Network configuration
Address allocation
3-17
Note For additional flexibility, separate DHCP relay agents can be enabled on access-controlled
VSCs. See DHCP relay agent on page 5-31.
Use the following guidelines when configuring DHCP relay:
Routes must be defined on the DHCP server, so that the DHCP server can successfully
send DHCP response packets back to the DHCP relay agent running on the controller.
These should be static and persistent HOST routes that must identify the IP address
assigned to the controller’s LAN port or additional VSC relay IP address, (i.e. 192.168.1.1).
On Windows, such a static route would look like this:
route add 192.168.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.22 metric 1 –p
DHCP relay is not supported via the Internet port when it is operating as a PPPoE client.
DHCP relay cannot work via the Internet port if the internal firewall is set to High and
NAT is enabled on the Internet port. The DHCP server must be able to ping the assigned
address to prevent duplicate assignments.
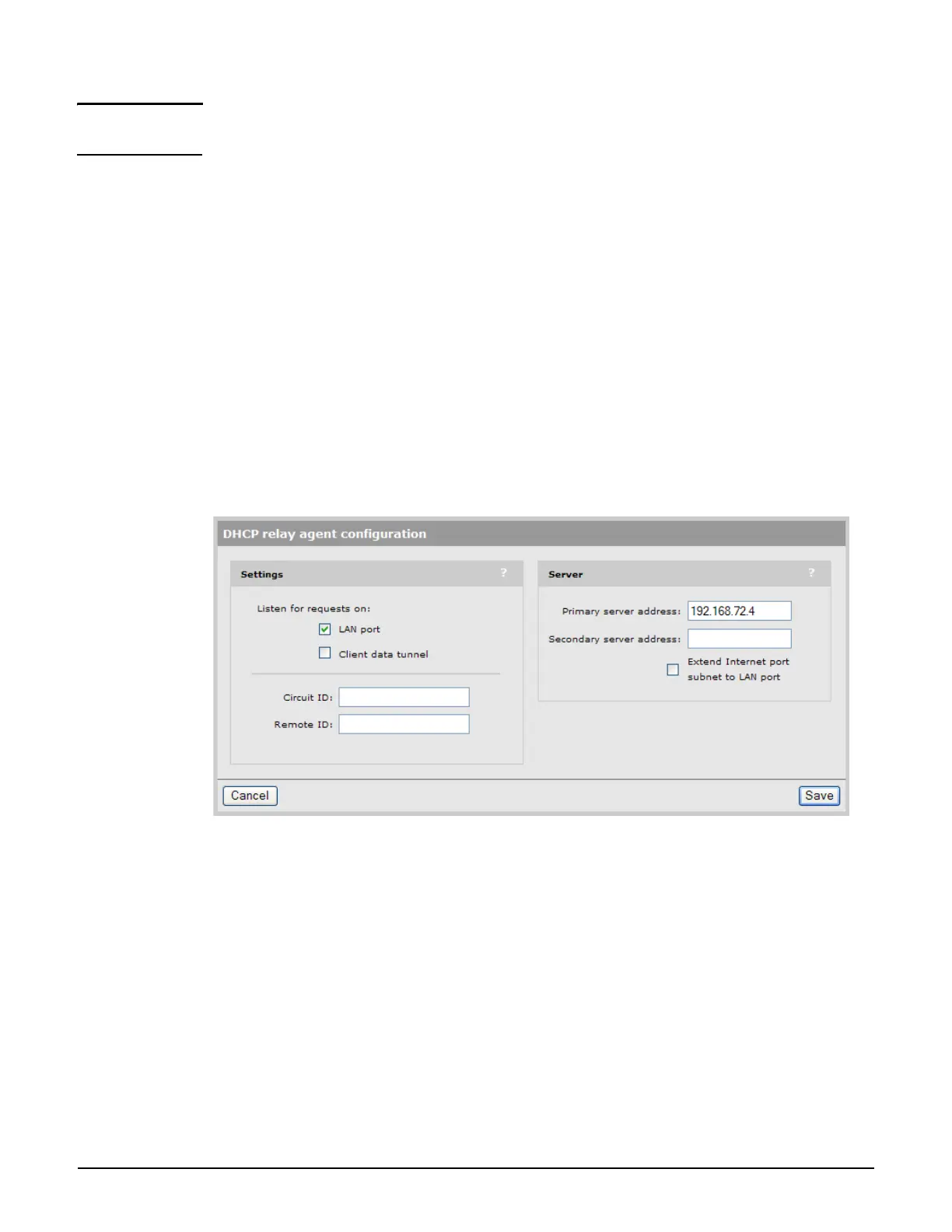
To configure the internal DHCP server, select Controller >> Network > Address
allocation, select DHCP relay agent, and then Configure.
Settings
Listen for DHCP requests on
Select the port on which the controller will listen for DHCP requests from users.
Listen for requests on
LAN port: Listens for DHCP requests on the LAN port and relay them to the remote
DHCP server.
Client data tunnel: Enable this option when the client data tunnel feature is active on
one or more VSCs, and you want tunneled users to be able to receive an IP address via the
DHCP relay agent. See Client data tunnel on page 5-13.
 Loading...
Loading...