6.62
SEL-421 Relay Instruction Manual Date Code 20171021
Protection Applications Examples
345 kV Tapped Overhead Transmission Line Example
Table 6.17 lists the results of the Z
AG
and Z
BC
calculations.
Select the phase-to-phase measurement from Table 6.17. Multiply this value by a
safety factor of 125 percent to obtain Zone 2 phase-distance element reach.
Equation 6.27
Z2MP := 11.00. Zone 2 Reach (OFF, 0.05–64 secondary)
Zone 3 Phase-Distance Element Reach
Zone 3 phase-distance protection is reverse-looking. Zone 3 at Station S must
have adequate reach to prevent unwanted tripping by the SEL-421 Relays at Sta-
tions R or T during external faults behind the local terminal. The Zone 3 reach at
Station S must cover overreach from the furthest reaching remote Zone 2 for
reverse faults when there is no infeed from the other remote terminal.
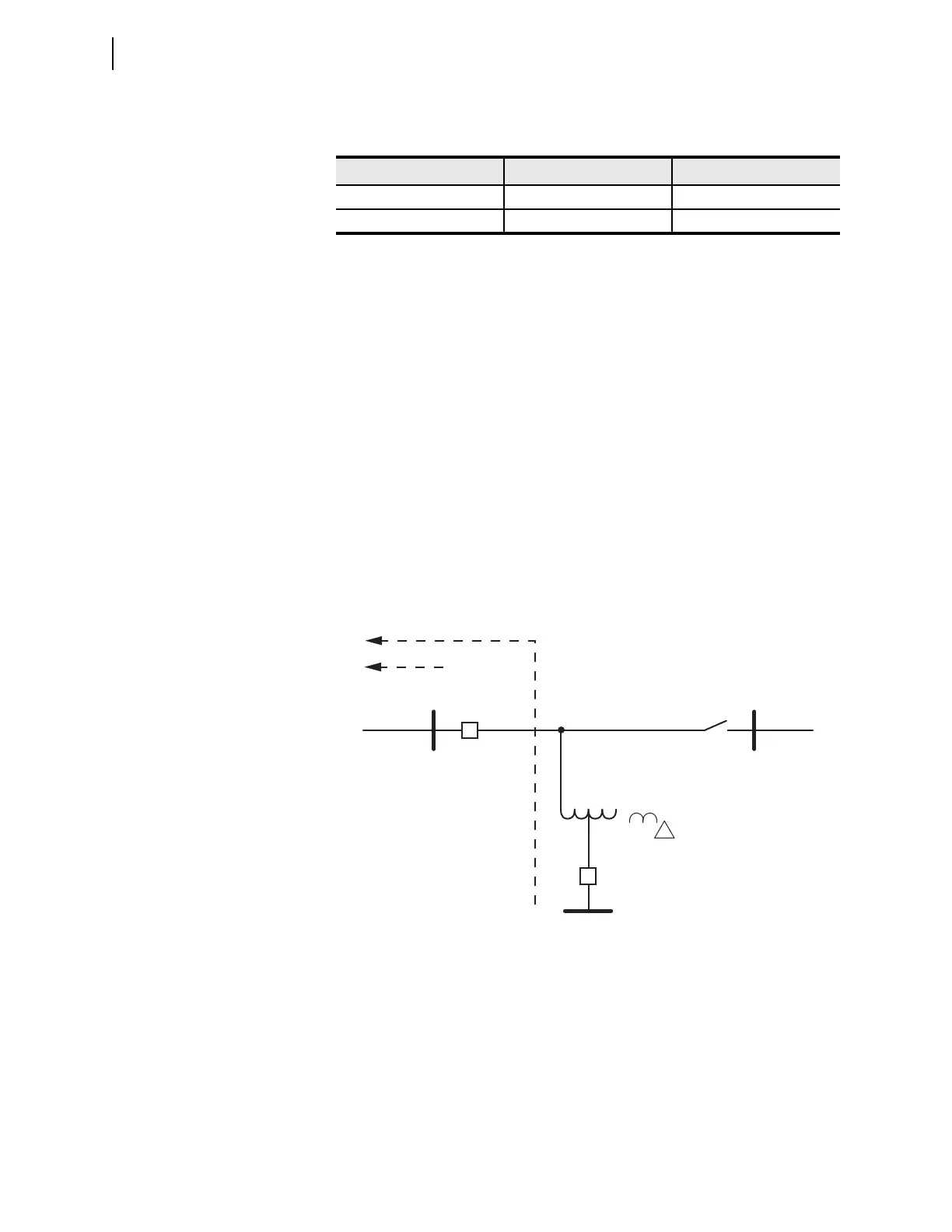
Figure 6.13 illustrates this coordination issue. You must set the Zone 2 reach at
Station T to account for infeed during faults beyond the tap on the 345 kV sys-
tem. However, when one 345 kV station is out of service, the Zone 2 at Station T
overreaches for faults on the other side of the tap on the 345 kV system.
Place AG and ABC faults at Station T and use Equation 6.23 and Equation 6.26
with respect to Station R to record the results in primary. Next place AG and
ABC faults at Station R and use Equation 6.23 and Equation 6.26 with respect to
Station T to record the results in primary. Tab le 6.18 lists the results in primary
and per unit.
Table 6.17 Local Zone 2 Fault Impedance Measurements
Fault Type |Z
AG
| |Z
BC
|
AG 7.77 NA
ABC NA 8.8
Z2MP 1.25 8.8 • =
11.00 =
Figure 6.13 Reverse Zone 3 Coordination

 Loading...
Loading...