10.11 PID (PID Operation)
■
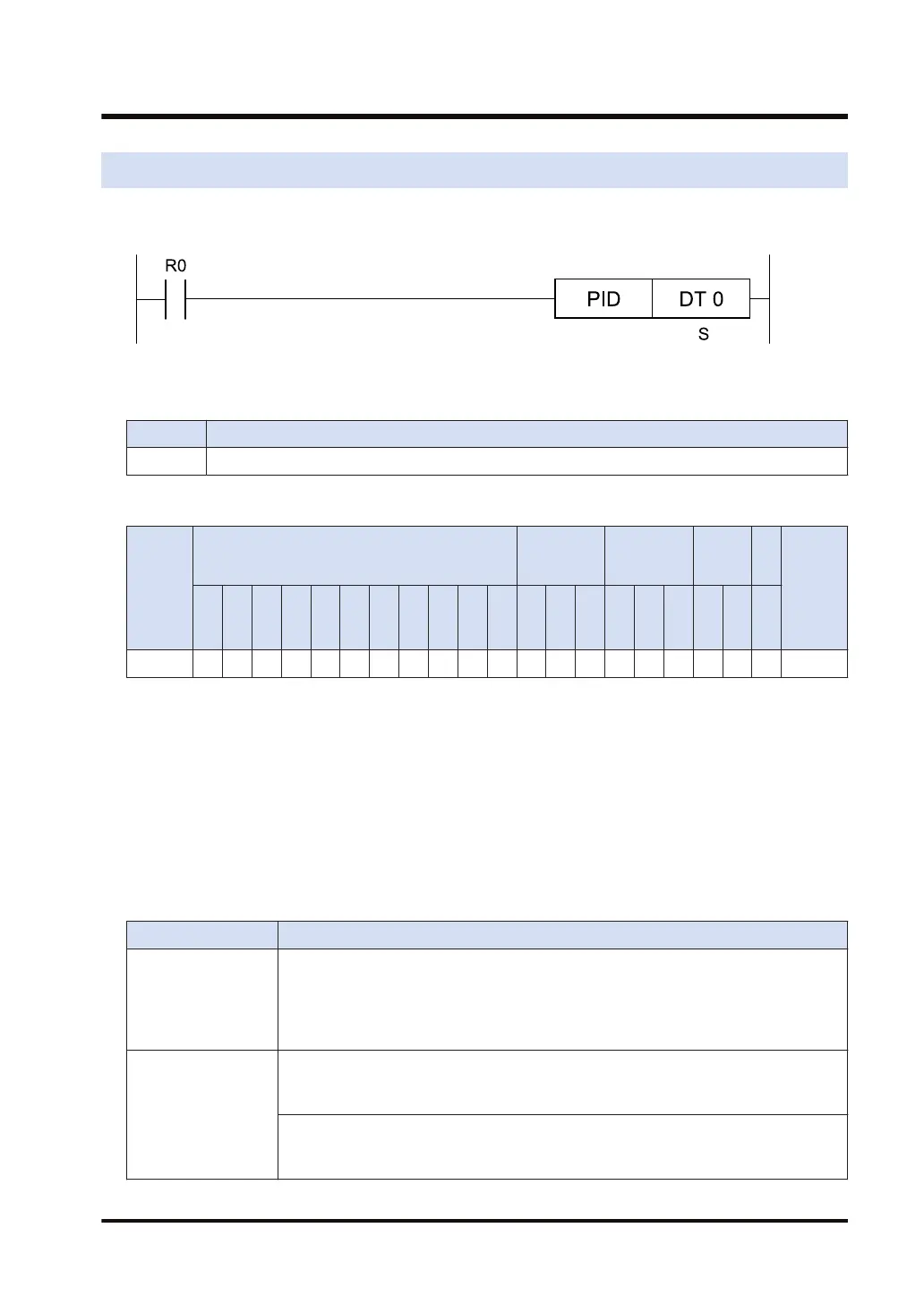
Ladder diagram
■
List of operands
Operand Description
S Starting number of the PID operation parameter area (30 words)
■
Available devices (●: Available)
Operan
d
16-Bit device:
32-Bit
device:
Integer
Real
numbe
r
St
rin
g
Index
modifie
r
W
X
W
Y
W
R
W
L
W
S
S
D
D
T
L
D
U
M
WI
W
O
TS
C
S
TE
C
E
IX K U H SF
D
F
" "
S ●
■
Outline of operation
● PID operation is carried out to retain the process value PV stored in [S+2], in consistency
with the set point value SP specified by [S+1].
● The operation result is stored, as a manipulated value [MV], in the area specified by [S+3].
● Methods for PID operation (derivative-first / proportional-plus-derivative-first, reverse
operation / forward operation) and coefficients used for PID operation (proportional gain,
integral time, derivative time), as well as the types and interval of operation, are set to the
parameter table [S] to [S+29].
■
Types of PID operation
Items Description
Reverse operation/
forward operation
Select the upward/downward direction of output in the case of change to the process.
Specify "reverse operation" if output is increased when the process value decreases
(e.g. heating).
Specify "forward operation" if output is increased when the process value increases
(e.g. cooling).
Derivative-first PID
/Proportional-plus-
derivative-first PID
Derivative-first PID:
Usually, when the set point value is changed, the output variation becomes larger but it
converges faster.
Proportional-plus-derivative-first PID:
Usually, when the set point value is changed, the output variation becomes smaller but
it converges slower.
10.11 PID (PID Operation)
WUME-FP7CPUPGR-12 10-39

 Loading...
Loading...











