Multicast Domain Name Service
◆
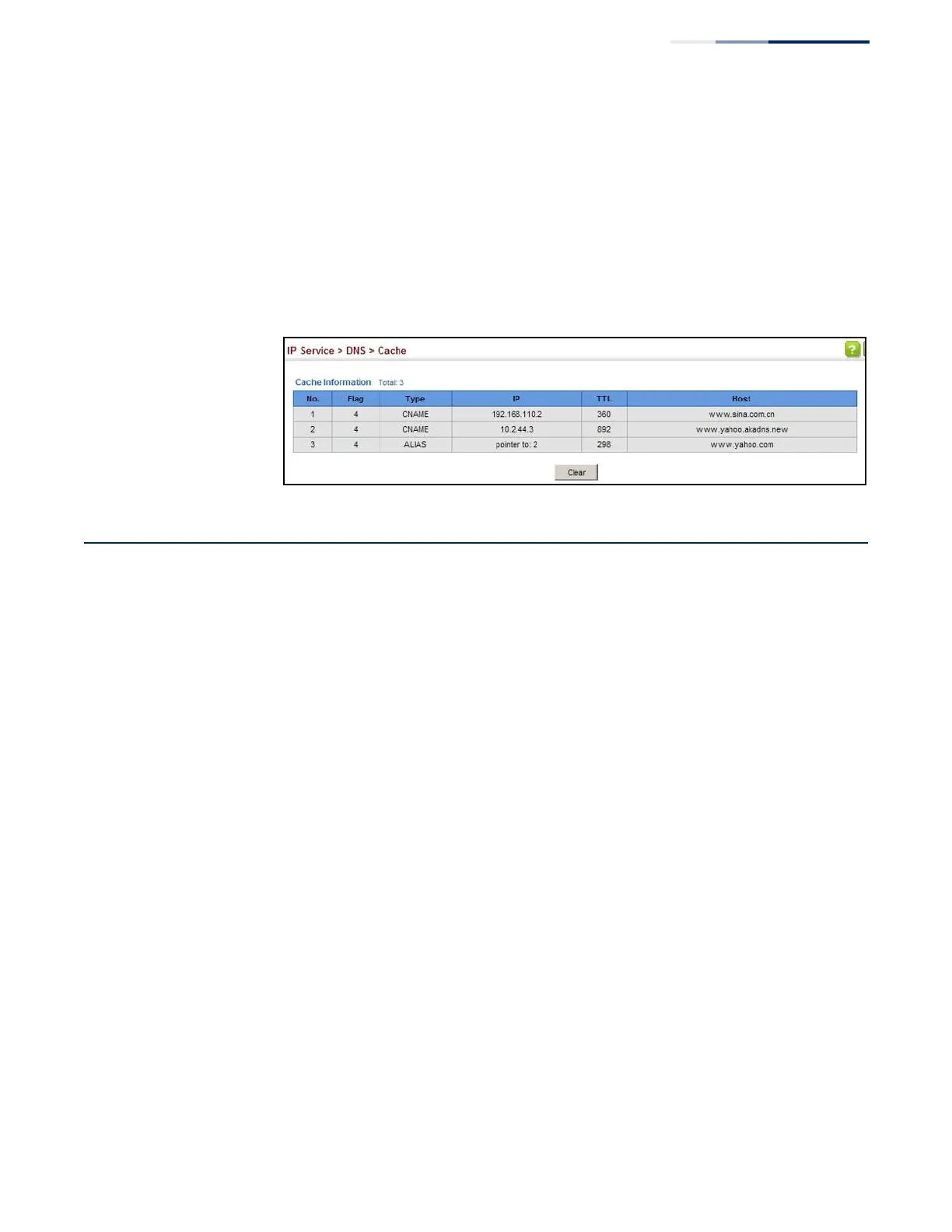
TTL – The time to live reported by the name server.
◆
Host – The host name associated with this record.
Web Interface
To display entries in the DNS cache:
1. Click IP Service, DNS, Cache.
Figure 352: Showing Entries in the DNS Cache
Multicast Domain Name Service
Use the IP Service > Multicast DNS page to enable multicast DNS host name-to-
address mapping on the local network without the need for a dedicated DNS
server.
Command Usage
◆
Multicast DNS allows a network device to choose a domain name in the local
DNS name space and announce it using a special multicast IP address. This
allows any user to give their computers a link-local mDNS host name of the
form “single-dns-label.local.” Any name ending in “.local.” is therefore link-local,
and names within this domain are meaningful only on the link where they
originate.
◆
When looking for the given host’s IP address, the client sends a single-shot
mDNS IP multicast query message to all the hosts sharing its local network. Any
DNS query for a name ending with “.local.” is sent to the mDNS multicast
address 224.0.0.251 (or its IPv6 equivalent FF02::FB).
The corresponding host replies with a multicast message announcing itself. All
machines in the subnet can then update their mDNS cache with the host’s
information sent in the reply message.
◆
To maintain an on-going cache of host names requires a process of continuous
multicast DNS querying. This is done in several phases:
■
Probing – The DNS responder sends a probe message to the local network
in order to verify that each entry its local cache is unique.
 Loading...
Loading...











