● The block check code (BCC) for the targeted data, which is the number of bytes specified by
[S3] starting from the calculation start position specified by [S2], is calculated with the
calculation method specified by [S1].
● The calculation result is stored according to the conversion method specified by [S1], starting
from the storage position specified by [D] and [S1].
■
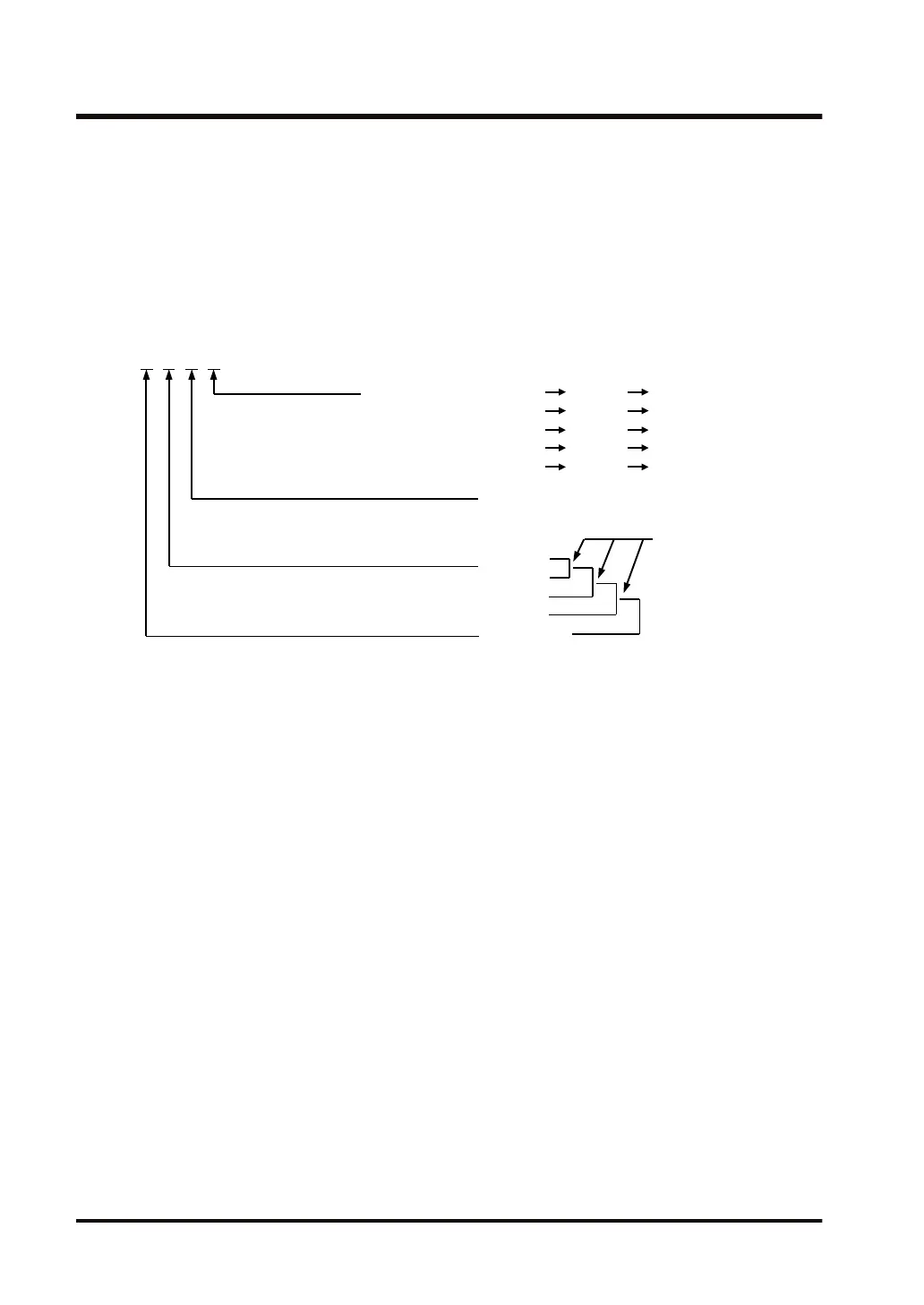
Specification of control data [S1]
H
Specify a calculation method
0: Addition
1: Subtraction
2: Exclusive OR
Calculation start position (bytes
from [S2])
0 to F
Storage start position (bytes from [D])
0 to F
Data to be converted
0: Binary data (1 byte)
1: ASCII code (2 bytes)
As indicated below, calculation should be
carried out as specified, for every eight bits.
% H 25 00100101 (a)
0 H 30 00110000 (b)
1 H 31 00110001 (c)
# H 23 00100011 (d)
R H 52 01010010 (e)
・・・・
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
・・・・
Specified calculation
[S3] = K0 : +
[S3] = K1 : -
[S3] = K2 : XOR
■
Conversion example
● Calculate the block check code (BCC) for a message to be sent "%01#RCSX0000", and
append the result to the message.
14.1 BCC (Block Check Code Calculation)
14-4 WUME-FP7CPUPGR-12

 Loading...
Loading...











