6.102
SEL-421 Relay Instruction Manual Date Code 20171021
Protection Applications Examples
EHV Parallel 230 kV Underground Cables Example
k0M := 6.105. Forward Zones ZSC Factor Magnitude (0.000–10)
k0A := 44.5. Forward Zones ZSC Factor Angle (–180.0 to +180.0 degrees)
k0MR := 6.105. Reverse Zones ZSC Factor Magnitude (0.000–10)
k0AR := 44.5. Reverse Zones ZSC Factor Angle (–180.0 to +180.0 degrees)
Distance Element Common Time Delay
Set the operation time delay of both the phase and ground-distance elements.
Zone 1
There is no need to delay Zone 1 distance protection; the relay trips instanta-
neously for faults in Zone 1.
Z1D = 0.000. Zone 1 Time Delay (OFF, 0.000–16000 cycles)
Zone 2
Zone 2 distance protection must coordinate with downstream Zone 1 distance
protection plus the downstream circuit breaker operating time and a safety mar-
gin. A typical Zone 2 phase and ground-distance time delay setting is 20 cycles.
Z2D := 20.000. Zone 2 Time Delay (OFF, 0.000–16000 cycles)
Short Adjacent Lines
You do not need to consider the following fault current return path scenario for
this application example; this information is provided here for applications with
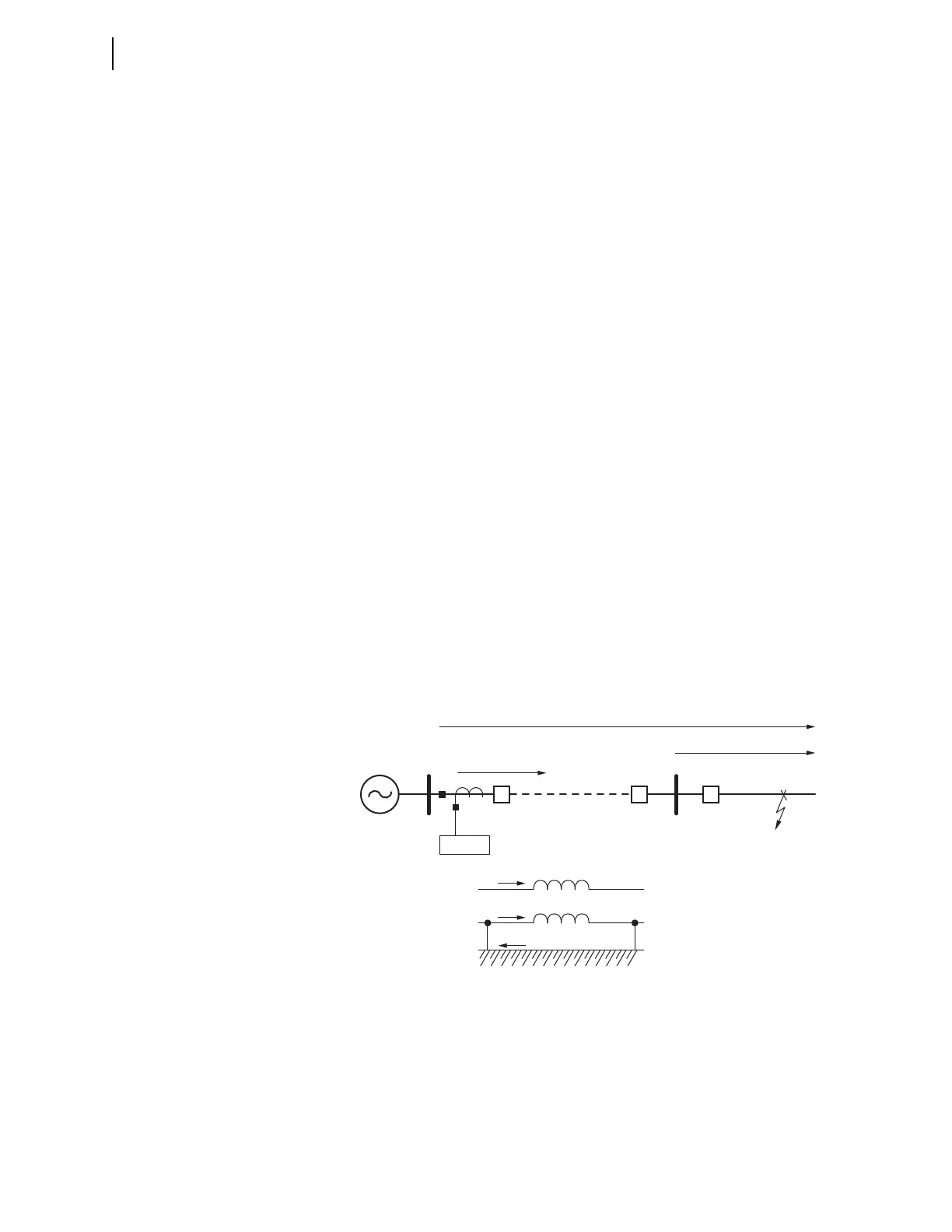
short adjacent lines. Figure 6.25 illustrates an important consideration if you
apply time-delayed Zone 2 ground-distance protection to backup downstream
Zone 1 ground-distance protection.
Fault current flows through the sheath and ground with respect to the cable
because the sheath is grounded at each end during external ground faults. How-
ever, because you must make sure that Zone 2 ground-distance elements see all
ground faults at remote Station R, the k0 setting was for the ground path only.
Therefore, Zone 2 ground-distance protection may overreach for external ground
faults, especially for the case of a short adjacent line. The solution is to increase
Zone 2 time delay.
Figure 6.25 External Ground Fault
SEL-421
Conductor
I
F
I
C
I
S
I
G
Sheath
Ground
RS
Zone 2 Ground Distance
Zone 1 Ground Distance

 Loading...
Loading...