6.99
Date Code 20171021 Instruction Manual SEL-421 Relay
Protection Applications Examples
EHV Parallel 230 kV Underground Cables Example
Nonhomogeneous Correction Angle
TANGG, the nonhomogeneous angle setting, also helps prevent overreach or
underreach for ground faults at a specific fault location by compensating the
angle of the reactance line.
Set TANGG to prevent the Zone 1 quadrilateral ground-distance reactance mea-
surement from overreaching for ground faults located at the remote bus. Use the
result from Equation 6.60 (T2 in Quadrilateral Ground Polarizing Quantity on
page 6.29).
TANGG := —2.2. Nonhomogeneous Correction Angle (–40.0 to +40.0 degrees)
Zero-Sequence Current Compensation Factors
Zero-sequence current compensation helps keep the phase and ground-distance
elements at the same reach if you set the phase reach and the ground reach equal
per zone (e.g., Z1MP = XG1). Ground-distance elements should measure fault
impedance in terms of positive-sequence impedance only.
The relay has three zero-sequence current compensation factors (k01, k0, and
k0R). The Zone 1 ground-distance element has a dedicated zero-sequence current
compensation factor (k01). Advanced Settings are enabled for this particular
example (EADVS := Y), so you must set two additional independent zero-
sequence current compensation factors, one for forward-looking zones (k0) and
one for reverse-looking zones (k0R).
The zero-sequence cable impedance depends on the return path of the ground
fault current during ground faults. The zero-sequence current compensation fac-
tors must be set so the Zone 1 ground-distance elements do not see ground faults
external to the protected cable, while Zone 2 and Zone 3 ground-distance ele-
ments must see all internal ground faults.
The SEL-421 uses Equation 6.61 to calculate the A-Phase-to-ground distance
reactance measurement.
Equation 6.61
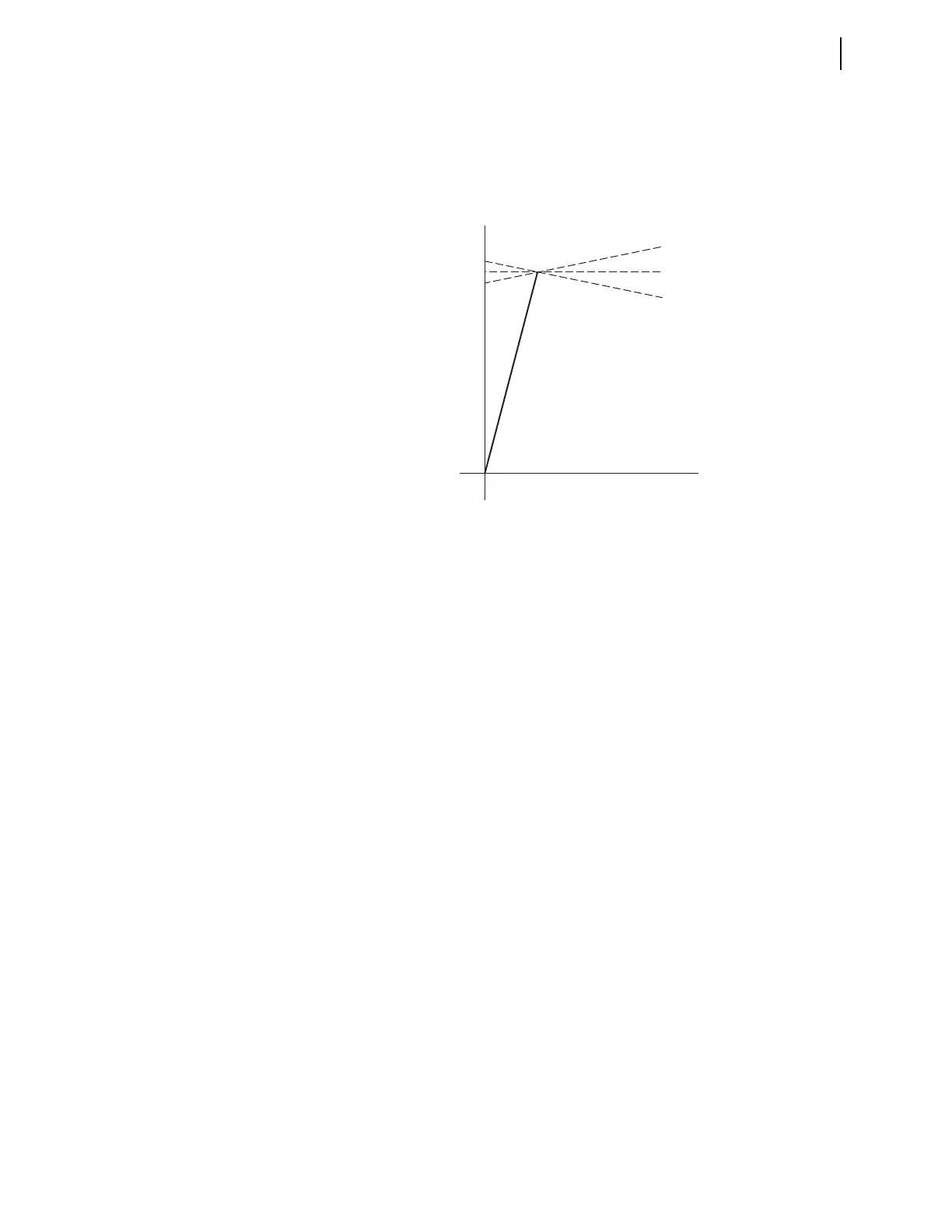
Figure 6.24 Nonhomogeneous Angle Setting
X
R
TANGG > 0
TANGG = 0
TANGG < 0
XAG
Im V
A
I
POL
e
j TANGG•
•
*
•
Im z1 I
A
k01 3I
0
• +I
POL
e
j TANGG•
•
*
• •
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------=

 Loading...
Loading...