3.20
SEL-421 Relay Instruction Manual Date Code 20171021
Testing
Checking Relay Operation
The B-Phase to C-Phase current vector, I
BC
, is:
Equation 3.10
Choose a convenient test source current magnitude, |I
TEST
| = 2.5 A; then
|I
BC
|=2• |I
TEST
| = 5 A.
Find the magnitude of the test source voltage |V
TEST
|:
Equation 3.11
where relay setting Z2MP (Zone 2 Reach) substitutes for the B-Phase to C-Phase
impedance Z
BC
. For setting Z2MP of 9.36 , the test voltage magnitude |V
BC
|
is:
Equation 3.12
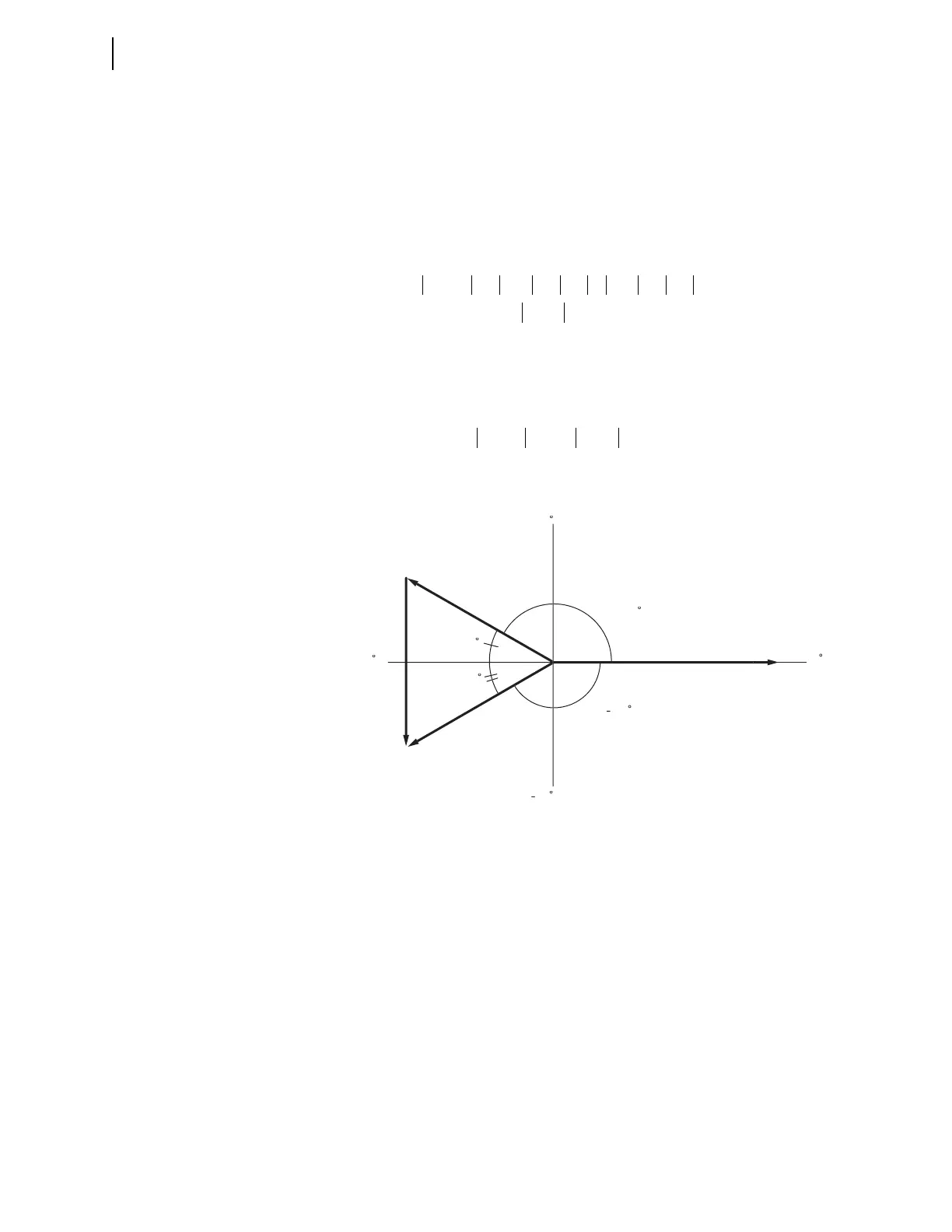
One way to create a V
BC
phasor is to equate |V
B
| and |V
C
| and determine the
appropriate angles to make an equilateral triangle, as shown in Figure 3.17.
Subtract 30 degrees (angle
1
) from 180 degrees to obtain the angle for test
source V
C
phasor; V
C
= 46.8 150° V.
Similarly, add 30 degrees (angle
2
) to –180 degrees to obtain test source V
B
phasor; V
B
= 46.8 –150° V.
Test voltage V
A
can be the nominal value, V
A
= 67 0° V.
Thus, the resulting phase-to-phase voltage is V
BC
= 46.8 –90° V, referenced to
the V
A
phasor at 0 degrees.
Figure 3.17 Finding Phase-to-Phase Test Quantities
I
BC
I
B
I
C
I
B
I
B
2I
B
2I
TEST
==+=–=
V
TEST
V
BC
I
BC
Z
BC
I
BC
Z2MP== =
2I
TEST
Z2MP=
V
TEST
2I
TEST
Z2MP=
2 2.5 9.36 46.8 V==
=
=
1
= 1
1
=
B

 Loading...
Loading...