, you disable
the public access interface and all users gain access to the protected network.)
HTML-based authentication is enabled.
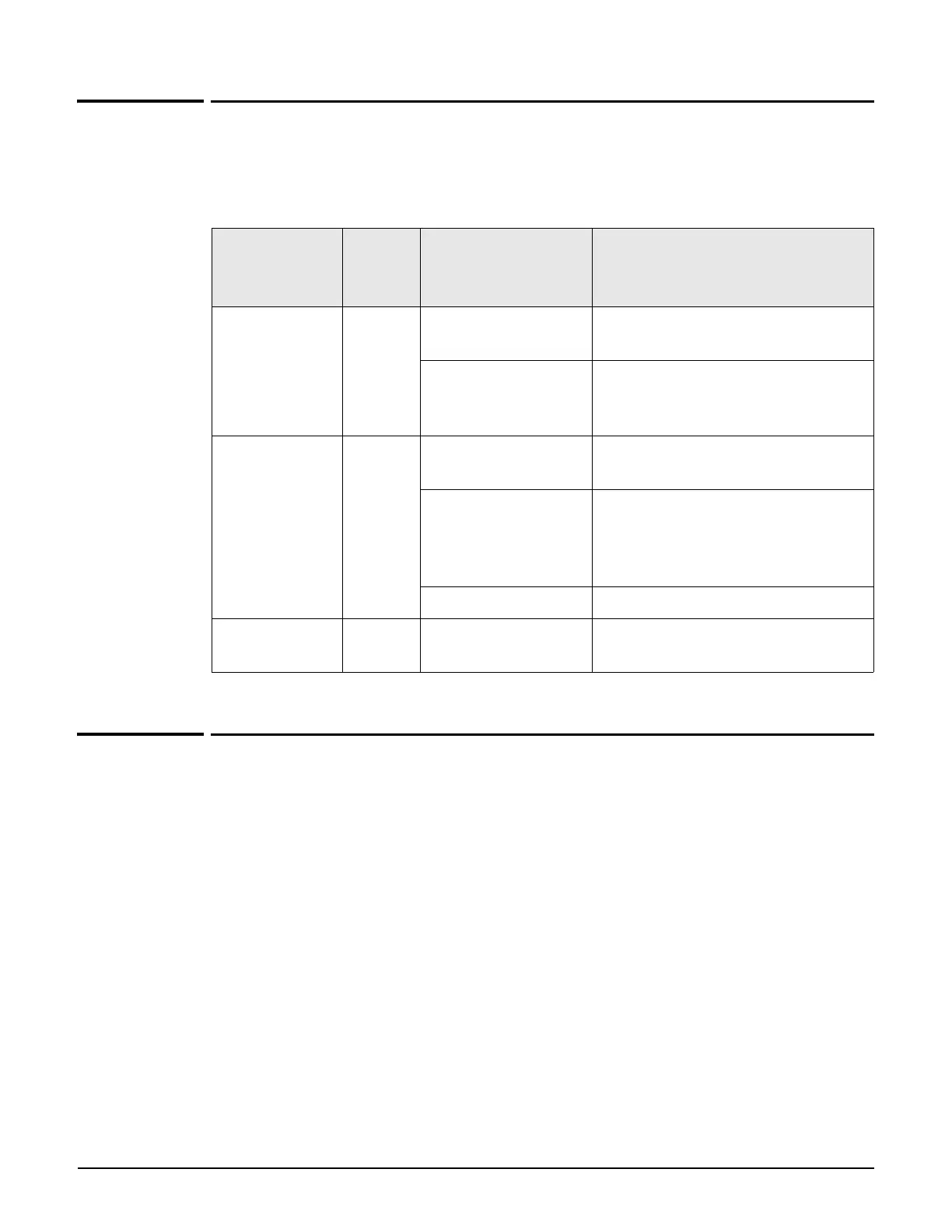
Incoming
traffic
properties
Port If ... Then ...
SSID and
untagged
LAN VSC with matching
SSID exists.
Traffic is sent on the egress mapping
defined on the matching VSC.
No VSC with
matching SSID
exists.
Traffic is sent on the egress mapping
defined on the default VSC.
SSID and VLAN
or
VLAN only
LAN or
Internet
VSC with matching
Ingress VLAN exists.
Traffic is sent on the egress mapping
defined on the matching VSC.
VLAN exists in VLAN
table (but is not
assigned to a VSC
ingress.
Traffic is routed according to the
global routing table.
No VLAN exists. Traffic is blocked.
Untagged LAN Traffic is sent on the egress mapping
defined on the default VSC.

 Loading...
Loading...