Working with autonomous APs
Working with third-party autonomous APs
19-6
Management with VLANs
When operating in a VLAN environment, management traffic can be carried on its own VLAN.
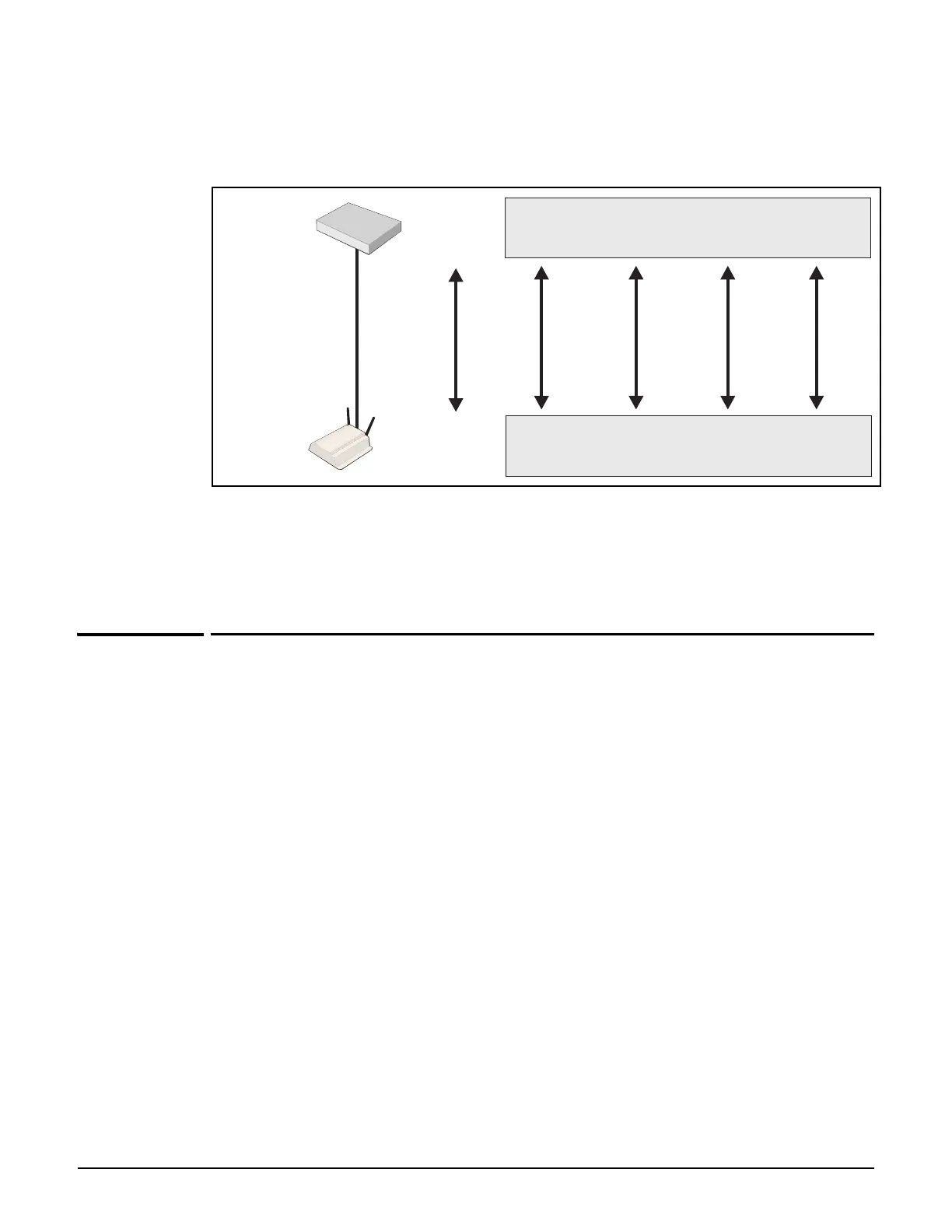
Configure the VSC on both the autonomous AP and the controller as illustrated here:
In this example, the traffic for each wireless network is carried on its own VLAN. This leaves
only management traffic from the autonomous AP on VLAN 10. A static IP is assigned on both
ends to permit the two devices to communicate.
Working with third-party autonomous APs
Third-party APs can be used with a controller with both access controlled and non-access
controlled VSCs.
VSC selection
User traffic from third-party APs is mapped to a VSC on the controller in the same way as for
MSM APs. See Using multiple VSCs on page 5-36. This means that traffic is assigned to the
default VSC, unless it is on a VLAN, in which case it is assigned to the VSC with matching
VLAN ingress definition.
SSID = VSC3
VLAN ID = 40
VSC Profiles
VSC Profiles
Default
VLAN ID = 10
IP address =
192.168.2.2
VLAN ID = 10
IP address =
192.168.2.1
SSID = VSC2
VLAN ID = 30
SSID = VSC1
VLAN ID = 20
SSID = VSC3
VLAN ID = 40
SSID = VSC2
VLAN ID = 30
SSID = VSC1
VLAN ID = 20
VLAN 10 = 192.168.2.1
LAN port = 192.168.1.1
VLAN 10 = 192.168.2.2
LAN port = 192.168.1.2
(IP = 192.168.1.1)
SSID = VSC4
VLAN ID = 50
Autonomous AP
Controller
SSID = VSC4
VLAN ID = 50
 Loading...
Loading...