Public/guest network access
Key concepts
14-4
Key concepts
Access control
When the Access control option is enabled on a VSC, it creates an access-controlled VSC.
This means that for all traffic on the VSC, the controller acts as the gatekeeper between two
distinct network segments: the public network and the protected network.
Public network: Access to the public network and its resources is generally made
available to all unauthenticated wireless users once they successfully connect to the
wireless network. Access is also generally made available to unauthenticated wired users
on any network that is connected to the controller’s LAN port.
Protected network: Access to the protected network is restricted by the controller and
typically requires that users be authenticated by the controller before they gain access.
Various authentication methods are available (HTML-based, MAC-based, 802.1X). The
most commonly used method is HTML-based, which enables users to login through their
Web browsers via the public access interface Login page. The controller can validate user
login credentials using locally defined user accounts or by using the services of a third-
party authentication server (RADIUS or Active Directory).
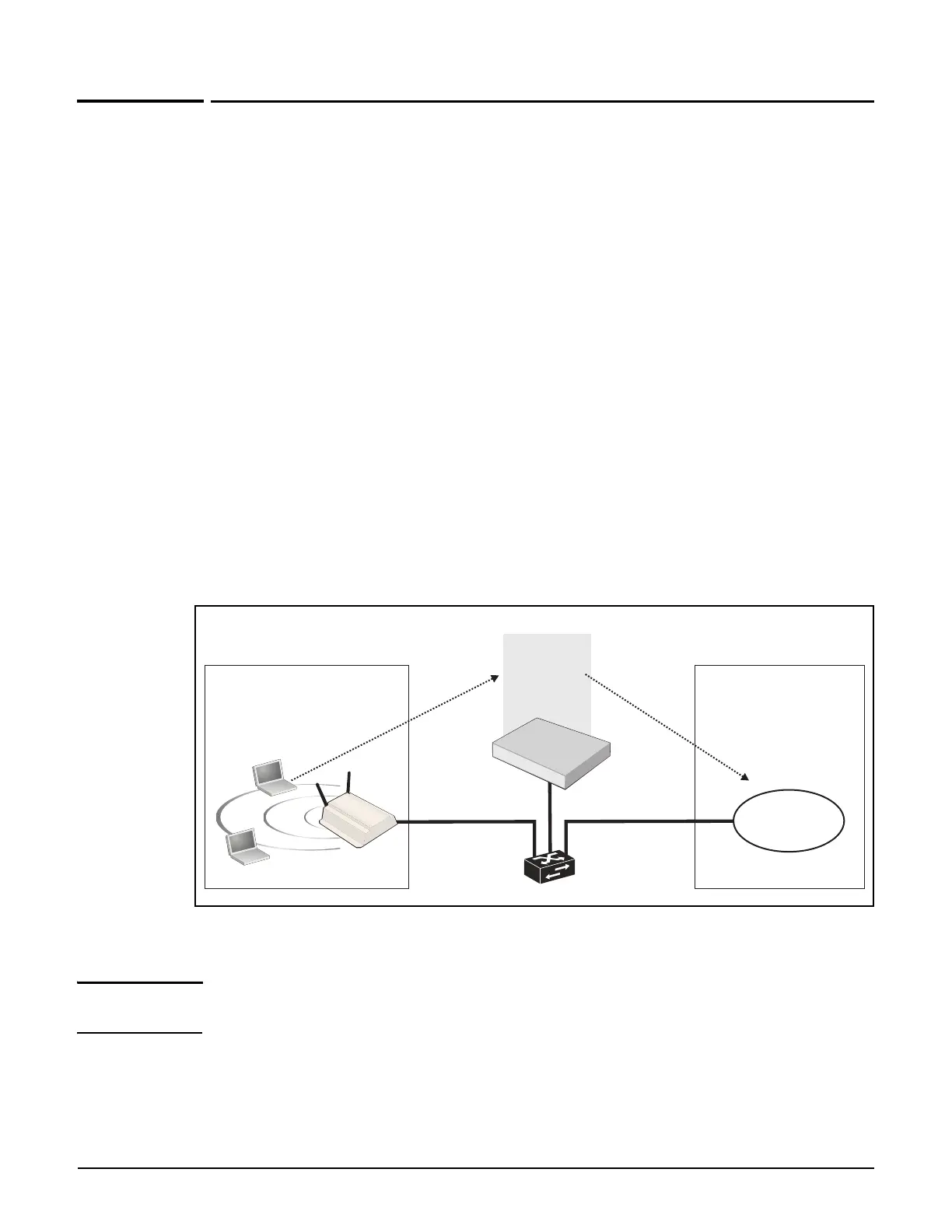
The following diagrams illustrates a basic setup in which a wireless user is authenticated by
an access-controlled VSC and then gains access to a corporate network.
For more information on access control, see Configuring global access control options on
page 14-8.
Note If authentication is not enabled on a VSC, all users connected to the VSC can access the
protected network.
Protected network
Public network
AP
User logs in
Access to network is granted
Access
controlled
VSC
Corporate
network
Controller
Router

 Loading...
Loading...