1‑33
Chapter 1 Troubleshooting
Version 1 2006.11.21
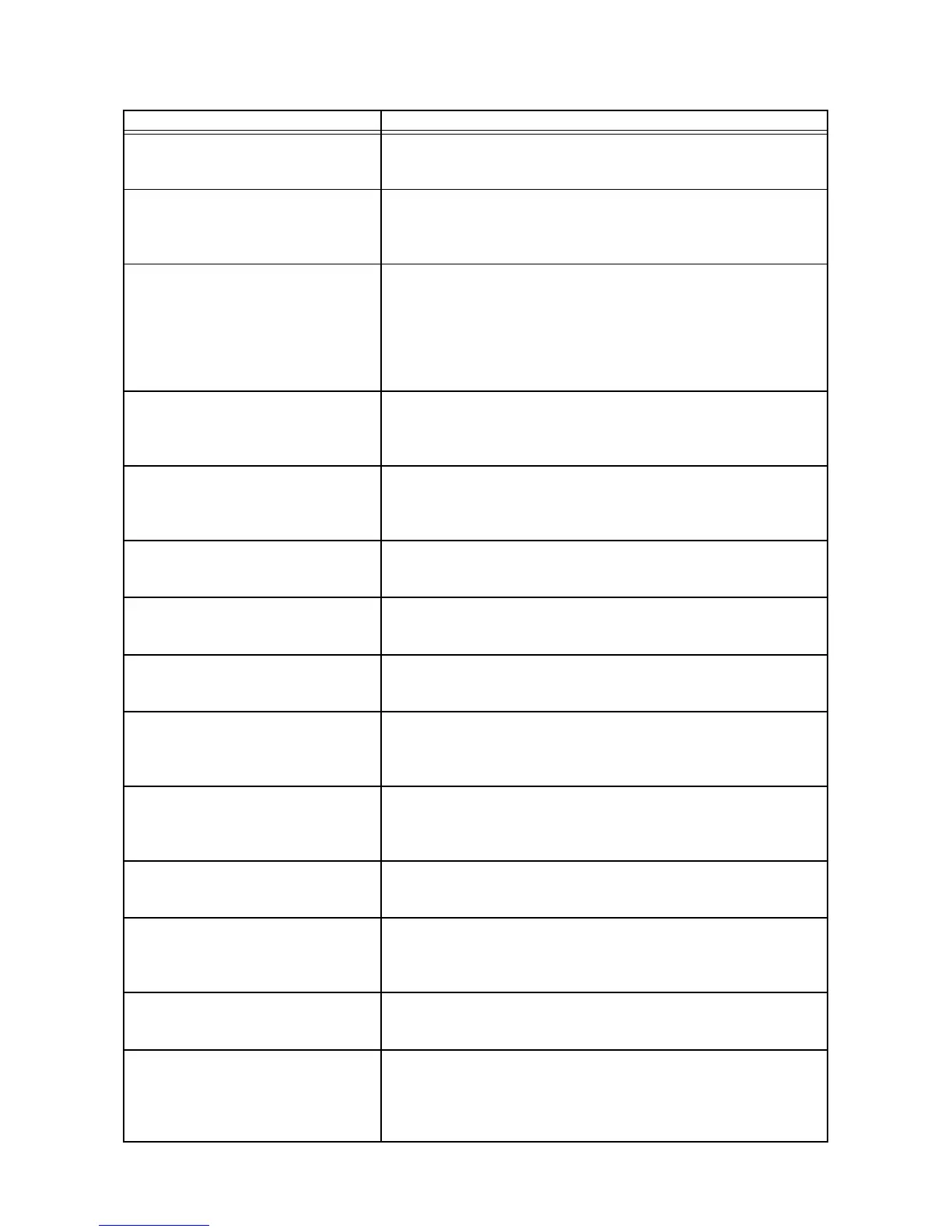
Descriptions of Signals
Signal Name Description
CNG
(Calling Tone)
A signal sent out by the sending side to notify that the incoming call
is a fax transmission. Upon detecting this signal, the receiving side
starts the fax reception procedure.
CED
(Called Station Identification)
A signal sent out by the receiving side as a response to an incoming
call to notify that the receiving side is an available non-voice (fax)
terminal, thereby allowing the sending side to determine that the call
was successfully answered.
NSF
(Non-Standard Facilities)
An optional signal sent out by the receiving side. Contains ITU mem-
ber country code, manufacturer code, type code, and manufacturer-
specific capabilities. The manufacturer-specific capabilities informa-
tion is used to notify that the receiving side can offer some capabili-
ties that are not covered by ITU-T T.30 and supported only between
fax terminals of the same manufacturer, such as high-quality mode,
high-speed mode, and proprietary ECM mode.
CSI
(Called Subscriber Identification)
An optional signal sent out by the receiving side. Contains the
receiving side’s identification information such as an international
telephone number. The sending side records this information as the
destination station number in its communication results
DIS
(Digital Identification Signal)
A signal that describes all of the G3-compliant capabilities of the
receiving side. Contains transmission rate, sub-scanning line den-
sity, coding capability (MH/MR/MMR/JBIG), paper size (width/
length), minimum transmission time per line, and ECM capability.
NSS
(Non-Standard Set-up)
An optional signal sent out in response to NSF sent from the receiv-
ing side. Recorded only when the call is established in a manufac-
turer-specific mode.
TSI
(Transmitting Subscriber Identification)
An optional signal sent out by the sending side. Contains the send-
ing side’s identification information such as an international tele-
phone number.
DCS
(Digital Command Signal)
A signal sent out by the sending side in response to DIS. Contains
transmission parameters that the sending side selected from the
receiving side’s capabilities presented via DIS.
NSC
(Non-Standard Facilities Command)
An optional signal sent out by the sending side to notify that the
manufacturer-specific communication mode presented by the
receiving side has been adopted for the current session. The infor-
mation elements are the same as those of NSF.
CIG
(Calling Subscriber Identification)
An optional signal sent out by the sending side. Contains the send-
ing side’s identification information such as an international tele-
phone number. The information elements are the same as those of
CSI.
DTC
(Digital Transmit Command)
A signal sent out by the sending side, in response to the capability
announcement via DIS, to make a polling request to the receiving
side. The information elements are the same as those of DIS.
TCF
(Training Check Frame)
A signal sent out by the sending side to determine the maximum
acceptable transmission rate. Continuous “0”s are transmitted for
1.5 seconds ± 10%. The data signaling rate is selected from 14400,
9600, 7200, 4800, 2400, and 1200.
CFR
(Confirmation to Receive)
A signal sent out by the receiving side to notify that TCF was suc-
cessfully received and that the receiving side is ready to receive the
image data.
FTT
(Failure to Train)
A signal sent out by the receiving side to notify that TCF was not
received successfully (“1” was received). Upon detecting this signal,
the sending side retransmits TCF. This is called “modem retraining.”
When the second retraining fails, the sending side retransmits TCF
at a rate re-established by sending out DCS (NSS, CIG).
 Loading...
Loading...











