Working with VLANs
Traffic flow for wireless users
7-9
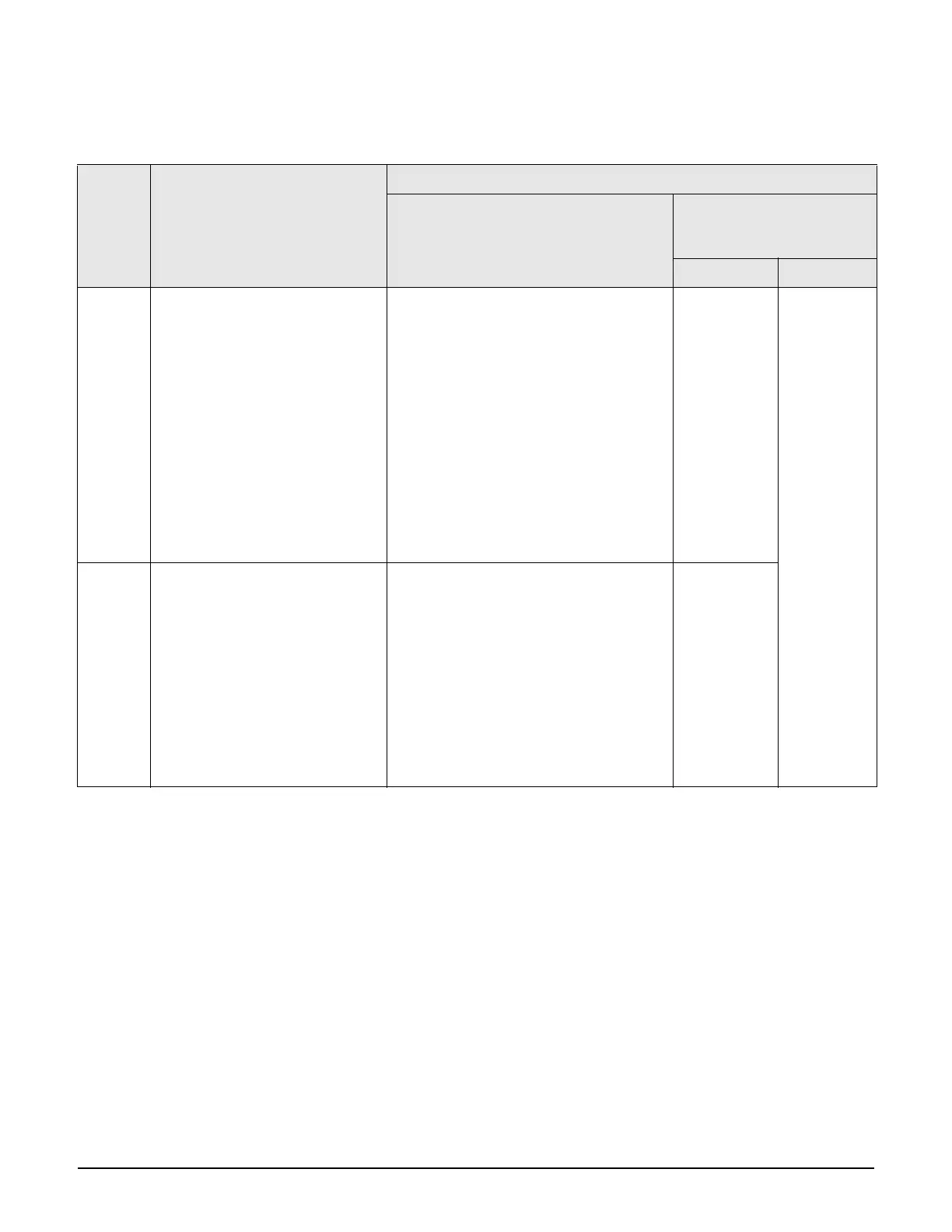
Binding to a VSC that has Wireless mobility and Subnet-based
mobility enabled
Egress
network
in VSC
binding
User-assigned VLAN is not
assigned via RADIUS or local
user accounts
User-assigned VLAN is assigned via RADIUS or local user account
User-assigned VLAN exists
in the mobility domain
User-assigned VLAN does
not exist in the mobility
domain
VLAN ID VLAN name
Defined. The IP address of the user is
compared against the list of home
subnets defined for the AP to
determine if the user is at home or
roaming.
If the user is at home, traffic is sent
on the AP Ethernet port tagged with
the VLAN specified by the Egress
network in the VSC binding.
If the user is roaming, traffic is
tunneled to the users home subnet
within the mobility domain, where it
egresses tagged with the VLAN
specified by the Egress network in
the VSC binding.
The IP address of the user and the VLAN ID
are compared against the list of home
subnets defined for the AP to determine if
the user is at home or roaming. (Both the IP
and VLAN must match the home subnet.)
If the user is at home, traffic is sent on the
AP Ethernet port tagged with the user-
assigned VLAN.
The Egress network in the VSC binding is
ignored.
If the user is roaming, traffic is tunneled to
the users home network within the mobility
domain, where it will egress tagged with the
user-assigned VLAN.
The Egress
network
setting in the
VSC binding is
is ignored.
User is
considered to
be at home
and traffic is
sent on the
AP's Ethernet
port tagged
with the user-
assigned
VLAN.
The user is
disconnected.
Not
defined.
The IP address of the user is
compared to the IP address of the
AP’s Ethernet port to determine if
the user is at home or roaming.
If the user is at home, traffic is sent
on the AP Ethernet port untagged.
If the user is roaming, traffic is
tunneled to the users home network
within the mobility domain, where it
will egress untagged.
The IP address of the user and the VLAN ID
are compared against the list of home
subnets defined for the AP to determine if
the user is at home or roaming. (Both the IP
and VLAN must match the home subnet.)
If the user is at home, traffic is sent on the
AP Ethernet port tagged with the user-
assigned VLAN.
If the user is roaming, traffic is tunneled to
the users home network within the mobility
domain, where it will egress tagged with the
user-assigned VLAN.
User is
considered to
be at home
and traffic is
sent on the
AP's ethernet
port tagged
with the user-
assigned
VLAN.

 Loading...
Loading...